Symptoms and clinical picture of ascariasis in children
If the number of worms entering the body is small, the disease may occur in an unexpressed form.
At an early stage, the following manifestations of ascariasis in children may be observed (associated with the penetration of larvae into the lungs and liver):
- deterioration in general health;
- temperature rise to 38 C;
- heavy sweating;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite;
- swelling of the eyelids and face;
- cough is dry or with mucous sputum streaked with blood;
- difficulty wheezing, wheezing;
- chest pain;
- dyspnea;
- suffocation;
- allergic reaction (urticaria);
- skin itching;
- enlargement of lymph nodes, liver and spleen.
Symptoms of ascariasis in children at the second stage - intestinal:
- bloating and flatulence, pale skin or mild jaundice,
- abdominal pain, most often in the umbilical area,
- constipation or loose stools, weight loss.
Further development of the disease leads to a significant weakening of the immune system and the development of serious complications.
Where do children get roundworms?
Infection of children with ascariasis occurs through the fecal-oral route. A person in whose body sexually mature individuals produce fertilized eggs excretes them along with feces. Children become infected with such eggs through soil, contaminated water, food, and dirty hands.
Routes of infection:
- Contact with infected children in a children's group;
- Toys;
- Door handles in public places, in transport;
- Banknotes and coins;
- Vegetables and fruits with soil microparticles;
- Transfer of roundworm eggs by insects.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of ascariasis in children is based on clinical and epidemiological data. In the intestinal stage, the diagnosis is made by the presence of eggs or roundworms in the feces.
Basic tests for ascariasis in children:
- complete blood count (shows the presence of leukocytosis and eosinophilia);
- microscopic sputum smear (detects the presence of larvae);
- stool analysis for worm eggs.
X-rays of the intestines and chest, endoscopic studies can reveal adult roundworms.
Treatment
Photo: molochnitsa.com
Ascariasis is an infection of the body by parasites, which are popularly called worms. Treatment for ascariasis should only be prescribed by a doctor after undergoing a full laboratory examination. And when the diagnosis has already been made, the attending physician selects individually for each drug that will be suitable specifically for his body. Medicines used to treat worms can have a number of side effects, so you should not self-treat.
How to properly treat ascariasis in adults?
All cases of this disease require immediate treatment with anthelmintic drugs. There is a specific treatment regimen for ascariasis:
- This disease can be treated at home, but in some severe cases the patient may be hospitalized with severe complications, in which case surgical intervention is necessary;
- Follow a special diet in which meals should be taken in frequent but small portions. There should be no long gaps between meals; you should always have a small snack. It is recommended to consume the following products: stale wheat bread, fish and meat broths, fermented milk products, pureed rice, semolina and buckwheat porridge, vegetables, soft fruits and berries. It is better to limit yourself at the time of illness from such foods as fresh bread, fatty meat and fish, sweets, onions, radishes, garlic, full-fat milk and sour cream;
- During illness, you should maintain personal hygiene and try not to contact others, have your own spoon and plate so as not to infect the rest of the family.
Also, treatment of ascariasis is carried out with special drugs, which can be individually prescribed by a doctor after an examination, but you should not choose them yourself:
- Antihelminthic drugs. Mainly used for treatment in adults are drugs such as levamisole, mebendazole, nemozol, pyrantel. The treatment regimen for ascariasis with nemozol is prescribed directly by the doctor. This drug is used most often due to the fact that after the first doses roundworms die quickly, and it is also less dangerous for the human body than other drugs;
- Enzymatic preparations: such as Creon, Mezim, Pancreatin. They are taken to improve the functioning of the digestive system and protect it, because worms have a detrimental effect on the intestines and sometimes cause complications;
- Antihistamines: such as Claritin, Erius, Suprastin, Tavegil. They are prescribed in a short course with all other drugs to avoid allergization of the body when expelling parasites;
- Useful probiotics: bifiform, linnex, bifidum forte. When infected with helminths, problems with the intestines may occur, stools may be disrupted, or even intestinal dysbiosis may begin. Therefore, the doctor prescribes these drugs to normalize the intestinal microflora.
Methods for treating ascariasis in children
Treatment of ascariasis in children is almost the same as in adults, the only difference is in the choice of drugs. Effective treatment of ascariasis is carried out with the following drugs such as decaris, pyrantel, vormox. In addition to these drugs, it is recommended to take enzymes to maintain intestinal microflora and other necessary medications, which are prescribed by a doctor based on the patient’s condition. If the child's condition worsens and vomiting and diarrhea begin, antiemetic drugs are also used and treatment with detoxification therapy is prescribed.
When complications occur and the disease develops into a severe form, a surgical method of removing roundworms is used. Infection with parasites can trigger the onset of anemic disease, so in such cases it is necessary to start using iron supplements. The oxygen procedure gives a fairly good effect. It is carried out on an empty stomach, air is introduced into the body using a probe, this procedure should be repeated 2-3 times. After three weeks, the child will need to undergo a repeat stool test, after which the effectiveness of this treatment will be visible.
