A mother's preparation for childbirth takes place on all fronts - not only moral, but also physiological. For example, before childbirth there are often so-called. Braxton-Hicks contractions, or preparatory contractions. This is how the body prepares for the real first contractions. When real contractions begin, the cervix adapts to produce a baby. There are two definitions for this process: “smoothing” (shortening) and “opening” (expansion). In this article we will tell you about cervical effacement. This way you will better understand what complex processes occur in the body and how they help you at each stage.
What does cervical effacement mean?
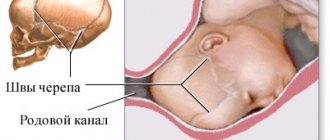
What is smoothing? Let's start with an excursion into anatomy. The cervix is a narrow, long section of the uterus that opens into the vagina at one end and into the uterine cavity at the other. As a rule, the cervix is tightly closed and elongated (usually its length is 3.5-4 centimeters). When contractions begin, the cervix flattens, relaxes and shortens. This phenomenon is called "smoothing".
The degree of smoothing is monitored by an obstetrician during a vaginal examination. It is impossible to check this on your own. However, do not worry, this is a completely natural phenomenon that will be monitored by a doctor.
The onset of labor - how does it all happen?
The female body prepares for childbirth not only in the later stages, but almost throughout the entire pregnancy. This physiological process requires multifaceted preparatory measures. And childbirth, as a culmination, is just the logical conclusion of amazing processes and transformations in the organisms of the mother and fetus. The onset of regular contractions or the breaking of water indicates the onset of labor. Childbirth, if it is not premature (pathological by default), begins when everything is ready for it.
Let's start with the uterus. During pregnancy, the female reproductive organ is a reliable “home” for the baby. So that nothing threatens the baby while he grows and develops, the cervix is tightly closed. With the onset of labor, she will have to gradually open up and give the baby the opportunity to leave the womb. Contractions contribute to this. But the uterus itself cannot contract—it is a muscular organ that is incapable of strong, rhythmic, prolonged contractions unless a number of conditions are met.
In order for contractions (contractions) to begin, a hormonal birth dominant with a predominance of the hormone oxytocin must be formed in a woman’s body. If progesterone during the entire period of gestation of the baby “took care” of maintaining the “interesting position” and continuing gestation, then before childbirth its concentrations decrease and decrease to such a level that estrogen begins to predominate. The mechanism of menstruation is exactly the same: a drop in progesterone and an increase in estrogen lead to the rejection of the endometrium, and menstruation begins. Before childbirth, the same hormonal change occurs, but is additionally supported by oxytocin produced by the pituitary gland and placenta.
The approach of labor is also assessed by the condition of the cervix. This round muscle prepares for opening in advance, softening and somewhat smoothing, due to which it becomes shorter and opens slightly before birth. From the inside, the fetal head presses on the cervix (the baby has sank and with all its weight, plus the weight of the water, the placenta, is trying to “lean” onto the cervix from the side of the internal os). At the same time, the cervical canal begins to produce new specific enzymes, which gradually make the membranes thinner. When the right time comes, the shells will be able to burst and the water will begin to drain.
Preparations are also underway in the child’s body. The lung tissue matures and the baby gains weight, as this will help him breathe on his own after birth and retain body heat. The nervous system is being developed and reflexes are being trained.
Only when all the conditions we have listed coincide, full-fledged, normal labor begins. The cervix gradually opens during contractions until the dilatation reaches its maximum fullness (10–12 centimeters depending on the size of the pelvis). At the second stage of labor, pushing begins, and the baby is expelled through the birth canal. At the final stage, the afterbirth is born, after which the recovery period begins, during which the uterus shrinks to its previous size over a fairly long period of time.
Once all internal preparation processes are completed, this will definitely happen. Much depends on the characteristics of pregnancy and women's health. For example, firstborns are in no hurry to be born, just like large babies, but you can’t persuade twins to “sit through” even before the PPD. The date indicated on the card as estimated is therefore called estimated, because no one guarantees that labor must begin on this day. According to medical statistics, no more than 5% of babies are born at this time, and all the rest choose a time before or after the PPD.
