“Three-day fever”, “summer flu”, “Boston fever”, “Turkish chickenpox” are just a few names for the Coxsackie virus. This heat-loving infection, contrary to popular belief, can ruin summer holidays not only on the Turkish coast. Infection with this disease is recorded annually, in addition to Turkey, in Greece, Spain, Bulgaria and even on the Black Sea coast of Russia. Is there any way to protect yourself from this infection? Who is at risk, who does the virus “choose” first? And how to treat if you are already infected?
- Symptoms of the coxsackie virus in children
- What products are recommended for patients?
- Is it possible to use Viferon for coxsackie?
- What antiviral drugs can be taken for prevention?
Every year, starting from 2021, Rospotrebnadzor issues leaflets for tourists planning to spend a summer holiday at sea in warm countries, which talk about the dangers of the virus, as well as some resort places where the likelihood of infection is especially high.
People traditionally go to the sea with whole families with small children to relax and improve their health, and instead of the gentle sea and beach they risk spending time isolated in a hospital bed. So what do you need to know about the virus to avoid getting sick, and if you do get sick, how to treat it to avoid dangerous complications?
Symptoms of the coxsackie virus in children
What is usually called the Coxsackie virus is actually a group of enteroviruses (29 strains) that enter the human body through the oral mucosa and then, reaching the intestines, begin to actively multiply there. The symptoms of the disease are very similar to chickenpox, which is why it is often called “Turkish chickenpox.” But there are also differences: in adults the disease is less severe than in children. Children, due to their underdeveloped immune system, are the easiest prey for the virus. In severe form, the disease can affect the nervous system, including the brain, as well as disrupt the functioning of the heart and affect changes in the muscle tissue of this organ, and negatively affect the liver.
The virus is extremely stable in the external environment and is perfectly preserved in the aquatic environment (drinking water from fountains, ice from raw water, swimming pools). You can also become infected with the virus through airborne droplets (from one person to another), contact (toys in the children's room, swimming in the pool) and food (through dirty dishes, unwashed vegetables and fruits, water). The contagiousness (infectiousness) of the virus is almost 100%. That is, if one child in the playroom gets sick, after a couple of days everyone who came into contact with him will feel unwell, including adults. Only in adults the disease can pass almost unnoticed; many tourists do not even realize that they are sick, attributing the malaise to fatigue or overheating on the beach, since they already have an established immune system. But if a person has reduced body resistance, then you cannot do without a doctor. So what symptoms indicate this enterovirus infection?
Symptoms in the initial stage of the disease:
- Intoxication, which is often indicated by a brown or yellowish coating on the tongue;
- High temperature up to 39-40ºС, against this background convulsions are possible;
- Headache, weakness and drowsiness, aches throughout the body;
- Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting;
- Redness in the throat, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes.
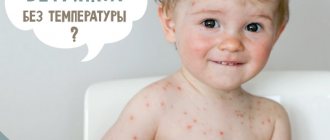
Rash period: mouth-hand-foot syndrome
- After 1-2 days, watery blisters with a diameter of about 2 mm form on the inner surface of the cheeks and lips, and around the outside of the mouth. They open themselves, which leads to the formation of ulcers.
- Simultaneously with the rashes in the mouth, the same blisters appear on the skin of the palms and soles. The rash may also appear on other parts of the body.
Recovery period
After 5 days, the immune system begins to produce antibodies. The temperature drops, the general condition of the child gradually improves. The recovery period lasts 5-7 days: ulcers on the mucous membrane heal, appetite returns. On average, the disease lasts 10 days. However, if the child’s immunity is weakened, the virus remains in the nervous tissue and periodically causes relapses of diseases: for example, serous meningitis, herpetic sore throat, conjunctivitis, viral heart disease, and so on.
How dangerous is the Coxsackie virus?
The enterovirus itself does not pose any danger; it lies in the forms of its manifestation, which are diverse and leave a number of complications in the body, affect the immune system, cause inflammation or degeneration of the brain, muscles, and heart. Coxsackie causes the development of the following diseases:
- Summer flu or enteroviral fever is the mildest form of the disease, accompanied by intoxication, weakness, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, liver, and spleen.
- Herpetic sore throat is characterized by inflammation of the tonsils, the appearance of whitish papules, turning into white blisters, and then into ulcers.
- Boston exanthema is expressed in redness of the throat and eyes, rashes on the arms, legs and mouth (sometimes in the buttocks and groin area).
- Myalgia - damage to the muscles of the whole body, pain in them, fever.
- Aseptic meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes of the brain, this form threatens the patient’s life, manifested by fever, severe headache, vomiting not associated with meals, and convulsions.
