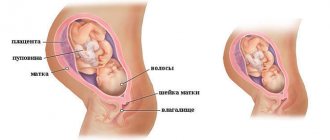
Let's start with the fact that it is impossible to calculate the duration of pregnancy (or gestation) with an accuracy of one day, and it is not necessary. The moment of conception is not always known, besides, a healthy pregnancy lasts from 38 to 42 weeks, and no one can predict exactly when your baby will be born. But knowing the expected date of birth, as well as the age of the fetus, is important for assessing the rate of intrauterine development of the child and for determining the time for basic screenings. Going on maternity leave is also a significant moment for the expectant mother. What methods do doctors use and how effective are they? This article was prepared by one of our professional doulas.
Obstetric and embryonic gestational age
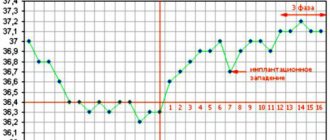
Doctors determine the gestational age using one main parameter (ultrasound) and two auxiliary ones (the date of the last menstruation and examination of the expectant mother).
It is known that pregnancy occurs at the time of ovulation, which occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle. A couple of days after the egg is fertilized, the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. Since the length of the cycle of even a particular woman is not constant, it is impossible to accurately determine the moment of conception. Therefore, in obstetrics it is customary to count the beginning of pregnancy from the first day of the last menstruation. This is called the obstetric stage of pregnancy. The obstetric period is calculated in two ways: 10 average menstrual cycles or 280 days are added to the first day of the last menstrual period, or 3 months are subtracted from the same date and 7 days are added (Naegele formula). The embryonic (real) gestation period is usually 7-14 days shorter. It can be most accurately determined if pregnancy occurs through IVF, since the date of fertilization is known.
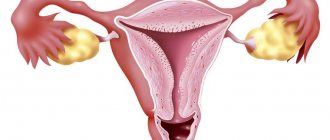
Ectopic pregnancy
If the fertilized egg, instead of the uterus itself, is attached to the wall of the fallopian tube or directly in the ovaries, such a pregnancy is called ectopic. It requires immediate interruption, since the growth of the fetus leads to rupture of the tube and a threat to the woman’s life. The main cause of this pathology is changes in the fallopian tubes due to inflammatory processes.
Diagnostics
The test determines an ectopic pregnancy in the same way as a normal one. Only ultrasound can detect the difference. If during this procedure the specialist does not see a fertilized egg in the uterus, additional examinations are prescribed that make it possible to determine the pathology at an early stage.
Treatment
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy is almost always surgical. Drug therapy is used only when the tube remains intact.
In the early stages of an ectopic pregnancy, laparoscopy is performed: a gentle operation is performed through a small puncture of the abdominal wall. Using a laparoscope (a special optical device), the doctor removes the fertilized egg, acting in a similar way to a mini-abortion. The safe and relatively painless procedure prevents injury to the fallopian tubes, and after some time the woman can become pregnant again and give birth to a healthy child.
If the fallopian tube is slightly damaged, salpingotomy is performed - a conservative operation. In case of threatening conditions - large blood loss, serious rupture of the tube, tubotomy is prescribed - a closed organ-preserving surgical operation. In extreme cases, a tubectomy is performed, where the affected tube is completely removed.
After effective treatment and rehabilitation therapy for 6-12 months, the next pregnancy may occur. Otherwise, an additional examination of the condition of the female reproductive organs is carried out.
| Prenatal and postnatal care programs: | |
| Prices | |
| Basic package "STANDARD" | 150,000 rub. |
| Basic package "STANDARD PLUS" | 230,000 rub. |
| Basic package "ALL INCLUSIVE" | 290,000 rub. |
| Basic package “ALL INCLUSIVE BEFORE AND AFTER” (from 6 weeks of pregnancy until 1 year after birth) | from 310,000 rub. |
Abortion services
| Services list | |
| Prices | |
| Surgical termination of pregnancy (from 6 weeks) | from 25,000 rub. |
| High-complexity surgical abortion | from 35,000 rub. |
| Medical termination of pregnancy (“Mifegin”) | from 23,000 rub. |
| Medical termination of pregnancy (Mifepristone) | from 19,000 rub. |
| Medical termination of pregnancy (Pencrafton) | from 17,000 rub. |
Premature and late first birth
Premature birth is considered to be a birth that occurs at 37 weeks after conception or earlier. Reasons for having a baby prematurely:
- inflammation and infections of the reproductive organs and urinary tract;
- stress and emotional tension of the mother;
- high blood pressure, preeclampsia;
- Rhesus conflict;
- chronic diseases;
- abnormalities in the structure of the uterus;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- placenta previa and other pathologies.
Cases when a child is born later than 42 weeks or more after conception are called late births. Causes of late labor:
- dysfunction of endocrine organs;
- mental stress;
- chronic liver and kidney diseases;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- unfavorable external conditions, malnutrition.
Prolonged stay in the womb is dangerous for the child, so obstetricians use artificial stimulation of labor in these cases, for example, inserting prostaglandin suppositories into the vagina. If there is no effect, a caesarean section is recommended.
At what stage of pregnancy do first births most often occur?
In everyday life, you can often hear the statement that pregnant women for the first time usually do not reach the due date set by the doctor and give birth before the appointed date. Is this opinion true or is it a myth? Statistics confirm that a first-time mother goes through her gestational period a little faster than a woman who has already given birth before.
For most women, their first pregnancy lasts 41 weeks and one day, which is 2 days longer than the normal gestation period for multiparous women.