Births from 38 to 42 obstetric weeks are considered normal (urgent, that is, occurring on time). Your PD is the end of the 40th week. Therefore, the absence of labor during this period is not considered a pathology.
How is revealing different from smoothing?
The degree of opening is expressed in centimeters, and the maximum opening corresponds to 10 centimeters.
During labor, the obstetrician will observe how much the cervix is effaced and dilated. During a vaginal birth, the cervix should be completely effaced and dilated by 10 centimeters.
The approximate duration of dilation can be determined as follows: after the transition to the active phase of labor, the average speed of dilation is 1-2 centimeters per hour. Of course, every birth is different and this is just a guideline. If the doctor thinks that the labor process has stopped or the baby is in danger, a caesarean section may be indicated.
How labor begins: signs and sensations.
Childbirth in primiparous and multiparous women begins with contractions - involuntary, rhythmic contractions of the uterine muscles with a frequency of at least 1 every 10 minutes, remotely comparable to very severe menstrual pain. The rupture of amniotic fluid does not mark the beginning of labor. It happens that labor occurs independently or does not occur at all when the waters break.
Only contractions provide gradual opening of the uterine pharynx and are assessed according to the following indicators: frequency, duration, strength and pain. At the very beginning of the “path”, contractions are rare and short: 10-20 seconds every 10 minutes. Further, the pauses between contractions are shortened, and the duration increases and reaches 50-60 seconds at the end of the first stage of labor.
It is very important at this time to be under the supervision of a doctor, since only a doctor will be able to determine the pathological process - weakness of labor forces, discoordinated labor, begin drug induction of labor when amniotic fluid has leaked, offer adequate and modern anesthesia at the very start and make adjustments for the further smooth course of labor .
In addition to the dynamics and pain of contractions, the doctor also evaluates the fetal heartbeat, cervical dilatation and the general condition of the woman - he always measures temperature, pulse and blood pressure.
Childbirth is one of the critical periods in the life of not only a child, but also a woman, therefore a progressive, but at the same time careful approach in the “do no harm” concept, which can only be implemented in medical institutions, is the key to the health of the expectant mother and baby.
Can Braxton Hicks contractions cause effacement?
If you've had infrequent, irregular contractions over the past few months, this does not mean that your cervix is effacing or dilating and that labor is imminent. They are also called Braxton-Hicks contractions, or “preparatory”, “false” contractions. Braxton Hicks contractions do not affect the cervix in any way. This is just a workout that helps the body prepare for real childbirth.
Training contractions have characteristic features that will help distinguish them from the harbingers of labor, labor pains.
Birth injury
The most common complication for a child during childbirth is birth trauma. Up to 80% of children are born injured to one degree or another, and only thanks to the infant’s very great ability to compensate does he remain completely healthy in appearance. However, birth trauma does not always go away without a trace.
The consequences of birth trauma manifest themselves over a very wide range - in infants it can be developmental delay, congenital dislocations of joints, torticollis, decreased immunity and adaptive abilities, up to the most severe, such as cerebral palsy.
During preschool and school age, these consequences may include frequent colds, poor health, mental instability, hyperactivity, and poor performance at school. In adults, many diseases arise from childhood traumas, including birth traumas.
That is why before giving birth it is necessary to prepare as thoroughly as possible, including visiting an osteopath.
FAQ
How do you know that the cervix is effacing?
If you have already started having regular, frequent contractions, you can assume that the body has started the process of smoothing and dilating the cervix. During childbirth, the degree of smoothing and opening is controlled by the obstetrician.
Can you feel your cervix opening and/or effacing?
At the first signs of labor, and with them the smoothing and opening of the cervix, you may experience discomfort, mild cramps, or you may not feel anything at all. The process of smoothing and dilation of the cervix can only be monitored transvaginally, usually by a doctor.