- During pregnancy, there is a high probability of infection of the fetus through the placenta; the child may be born with pathologies, developmental abnormalities, or die.
As a result of the damage, extensive inflammatory processes can begin, diseases such as meningitis, encephalitis, hepatitis, etc. develop. The immune system loses its defenses, and the body becomes more susceptible to the negative effects of other viruses and bacteria. The consequences of the Coxsackie virus can be fatal if the symptoms that appear are ignored.
The danger of enterovirus also lies in its survivability; Even if the wave of the epidemic has passed, the likelihood of infection will not decrease. In addition, if you once had to suffer from this disease, this does not guarantee protection from relapse. This is due to the fact that the virus has more than 30 different types, and the presence of antibodies to one in the blood does not protect against the other.
What antiviral agents for Coxsackie virus are recommended for patients (at the INN level)
For any disease, comprehensive treatment under the supervision of a doctor is necessary. And enterovirus infection is no exception. As a rule, when characteristic signs of the disease are detected in a small patient, both antiviral antiviral and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. Among antiviral drugs, drugs containing interferon are used. Such drugs include Viferon Suppositories.
Suppositories containing human interferon do not give the virus a head start of several days until the body itself begins to fight the infection, but begins to act immediately, thereby reducing the recovery time. For symptomatic treatment, the following is used:
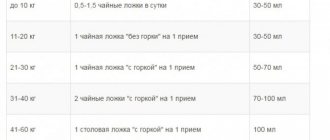
- Antipyretic syrups or suppositories containing paracetamol or ibuprofen.
- To avoid dehydration and alleviate the symptoms of intoxication, you should drink plenty of water (boiled or bottled), water with lemon;
- For diarrhea, it is advisable to take absorbent agents, such as activated carbon;
- To relieve pain in the mouth, you can use gels used for teething in babies.
- To speed up healing and prevent infection of mouth ulcers, antibacterial sprays are used;
- Although the rash usually does not cause itching in children (unlike chickenpox), if it bothers the baby, antihistamines can be used.
Is Coxsackie virus infection contagious?
The Coxsackie virus is highly contagious. These viruses are most often transmitted through the fecal-oral and respiratory routes.
How long are people with Coxsackie virus infectious?
The patient is most contagious during the first week, starting from the appearance of the first symptoms. However, viable coxsackie viruses were detected three weeks after the onset of the disease in the respiratory tract, and were present in feces even up to eight weeks, but during this time the viruses became less infectious. Thus, a person remains contagious with the Coxsackie virus for several weeks after recovery, although not as much as at the beginning of the disease.
What is the incubation period for the Coxsackie virus?
The incubation period for Coxsackie infection is relatively short; it lasts from one to seven days.
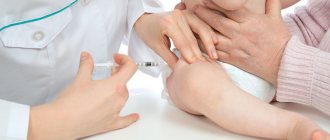
Is it possible to use Viferon for coxsackie?
According to the instructions, the drug is recommended for the treatment of enteroviral infections in complex therapy, including as an antiviral agent against the Coxsackie virus.
The recommended dose for newborns, including premature babies with a gestational age of more than 34 weeks, is VIFERON 150,000 IU daily, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours. The course of treatment is 5 days.
Premature newborns with a gestational age of less than 34 weeks are recommended to use the drug VIFERON 150,000 IU daily, 1 suppository 3 times a day after 8 hours. The course of treatment is 5 days. The recommended number of courses is from one to two with a break of 5 days.
Children under 7 years of age, daily 1 suppository of 150,000 IU 2 times a day with an interval of 12 hours for 5 days (if indicated, treatment can be continued with a break of 5 days).i
How to avoid getting sick with the Coxsackie virus?
Preventive measures will help protect against the Coxsackie virus. In rare cases, infection is possible, since acquired immunity does not guarantee complete protection. For this reason, the following precautions are recommended:
- A healthy person should avoid contact with a sick person.
- Playrooms with a large number of objects that all children touch can be a place for the spread of infection, so they should be visited as little as possible.
- Catering places where cutlery and dishes can be touched by all visitors should be avoided.
- You should not swallow water in the pool.
- In case of mass infection, it is prohibited to use tap water for brushing teeth and washing food.
- Maintaining good personal hygiene is an important part of prevention, so it is necessary to thoroughly wash your hands and fruits, as well as regularly change your personal towel for your hands and face.
- Enclosed spaces where there are many people should be avoided, and walks in the fresh air should be carried out more often.
- The premises must be ventilated, as bacteria begin to multiply when the humidity level in the room is high.
