Signs of molluscum contagiosum
The usual element of molluscum contagiosum is a compacted papule (nodule) pink or flesh-colored with a round or oval shape. In case of palpation, an acute painful sensation appears. Molluscum contagiosum has a standard size of two to ten millimeters. Of course, there are also cases of the appearance of huge nodes with dimensions up to several centimeters. Often, nodules can unite and form conglomerates. Such formations merge into groups and can actively continue to spread throughout the human body.
The surface of the nodules is shiny and smooth. There is an umbilical depression on it. When pressed, a white cheesy liquid begins to flow out of it. Such secretions are called horny masses in medicine.
Clinical picture of the disease
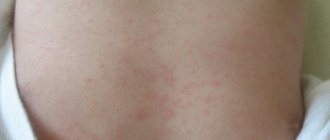
Molluscum contagiosum is characterized by the appearance of a characteristic rash on the skin and mucous membranes, in most cases without any subjective sensations. Sometimes patients are bothered by itching and burning. Atypical forms of the disease are very rarely recorded.
Localization. The rash in children is localized on the skin of the face (often in the forehead and eyelids), neck, upper chest (including the armpits), upper and lower extremities. Most often, the rash appears on the face, torso, armpits and diaper area. If a rash appears in the genital area, the assumption of sexual abuse should be excluded.
Prevalence. Nodules in the disease are usually single - from 5 to 20 pieces, grouped in one area. In immunodeficiency and in persons with atopic dermatitis, they appear in large numbers, scattered throughout the body.
When scratched, the lesions spread in a linear direction.
Characteristics of the rash. At the beginning of the disease, small (1 - 2 mm in diameter) papules appear on the skin. Gradually they increase in size (up to 5 - 7 mm) and take on the appearance of a dome-shaped nodule. The nodules are hard, flesh-colored or whitish with a pearly sheen. Most of them have a depression in the center, which is clearly visible when magnified. When pressed from the sides, a dense, mushy mass emerges from the nodule, containing keratin and “mollusc bodies” filled with a huge number of virions. In atypical or advanced cases, this sign is absent.
Course of the disease. Molluscum contagiosum is characterized in most cases by self-healing within several months. With constant scratching and the spread of infection to other areas of the skin, nodules appear again and again, and healing is delayed up to 6 - 9 months or more. Sick children are subject to isolation from the children's group until complete recovery.
Complications. Complications of the disease include cases of secondary infection and spread of infection to the eye tissue.
Rice. 5. Scheme of the structure of a nodule in molluscum contagiosum.
Rice. 6. Molluscum contagiosum. Type of rash on the skin.
Forms of molluscum contagiosum
There are several types of molluscum contagiosum:
- The typical form looks like several assembled elements, which are located very close to each other, namely in the vicinity of one anatomically infected area;
- The generalized form is determined by the localization of nodular rashes on various parts of the human body;
- A complicated form appears when a bacterial infection occurs. Redness, pus discharge and pain are a typical form of the disease in sexually transmitted infections. Another feature of the manifestation of molluscum contagiosum in patients with HIV is its active localization in the facial area of the nasolabial area and chin.
Epidemiology
Molluscum contagiosum is found everywhere. Both adults and children aged 1 to 12 years are affected, most often from 1 to 4 years.
The main reservoir and source of infection is a sick person. The transmission factor is the patient’s personal belongings and common items. The virus remains viable for several days on toys and school bus seats.
The most susceptible to the disease are people with immunodeficiency, those suffering from atopic dermatitis, eczema and those receiving glucocorticoids. The disease is more often recorded in regions with hot and humid climates. Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules, overcrowding and poor living conditions contribute to the spread of infection.
- First of all, the disease spreads in the family among sisters and brothers.
- Children under one year of age become infected when visiting a clinic or swimming pool, as well as when receiving a massage.
- Older children become infected in kindergarten, school, while playing contact sports or visiting a swimming pool.
- In adolescents and young people, infection can occur during sexual intercourse and in contact with the skin of a patient.
The incubation period ranges from 1 week to several months (average 2 - 7 weeks).
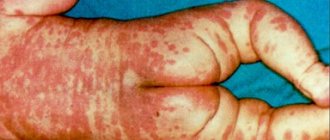
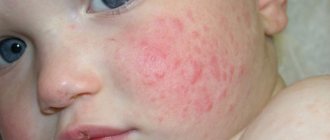
Rice. 3. Most often, a rash with molluscum contagiosum appears on the face.
Rice. 4. Molluscum contagiosum in children.
Similarities with other diseases
Molluscum contagiosum consists of a huge number of elements. This is why it is very easy to confuse it with other skin diseases.
These include:
- Genital warts;
- Flat warts;
- Vulvar micropapillomatosis;
- Hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands;
- Pearly penile papules;
- Syringiomas.
If a single large element is detected, differential diagnosis is made with keratoacanthoma, basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer.
How is molluscum contagiosum transmitted?
Transmission of the molluscum contagiosum virus occurs only from person to person. You can become infected through contact and household contact: through bodily contact and common objects (dishes, toys, towels). Waterborne (when visiting a swimming pool) and sexual transmission of molluscum contagiosum is also possible.
Factors contributing to the development of the disease include:
- hormonal changes in the body;
- skin damage;
- tendency to allergies;
- decreased immunity;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
Course of the disease
In most cases, especially during childhood, molluscum contagiosum disappears spontaneously after a maximum of six months. In rare cases, a recurrent form may appear, that is, the appearance of new elements of the rash. In principle, molluscum contagiosum is not a threat to life. Moreover, it can be attributed to a general cosmetological problem.