Effacement in itself is not a sign of labor. This is a physiological change that tells your doctor where you are in the labor process. Knowing what's going on in your body is helpful, but it's important to remember that your doctor knows best, so just relax and concentrate. Very soon you will have a long-awaited baby, and all the physiological details will no longer be so important.
How does a baby feel before giving birth?
| CHUZ "RZD-Medicine" Vikhorevka" |
Before giving birth, every mother wonders whether the baby feels that he will soon be born and how he feels in anticipation of going out into public. There are answers to this, both from mothers who have successfully given birth, and from experienced doctors.
Strong and frequent movements begin, especially starting from the 36th week. The baby turns over, taking a position with his head down, and moves not only because he takes the correct position, he also tries to independently take the correct position for exit (with correct presentation):
- presses his arms to his chest;
- squeezes the legs at the knees;
- spinning, trying to free himself a little from the umbilical cord.
And there were even cases when the child tried to start breathing already in the mother’s womb. But, of course, this is a pathology, which means that the child does not have enough oxygen, which is transmitted through the mother’s blood. This is unacceptable, it is imperative to spend time in the fresh air more often, breathe softly and deeply, and not bring the baby to hypoxia.
The baby often “knocks” on his mother’s tummy, the frequency is approximately 50-60 movements per day, you can count them. But you shouldn’t worry too much if there are ten fewer of them, the babies are different, perhaps the fruit is simply underweight or, on the contrary, overweight. There are actually a lot of reasons.
The baby also moves downwards, putting pressure on the mother’s bladder, which increases urination and makes walking more difficult. The child, feeling that he will soon be born, rejoices in every possible way about this, and in order to avoid excessive activity, you should calm him down a little:
- sing a song;
- coo to him;
- stroke your tummy;
- ask dad to stroke and calm the baby;
- walk around;
- drink milk with honey (half a cup, warm);
- Read aloud to him, turn on calm music.
The baby does not move before birth
This should raise serious alarms as this is not normal.
You should consult a doctor if you do not feel fetal movement after 36 weeks for the following reasons:
- fetal freezing;
- injuries;
- alcoholism;
- heavy smoking;
- addiction;
- ARVI;
- hypertonicity.
What to pay attention to
A week before giving birth, the movements subside slightly, this is not scary.
There may be false contractions, this is also the norm, but it is better to take care and calm down. Lie down, drink drotaverine, moderate physical activity. Lie only on your left side. This activates the child.
Avoid unnecessary irritation and nerves. Choose an environment where you feel comfortable.
Address: Vikhorevka, st. Komsomolskaya, 1a Contact numbers
Modern methods of preparing the body for childbirth, labor induction and labor stimulation
Ultrasound scanner HS60
Professional diagnostic tools.
Assessment of tissue elasticity, advanced 3D/4D/5D scanning capabilities, BI-RADS classifier, options for expert cardiological studies.
Modern principles of preparation for childbirth and its management should ensure the birth of not only a living, but also a healthy child. Accordingly, the further physical development and health of the child largely depends on the success of preparation for childbirth and the quality of its implementation. For the effective start and further progression of normal labor, one of the important conditions is the presence of a “mature” cervix, which reflects the readiness of the mother and fetus for childbirth. With an “immature” cervix, it is impossible to induce labor and intensify labor due to the risk of disrupting the contractile activity of the uterus, causing hypoxia and injury to the fetus.
Prostaglandins
According to modern ideas, the preparation of the cervix for childbirth occurs not only under the influence of hormones, but primarily under the influence of substances called prostaglandins. In this case we are talking about two types: prostaglandin E2 and F2α. So, in particular, prostaglandin E2 is produced by the fetal part of the placenta, in the fetus’s body, as well as in the tissues of the cervix. It helps to change the structure of the tissue of the cervix, ensuring its maturation, and also has a certain relaxing effect on the isthmus, cervix and lower segment of the uterus. When the proper degree of ripening of the cervix is achieved, under the influence of prostaglandin E2, the development of labor gradually begins. Consequently, it is prostaglandin E2 that plays the triggering role of the onset of labor. Prostaglandin F2α is produced in the maternal part of the placenta and in the walls of the uterus. It supports labor that has already begun, providing the most powerful and effective reducing effect, and helps limit blood loss during childbirth.