- It is not advisable to consume food that has been open for a long period of time in a public place.
To avoid becoming a victim of complications, you need to wash your hands with soap. For this, running water and an antibacterial agent, which is sold at a pharmacy or store, are suitable. If it is not possible to carry out the procedure, you can use alcohol wipes.
Infected persons must use a disposable mask, which is changed every 4 hours. To prevent the spread of infection, feces and diapers are treated and disposed of. Surfaces and common items should be washed with a solution containing household bleach or bleach. To prepare the mixture, add 1 tbsp to 1 liter of water. l. facilities.
It is recommended to additionally treat pacifiers, toys and rattles on which the baby’s saliva remains with boiling water. Due to the lack of a vaccine against the virus, women must be extremely careful during pregnancy, as the disease harms not only the expectant mother, but also negatively affects the development of the fetus.
What antiviral drugs can children take to prevent coxsackie?
Usually, before traveling to resorts, questions arise about the prevention of a particular disease that is present in a hot climate, and against which people from other regions have no immunity. Of course, it would be great to give some antiviral drugs for children against Coxsackie to your child and then go on vacation in peace. But, unfortunately, as in the situation with the flu, there are no such drugs that 100 percent protect against infection. And there are two ways: either not to visit places with small children that are potentially dangerous for them in terms of infection, or to observe all possible precautions, first of all, personal hygiene and the hygiene of the child. Make sure that he does not touch his face and mouth with dirty hands, does not use other people’s things, including toys, and eats only clean, heat-treated water and only well-washed fruits. It is clear that in resort conditions, it is not always possible to wash your hands with soap, so it is worth stocking up on disinfectant gels that you can use to treat your hands. Also, as a preventive measure, antiviral drugs for Coxsackie can be used, which in the form of sprays, gels or ointments are applied to the nasal mucosa to avoid infection by airborne droplets.
How is the Coxsackie virus spread?
Transmission of the virus occurs from a sick person to a healthy person. Bacteria are found in the bodily fluids and secretions of an infected person, which may touch objects, clothing and other surfaces. The infection is transmitted when these objects are taken by a healthy person and then touched to the mouth, nose or eyes.
Another common way for the virus to enter the body is among children and adults. When fecal matter containing harmful microorganisms gets onto the hands and the child subsequently touches the face. Kindergarten or nursery workers should take this into account when processing diapers. Diarrhea indicates an intestinal infection.
The accumulation and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms occurs in the mucous membrane and tissues of the oral cavity and nasopharynx. From here the bacteria are transferred to the digestive system. When they enter the bloodstream, they spread throughout the body, causing inflammation. Protective functions are triggered when the virus begins to parasitize healthy cells.
conclusions
The lack of specific immunity makes almost every person vulnerable to diseases caused by pathogens of the enterovirus group. You should not treat “resort infections” irresponsibly; they often lead to serious complications. Most patients infected with the Coxsackie virus do not require hospitalization, have no negative consequences, and recover within 10-14 days. But children under 3 years of age are at high risk of developing dehydration, especially with vomiting and diarrhea. And if, nevertheless, a trip with a small child to the resort must take place, then the mother needs to take care of both additional hygiene products and the presence of a first aid kit with essential drugs in her luggage, so as not to run around local pharmacies in search of “antiviral drugs for coxsackie”. And, of course, when applying for insurance, you need to make sure that with this infection you can count on the help of a doctor, which is especially important if the disease suddenly causes complications.
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
iExperience of using Viferon in complex therapy of serous meningitis of enteroviral etiology” / S. P. Kokoreva, A. M. Zemskov, N. P. Kuprina // Pediatrics. – 2002. – N 5. – P. 68-71. – ISSN 0031-403X
Loading...
Take other surveys
Infectious period of the Coxsackie virus
The virus lives in the gastrointestinal tract for an average of 10 to 20 days. The possibility of contracting the disease exists within 60 days after a person has fully recovered. Harmful bacteria may be present in the patient's saliva, so the risk of developing pathology remains high. You can confidently contact someone who has suffered an infectious disease after 6 months.
To effectively combat the virus, you need to know how contagious a person is and what temperature conditions help destroy germs. Coxsackie can withstand temperatures as low as -70°C. It adapts to these conditions and lives in them for years. The infection continues to exist after defrosting. High temperatures lead to its death.
In 30 minutes, the virus will be destroyed at a temperature of +60°C, and if you place harmful microorganisms in boiling water, they will die instantly. A person who comes into contact with a patient with Coxsackie becomes infected in 98% of cases, but if he has previously suffered from this disease, the acquired immune defense helps protect him from the penetration of bacteria.