This period is very average and it would be a mistake to rely on it. When the doctor names the expected date of birth, this does not mean that the long-awaited event will occur exactly on the appointed day. If the pregnancy proceeds normally, then the complete formation of the child ends by the 38th week, and from this moment the baby is ready for its birth. However, he has every right to linger in the mother’s belly for up to 42 weeks. This is confirmed by the 10% of women who give birth to absolutely healthy babies at 42 weeks.
The duration of pregnancy depends on the individual characteristics of the woman and the external conditions surrounding her. Any day between 38 and 42 weeks of gestation is normal due date. Some doctors take this into account and prefer to use “floating” dates instead of the exact day of birth. This helps save the woman and her immediate circle from unnecessary worries and disappointment over the fact that she was unable to give birth exactly on the day that the doctor indicated in the exchange card.
How does the obstetric period differ from the embryonic period?
information As already mentioned, the obstetric period is determined by menstruation, and the embryonic period is determined by the date of conception. With a regular 28-day menstrual cycle, the first is longer than the second by an average of 14 days, since ovulation occurs in the middle of the cycle (and it is during this period that conception occurs). However, if a woman has an irregular menstrual cycle, the difference can be more than a month.
For example, if a woman ovulated on the 53rd day of her cycle, then the difference in this case is 53 days. This is possible with polycystic ovary syndrome, hormonal disorders, stress, and taking certain medications.
There are also cases when a woman had her last period before her previous pregnancy. Then she breastfed, and at that time there was lactational amenorrhea (lack of menstruation). With a decrease in the amount of feeding, her egg began to mature, and then, when it met a sperm during ovulation, pregnancy occurred. In this case, there is no need to talk about the obstetric period as such, because menstruation occurred more than a year ago!
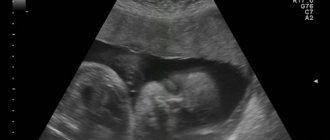
Obstetric term with ultrasound
Ultrasound examination is one of the ways to determine the obstetric stage of pregnancy. In some cases, it is the main one (as, for example, in a situation with pregnancy against the background of lactational amenorrhea or with irregular periods).
In the first trimester, the main indicator for determining the gestational age is the CTE (coccygeal-parietal size) and the size of the ovum. The doctor compares these indicators with the average and gives an opinion regarding the period. During this period, children differ least from each other in size. Subsequent ultrasounds evaluate the circumference of the fetus’s abdomen and head, and the length of its thigh. But in later stages, all babies, like us, are different from each other: some are taller, some are a little bigger, some have longer legs... Therefore, when comparing the results with the average, there is a large error due to the physiological characteristics of each child. Also, fetal development disorders (hypotrophy, hypoxia, hemolytic disease, fetoplacental insufficiency) can make their own adjustments here.
additionally, the gestational age determined by ultrasound is almost no different from the obstetric one during a normally developing pregnancy, since those 2 weeks from the moment of menstruation to conception have already been added to the tables of average sizes. Only when an ultrasound is performed at the very beginning (up to 4-6 weeks), the set period can coincide with the embryonic one.
Based on the above, the most accurate gestational age is the one set before 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Does the date of first birth depend on the gender of the child?
To answer this question, you should turn to statistics. On average, first-time mothers carrying girls give birth 1-2 weeks earlier than expectant mothers pregnant with boys. This is explained by the fact that girls develop a little more actively than boys, and their bodies are ready for birth faster. This advance in physical development continues after birth, in preschool and early school age, as a result of which girls normally look larger and more developed than their peers of the opposite sex.
The maturity of the baby and the criteria for determining it
When a child is born, obstetricians and pediatricians assess his physical condition. To determine the maturity of a newborn, doctors use the following criteria:
- height (normal height is considered to be from 46 to 52 cm);
- weight (about 3200-3400 g);
- the presence of a subcutaneous fat layer, due to which the body of a child of the European race has a pink color;
- developed and elastic cartilages of the ears and nose;
- the presence of nails, the ends of which protrude slightly beyond the edges of the fingers;
- length of hair on the head – at least 2 cm;
- In boys, the testicles are located in the scrotum; in girls, the labia majora cover the labia minora;
- shout;
- active body movements.
With the advent of ultrasound, doctors have an additional opportunity to assess the maturity of the fetus before its birth. Measuring bone length and head diameter is not considered a reliable indicator, since these parameters can vary greatly between children. To determine the maturity of the fetus, ultrasound measures the ratio of the cortical and medulla layers of the adrenal glands - the adrenal coefficient.
The second important criterion is the degree of development of lung tissue. The condition of the lungs determines the child’s ability to breathe after leaving the mother’s womb into the external environment. Modern ultrasound techniques make it possible to measure the size of the lungs, echogenicity, and also evaluate their blood supply.
According to ultrasound data
Often, obstetricians-gynecologists determine the date of birth based on ultrasound results. Determining the timing of pregnancy and date of birth using ultrasound is the most accurate method. You can determine the baby’s date of birth using one of 2 methods:
- Based on the first ultrasound at 11-14 weeks, the doctor will determine the exact gestational age; all that remains is to count the period until birth from the due date.
- Based on the results of the 3rd ultrasound at 32-34 weeks. In this case, the gynecologist will focus on the condition of the placenta, the location of the fetus in relation to the woman’s pelvis, the readiness of the cervix to dilate, the maturity of the fetus and other factors that indicate the readiness of the woman and child for childbirth.
You can determine the PDR using a special calendar/table.