How to treat ascariasis in pregnant women?
It is quite difficult to identify ascariasis in pregnant women, because the signs of this disease are somewhat similar to the symptoms of the disease itself. If infection with worms occurs during pregnancy, a dry cough may appear, allergic reactions and pain in the liver area may begin to develop, all this occurs due to the migration of larvae throughout the body.
Ascariasis is quite dangerous for a child, because the larvae can penetrate to the fetus through the bloodstream, and at birth the baby may develop bronchopulmonary diseases, allergic reactions, and liver disorders. Treatment of ascariasis in pregnant women is carried out with drugs such as piperazine, sancophen, and heptylresorcinol. Treatment with oxygen procedures can also be used.
Basic treatment methods and contraindications
Ascariasis can only be treated with medication.
In the acute phase, desensitizing and anthelmintic drugs are used - Thiabendazole or Mebendazole. Bronchodilators and corticosteroids are also prescribed to relieve pulmonary manifestations.
In the intestinal stage, Levamisole or Pyrantel is used once, as well as multivitamins, iron supplements, and enzyme preparations.
Usually the disease is completely cured. A month later, a control stool test is prescribed (done three times).
Treatment of roundworms in children
Treatment of roundworms in children comes down to taking anthelmintic drugs. In no case should you select this or that remedy yourself; only a doctor can do this.
Firstly, not every drug can be used to treat children. Secondly, the dose for them is selected individually. Thirdly, all anthelmintic drugs have a toxic effect on the body, so self-medication can cause significant harm to health.
If roundworm is diagnosed in a child during the migration phase, then desensitizing drugs and anthelmintics are indicated. Most often, Tiabendazole (Mintezol) or mebendazole (Vermox) is prescribed in childhood. They have a wide spectrum of activity and have a detrimental effect on ascaris larvae. If a child has severe pulmonary symptoms, then a dose of bronchodilators and corticosteroids is selected.
When roundworms in the intestinal stage are detected in children, the following drugs are prescribed to choose from:
- Vermox (Mebendazole).
- Decaris (Levamisole).
- Pyrantel (Kombantrin).
- Piperazine.
These drugs are highly effective and often one course of treatment is enough to rid the child of the infection. 30 days after treatment, re-diagnosis of the disease is necessary.
If a child suffers from acute ascariasis, regardless of the prescription of the drug, antihistamines are a mandatory component of treatment. They stop allergic reactions resulting from the release of toxins by helminths. For sensitization, calcium gluconate, calcium chloride, ascorbic acid, and glucocorticosteroids are used.
Drugs for the treatment of ascariasis:
- Mintezol. The daily dose is 25 mg/kg/day, it is divided into 3 doses, the course of treatment is 5 days.
- Medamin. The daily dose is 10 mg/kg/day, it is divided into 3 doses, taken throughout the day, with massive invasion the course takes 2-3 days.
- Decaris (Levamisole). The daily dose is 2.5 mg/kg/day, divided into 2-3 doses, taken throughout the day.
- Kombantrin. Used in tablet form according to age and body weight.
- Vermox (Mebendazole). The daily dose is 25-50-100 g/day, it is divided into 2 doses, the course of treatment is 3-4 days. Not used in children under 2 years of age, as well as in cases of mass infestation, as it can cause roundworms to enter the lungs, throat, stop intestinal motility, vomiting, and acute pain.
During treatment, it is advisable to transfer the child to a dietary regimen, with meals rich in vitamins and proteins of animal origin. You need to give up simple carbohydrates (sweets, flour and confectionery), and fatty foods.
To correct intestinal microflora, patients are recommended to take Bifiform, Linex and other prebiotics and probiotics. Enterosorbents prescribed after a course of anthelmintic therapy. They are aimed at reducing desensitization of the body. These may be drugs such as Polyphepan, White activated carbon, Polysorb, etc. In addition to specific drugs, enzymes, multivitamins, and iron supplements are prescribed (if anemia is present).
The effectiveness of treatment is monitored 3 weeks after completion. In laboratory conditions, stool is examined three times. The prognosis for treatment of ascariasis is favorable; special care should be taken when treating helminthic infestations in infants. Asphyxia after migration of roundworms into the respiratory tract can be fatal; it is relieved during urgent surgical intervention. As a rule, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. Complications do not develop often, but in emergency cases surgery may be required.
Ascariasis
Clinical manifestations of the early phase of ascariasis , caused by the migration of ascaris larvae in the bloodstream, vary in severity. Often, with low-intensity infection, this phase is subclinical or asymptomatic. In clinically pronounced cases, complaints of general weakness, malaise, headaches, fatigue, loss of ability to work, sometimes fever, and the appearance of itchy rashes such as urticaria prevail on the skin. Less commonly, usually with intense infections, a picture of pulmonary pathology appears in the form of cough, sometimes with sputum mixed with blood, with an asthmatic component, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Auscultation reveals wheezing, pleural friction noise, and phenomena of exudative pleurisy. X-ray examination of the lungs reveals eosinophilic infiltrates described by Leffler in 1932, characterized by variability in their size, configuration, and position - “volatile infiltrates.” As a rule, focal infiltration of the lungs is accompanied by blood eosinophilia, sometimes the number of blood eosinophils reaches 35 - 60%.