To prepare the cervix for childbirth, the most physiologically justified and rational is the use of natural stimulants for the development of labor, i.e. drugs containing prostaglandin E2. The introduction of prostaglandin E2 should lead to both ripening of the cervix and cause contractions of the myometrium, being the trigger for the onset of labor. To prevent excessively strong contractile activity of the uterus, when using prostaglandin E2, it is necessary to achieve a balance between the ripening of the cervix and the degree of its maturity, on the one hand, and stimulation of contractile activity of the uterus, on the other. In this regard, local use of prostaglandin E2 by introducing the drug into the cervical canal or into the posterior vaginal fornix is most preferable.
The method of topical use of prostaglandins became widespread after special gels containing the required dose of the drug were developed. Typically, to achieve sufficient maturity of the cervix and prepare it for childbirth, a prostaglandin gel is injected into the cervical canal. To successfully use the drug and prevent possible complications when using it, a number of conditions must be observed, as well as relevant indications and contraindications. Thus, the need to use prostaglandin gel to prepare the cervix arises in the absence of biological readiness of the body for childbirth (immature cervix) and there are indications for urgent delivery in case of various obstetric or other complications (for example, post-term pregnancy, preeclampsia, fetoplacental insufficiency, etc. ).
Contraindications for the use of the drug are: the presence of a scar on the uterus after a cesarean section or after other operations on the uterus; placenta previa; multiple pregnancy; pronounced signs of fetal impairment; narrow pelvis; leakage of amniotic fluid; allergy to prostaglandins; asthma; increased intraocular pressure. Prostaglandin gel is used only in a hospital in the following cases: the presence of an immature or insufficiently mature cervix; whole amniotic sac; no contraindications for vaginal delivery.
Labor induction, cervical preparation
Before using the drug, it is necessary to determine the condition of the cervix, pulse and respiration rates, blood pressure, and also assess the condition of the fetus and the contractile activity of the uterus. The gel is injected into the cervical canal with the pregnant woman in the supine position, under the control of mirrors. To prevent the gel from leaking out, the pregnant woman is left in a lying position for 30 minutes.
During subsequent observation of the patient, monitor the contractile activity of the uterus and the condition of the fetus. The condition of the cervix (every 2-3 hours), pulse, blood pressure and respiratory rate are assessed. Under the influence of the drug, not only does the cervix ripen, labor can begin. In this case, after reaching a sufficient degree of maturity and opening the cervix by at least 4 cm, the amniotic sac is opened, if it has not opened on its own before. Most often, after using prostaglandin gel in the first 3-4 hours, more than half of the patients already experience noticeable changes in the condition of the cervix. At the same time, it shortens and softens, positioning itself along the axis of the pelvis. In the next 3 hours (6 hours after administration of the gel), a mature cervix is observed in another 1/3 of the patients. In many patients, on average, labor develops after 9-10 hours. If after using the gel for 6 hours, the cervix remains immature, then the drug is re-administered in the same dose.
The maximum allowable injection of the gel is three times within 24 hours. In case of prenatal or early rupture of amniotic fluid, repeated administration of the gel is contraindicated, and further labor is carried out depending on the obstetric situation. The use of the gel is considered effective when a sufficient degree of maturity of the cervix is achieved within 12 hours, and labor begins within 24 hours from the moment of its administration. Usually, after using the gel, the contractile activity of the uterus is normal, and there are no pathological changes in blood pressure and pulse rate in the mother, and there are no signs of abnormalities in the fetus.