More attention should be paid to complicated, generalized and recurrent forms. In such cases, it is necessary to consult a specialist - an immunologist and take an immunogram with further examination for HIV infection.
During mechanical damage to the discharge elements, that is, cuts, scratches, squeezing or shaving, autoinoculation may occur. Autoinoculation is a strong spread of this infection.
Treatment of molluscum contagiosum in children
Very often, the disease with molluscum contagiosum ends in self-healing. The reverse development of the rash occurs from 7 to 12 weeks after infection. The nodules soften and slowly die. Complete cleansing of the skin occurs by 6–9 months. In cases where parents insist on a speedy cure, different types of treatment are used.
In Western countries, treatment for molluscum contagiosum in children consists of strengthening the immune system and carefully performing all hygiene procedures. Pathogens affect only the superficial layers of the skin. When cured, the viruses disappear completely, and the body produces antibodies to them.
Domestic doctors have a different opinion - they believe that foci of infection must be removed to avoid the transfer of viruses to other parts of the body through scratching.
Rice. 9. Molluscum contagiosum rash on the face.
Rice. 10. Rash due to molluscum contagiosum in adolescents.
Removing foci of infection
- The simplest method for removing molluscum contagiosum is squeezing out, destroying the nodules using liquid nitrogen and cauterizing with phenol using a wooden stick.
- Removal of foci of infection can be carried out by curettage, when the core of the lesion is removed with a curette, followed by treatment with a solution of iodine or potassium permanganate. The use of this technique does not provide a 100% guarantee of cure. The outbreaks can appear again and again - 2 - 3 more times, but then disappear without a trace. When performing curettage in children, anesthetic cream "Emla" and lidocaine-prilocaine ointment are used, applied 40 - 60 minutes before surgery. If the child is not calm, they resort to the use of sedatives or anesthesia.
- Laser therapy in children for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum is used extremely rarely due to the constant anxiety of the child and requires great patience from parents.
Rice. 11. Schematic representation of removal of the lesion in molluscum contagiosum (curettage).
Rice. 12. Treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Laser therapy.
Rice. 13. Treatment of molluscum contagiosum. Cryodestruction of lesions.
Use of drugs
- The lesions are treated with antiviral drugs in the form of cream, ointment or gel. The duration of treatment ranges from 1 week to 2 months.
- Immunotherapy is aimed at strengthening and stimulating the child’s immune system. The stronger the immune system, the faster the child’s body will cope with the infection.
Immunotherapy is indicated for persons with atopic dermatitis, recurrent fungal, bacterial and/or viral infections. It is carried out under the control of immunological parameters. The use of immunomodulators Lykopid and Polyoxidonium, as well as Isoprinosine, which has antiviral and immunomodulatory activity, is indicated.
Rice. 14. Molluscum contagiosum rash on the extremities.
How to treat molluscum contagiosum?
Treatment for molluscum contagiosum usually involves drug therapy and invasive treatment. Drug therapy involves taking antibiotics, antivirals and drugs that help strengthen the immune system.
Methods of invasive treatment of molluscum contagiosum include:
- cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen;
- laser therapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- curettage (mechanical removal of molluscum contagiosum).
It is not recommended to treat molluscum contagiosum with folk remedies. After all, treatment of molluscum contagiosum at home may be associated with a mechanical effect on the molluscum nodules, which leads to the rapid spread of the disease and the development of a secondary infection.
For quick and effective treatment of molluscum contagiosum, you need to contact a dermatologist who will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe additional tests. After diagnosis, the doctor will draw up an individual treatment regimen, compliance with which guarantees complete recovery.
1
1
1
Article rating:
4 out of 5 based on 1 rating
Author: Ustinskaya Inna Ivanovna
Dermatologist, pediatric dermatologist, trichologist. Highest category. Work experience 23 years.
Diagnostics
Photo: shareably.net
The diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum is based on the clinical picture - the detection of specific nodules on the patient’s skin. However, in cases of atypical forms, scraping of elements will be required for microscopic examination. Using special dyes, large brick-shaped viral bodies are detected under a microscope in epithelial cells.
For the differential diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum, skin diseases such as vulgar warts, flat warts, keratoacanthomas, milia, and acne are excluded.
Description
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral disease that is manifested by the formation of nodules on the skin and mucous membranes.
The disease occurs at any age, mainly in children and adolescents. In adults and older people, the incidence is often associated with decreased immunity, for example, while taking hormonal and antitumor drugs or in HIV-infected people. The virus that causes the disease got its name because of its external similarity to ranovato, and the word “contagious” is translated as “infectious.” Molluscum contagiosum has a contact type of transmission, that is, infection occurs through bodily contact with a sick person or a carrier of the virus - in the pool, while playing contact sports, and also indirectly through common household items - towels, clothes, children's toys, bed linen. Among young people, the sexual type of infection is common.
The disease is caused by 4 types of molluscum contagiosum virus, which differ slightly from each other. However, the first type (which is called “childish”) is found in patients most often - more than 95% of cases of molluscum contagiosum. The second type of virus is specific to the sexual type of transmission of the disease - it accounts for about 3% of all cases. In the body, the virus multiplies exclusively in epithelial cells, and therefore does not cause any serious complications. Currently, molluscum contagiosum can be successfully treated with drug therapy at any stage of the disease.
After infection, the first manifestations of the disease take from one week to several months. During this time, the virus that has penetrated the epithelial cells multiplies in sufficient quantities to trigger an immune response. Typically, elements of molluscum contagiosum in adults can disappear on their own after a few months, even in the absence of treatment. However, in children there is a long course - from six months to 5-6 years.