Migrating roundworm larvae can cause severe pulmonary phenomena - acute pneumonia and bronchitis, which was proven in a self-experiment by Koino (1922), who swallowed 2,000 mature roundworm eggs. In severe pneumonia of ascariasis etiology, accompanied by allergies, extensive hemorrhages caused by the rupture of migrating larvae in the lung capillaries with the subsequent development of inflammatory phenomena play an important role in the development of the disease.
These clinical manifestations of the early phase are supplemented in some patients by symptoms of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and liver.
The second, the intestinal phase of ascariasis , is also characterized by a variety of pathologies and severity. Invasion can occur with mild symptoms or even asymptomatic. In clinically pronounced cases, gastrointestinal pathology and often asthenic syndrome prevail. Frequent complaints of patients are disorders of appetite, decreased appetite, “capricious appetite” in children, nausea, increased salivation, “saliva rolls in a cloud” more often in the morning on an empty stomach, etc.
In some cases, there is a tendency to diarrhea or constipation; more often they alternate; progressive enteritis is less common. In children, dyspeptic symptoms predominate, accompanying abdominal pain, often cramping and quite severe, occurring spontaneously or upon palpation. Functional and morphological disorders in the small intestine were detected x-ray in the form of changes in the relief of the mucous membrane, etc. Sometimes there is an unpleasant sensation of something moving in the intestine, bloating.
Pain on palpation of the abdomen during the intestinal phase of ascariasis is not uncommon, and in children it is most often diffuse, in adults it is local - in the midline above the navel, and to the right of the midline. Gastric secretion in infected people is often reduced.
In almost all cases of ascariasis in children, symptoms from the nervous system are observed, asthenic manifestations such as weakness, poor health, irritability, headaches, often absent-mindedness, memory loss, restless sleep, night terrors, twitching, less often hysterical and epileptic seizures, symptom complex Meniere's, decreased intelligence.
Sometimes it is these asthenic phenomena that prevail over the others.
In the phase of intestinal ascariasis, sometimes, as in the first phase, allergic phenomena are observed, such as a rash like nettle fever, eosinophilia, although less pronounced. In the blood, especially in children, a frequent companion to ascariasis is moderate hypochromic anemia.
From the cardiovascular system, a decrease in arterial and venous pressure was noted.
In the intestinal phase of ascariasis, both intestinal and extraintestinal complications can occur. Most of them are associated with increased motor activity of adult roundworms: intestinal obstruction, perforated peritonitis, ascariasis of the liver, ascariasis of the pancreas, respiratory tract, etc.
Ascariasis infestation in the obstetric clinic also does not remain without consequences. The negative effect of ascariasis on the course of pregnancy has been proven. In infected pregnant women, toxicosis and fetal development disorders are more often recorded, and the course of labor and the postpartum period becomes more complicated.
A frequent complication of ascariasis is intestinal obstruction , which is caused by the closure of the intestinal lumen with a ball of roundworms or due to a violation of the neuromuscular regulation of intestinal tone. When palpating the abdomen in patients with similar complications, one can feel a round, doughy consistency tumor-tangle of roundworms, which can be localized in any part of the intestine. In some cases, with a thin abdominal wall, it is possible to palpate the bodies of individual helminths in the intestinal lumen.
A severe complication of ascariasis is the penetration of helminths into the bile ducts and gallbladder . In these cases, severe pain occurs that is not relieved even by narcotic analgesics. Against the background of these attacks, vomiting often occurs and helminths are sometimes released with the vomit. In cases of cholangiohepatitis and mechanical blockage of the common bile duct by roundworms, jaundice occurs. The temperature during the development of complications can be of a septic nature with stunning chills. As a result of the addition of a bacterial infection, purulent cholangitis and multiple liver abscesses often occur, which in turn can be complicated by peritonitis, purulent pleurisy, sepsis, and abscesses in the abdominal cavity.
Penetration of roundworms into the pancreatic ducts causes acute pancreatitis. If they enter the vermiform appendix, it causes appendicitis or appendicular colic without inflammatory manifestations.
In some cases, roundworms, ascending the digestive tract, reach the pharynx and from here crawl into the respiratory tract, which causes death from asphyxia.
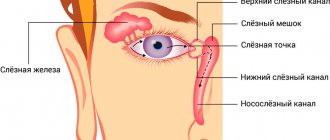
In rare cases, roundworms are found in the genitourinary organs, nasolacrimal canal, eustachian tube, middle ear, external auditory canal, and perinephric tissue.
Infestation by roundworms aggravates the course of various infectious and non-infectious diseases and disrupts immunogenesis in infectious diseases.