To induce labor with a sufficient degree of maturity of the cervix, it is advisable to use a gel containing prostaglandin E2 in the vagina. The drug is used in cases where there is a need for urgent delivery due to obstetric or some other complications. The conditions and contraindications for using vaginal gel are the same as when using prostaglandin gel for insertion into the cervical canal.
The main purpose of administering this drug is, first of all, the development of labor. As an additional effect, its positive effect on the process of cervical ripening when it is not sufficiently ready for childbirth is noted. During subsequent observation and management of patients, the following principles must be observed: every 3 hours after administration of the vaginal gel, the condition of the cervix is assessed. If the dilation of the cervix occurs less than 3 cm after 6 hours from the moment of administration of the gel, or there is no regular labor during this period of time, then the drug is re-administered 1 or 2 more times, also with an interval of 6 hours. If spontaneous opening of the membranes occurs before 6 hours have elapsed from the last administration of the gel, the drug is no longer administered. If, after administration of the drug, the cervix opens by at least 4 cm during regular labor, opening of the amniotic sac is possible, but not earlier than 6 hours after administration of the gel. If necessary, it is possible to administer oxytocin intravenously by drip for labor stimulation, however, not earlier than 6 hours after administration of the gel.
In the process of monitoring the woman in labor, monitor the condition of the fetus, the contractile activity of the uterus, and monitor the pulse, blood pressure and respiratory rate. Correction of weak contractile activity of the uterus and ineffective labor should include the use of the most effective medications in accordance with scientific data on the mechanisms of labor development.
In obstetric practice, to enhance the contractile activity of the uterus when labor is weak, various drugs are used that are administered intravenously. The most popular among them is still oxytocin. However, in some cases, for example, with an insufficiently mature cervix and prenatal rupture of amniotic fluid, it is possible to use an intravenous drip of a drug containing prostaglandin E2. And in case of primary weakness of labor, intravenous drip administration of a drug containing prostaglandin F2α is advisable.
Features of the use of oxytocin
The results of the studies indicate that in the process of artificially enhancing the contractile activity of the uterus, the anti-stress resistance of the fetus is reduced and its protective and adaptive capabilities are suppressed. At the same time, the use of oxytocin to enhance labor has the least favorable effect on the course of labor, the condition of the fetus and newborn in comparison with drugs containing prostaglandins E2 and F2α, which are used for the same purpose and in a similar obstetric situation.
The adverse effects of oxytocin can be especially pronounced in cases where the fetus experienced hypoxia even before the onset of labor, and the administration of oxytocin lasted more than 3 hours. The findings highlight the high risk to newborn health with long-term use of oxytocin. The combined intravenous use of a solution containing prostaglandin F2α and oxytocin in half the dosage has a milder effect on the fetus and is advisable if it is necessary to intensify contractions during the active phase of labor.
Labor stimulation
Birth stimulation with drugs containing prostaglandin E2 allows you to achieve the best effect in case of primary weakness of labor, insufficient maturity of the cervix and prenatal rupture of amniotic fluid. To achieve the best effect from the administration of drugs to correct weakness of labor, it is necessary to comply with certain principles and conditions. Thus, before labor stimulation, it is important to exclude a narrow pelvis, inferiority of the uterine wall due to numerous or complicated induced abortions or inflammatory processes.
The use of labor stimulation is contraindicated in the presence of a scar on the uterus after a cesarean section or other operations, as well as in unsatisfactory condition of the fetus. Labor stimulation should imitate the natural development of labor in order to achieve a physiological pace of labor. During the process of labor stimulation, constant monitoring is carried out over the condition of the fetus and the contractile activity of the uterus. The duration of labor stimulation should not exceed 3-4 hours. If excessive contractile activity of the uterus occurs or if the condition of the fetus worsens due to the administration of drugs, labor stimulation is stopped.
Ultrasound scanner HS60
Professional diagnostic tools.
Assessment of tissue elasticity, advanced 3D/4D/5D scanning capabilities, BI-RADS classifier, options for expert cardiological studies.