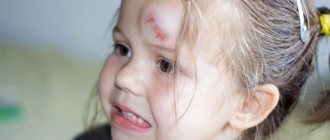
What types of wounds are there?
A wound is a tissue damage that is characterized by a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes. The wound is accompanied by pain and bleeding.
The first sign is pain. It occurs due to damage to local nerve endings, and subsequently due to swelling, which puts pressure on the nerve and irritates it. In this case, pain can spread not only along the surface of the wound, but also along the damaged nerve.
The second mandatory sign of a wound is bleeding. It occurs as a result of damage to capillaries, veins or arteries. Bleeding can be weak and drip, for example, with a small cut, and severe when the integrity of the vein and artery is damaged.
The third sign of a wound is gaping. However, gaping appears only with deep wounds, for example, with abrasions it does not exist. Gaping is the divergence of the edges of the wound on either side of the axis of the cut. If there is severe gaping, the wound is usually sutured.
There are many types of wounds. For a person in everyday life, it is necessary to know several classifications. The first is based on whether there is an infection in the wound. Wounds may be aseptic, contaminated, or infected.
An aseptic wound is a pure injury to the skin. Usually these are surgical wounds that are performed in order to penetrate the internal organs. Children most often experience contaminated wounds. This means that microbes have entered the area of skin damage. At first, these are relatively safe wounds: local protective mechanisms inhibit the development of microorganisms. If a contaminated wound is not treated, it becomes infected: an infectious process develops, which is accompanied by inflammation, severe pain and suppuration. An infected wound can cause a strong reaction in the child’s body: body temperature rises, chills, drowsiness and apathy appear.
Depending on the nature of the damage, there are the following wounds:
- punctured - they occur when punctured by a narrow and piercing object, for example, when a child falls on a nail. Typically, a puncture wound bleeds slightly and hurts. Outwardly it may seem that this is a safe wound, but this is not so: large vessels, nerves are often damaged, and even an infection occurs;
- cut - occur upon contact with a sharp oblong object: a knife, razor, sharp scissors, a shard of glass and paper. With an incised wound, the tissue is usually slightly damaged. The wound bleeds heavily and hurts moderately;
- Chopped wounds occur when damaged by a heavy sharp object, such as an ax. Usually the bleeding is moderate, but the wound is very painful and gapes. May lead to serious condition;
- a bruise wound appears when struck with a blunt object or falling on asphalt. Most often, the bruised wound is located on the head, elbows and knees. The edges of a bruised wound are uneven and soaked in blood. It bleeds slightly and is moderately painful.
There are also bite wounds that occur when children are bitten by animals or other children. The difficulty with this wound is that in most cases it contains infection from the animal's oral cavity. This is how rabies, insect and snake poison, and putrefactive infection are transmitted.
The wound process consists of several stages:
- In the first seconds after skin damage, local blood vessels reflexively constrict and biologically active substances are produced - platelets, which adhere to the wound area and close the damaged vessel. The blood clotting system turns on, stopping the bleeding. In a healthy child, bleeding stops on its own within 15 minutes.
- Inflammation. Lasts 3 days from the moment of injury. Inflammation is manifested by pain, redness and local fever. Also, swelling in the form of a tumor appears on the wound within two hours.
- 2–4 hours after injury, leukocytes migrate to the area of injury. They absorb foreign particles and cleanse the wound of microorganisms.
- Healing phase. Begins 3–5 days after injury. Bioactive substances arrive to damaged tissues, which restore vascular and skin tissue.
- Epithelization phase. Begins 2 weeks after injury. The wound mark becomes pale and a scar forms. The epithelialization phase may be delayed if bacteria are present in the wound.
My lip is swollen from a blow, what to do at home – Dentistry
A lip bruise is called damage to the soft tissues of the specified area. Such injuries occur frequently due to the thinness and sensitivity of the lip structure. Often this type of damage is observed in children who usually move actively.
ICD 10 code
According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10), lip bruise has code S00.5. According to the classifier, the name of the wound in this case sounds like “Superficial injury of the lip and oral cavity.”
Causes
This type of injury occurs as a result of:
- falls,
- participation in fights, which led to injury to the face and lip area in particular,
- industrial injury,
- collision of a part of the face with a hard object.
Often such an injury occurs in children who, while learning about the world, behave too actively and therefore often hurt themselves.
Manifestations
When the lip is injured, characteristic symptoms appear such as:
- pronounced swelling. The tissues in the lip area swell very quickly, literally before our eyes,
- formation of a seal inside the lips,
- pain, discomfort in the damaged area,
- bleeding if the integrity of the structures has been compromised and there is a wound surface,
- redness of the skin near the injury site.
The swelling may last for several days without changing in severity.
A child often has abrasions near the mouth along with swelling, which is the result of falling face down.
First aid methods
If a child or adult’s lip is swollen after a blow, what should you do? In this case, first aid is to:
- carefully rinse the damaged area,
- wipe the open wound with Miramistin or Chlorhexidine solution to prevent the possibility of infections. If there is a violation of the integrity of the tissues on the inside (in the oral cavity), these products can also be used for disinfection. An external lip injury can also be treated with hydrogen peroxide, but in no case should you use brilliant green or iodine - they can cause a burn,
- Apply a cold compress to prevent widespread swelling. Do not leave the compress on for more than 15 minutes, otherwise tissue frostbite may occur.
Pelvic contusion
If blood continues to flow from the wound, you need to fold a piece of bandage several times and place it between your lip and teeth so that it is absorbed.
Even though such an injury is not serious, the child should still be taken to see a specialist. A fall that causes a lip injury could result in a severe impact resulting in superficial head injuries.
Diagnosis and treatment
In the case of a lip bruise, a visual examination is sufficient to assess the nature and severity of the injury.
It is possible to treat such damage at home. Therapy includes:
- constant treatment of the wound surface on the lip with antiseptics,
- treating the injury site with sea buckthorn oil, zinc ointment, Solcoseryl up to 4 times a day,
- use of mouth rinse solutions if the lip has been broken from the inside. To do this, use chamomile decoction, chlorhexidine solutions, propolis in water,
- external use of Troxevasin ointment. This drug allows you to remove the tumor and eliminate the hematoma.
For severe swelling and bruising, you can use the following remedies:
- applying a fresh cabbage leaf. The raw material is applied to the site of injury, left for several hours, secured with an adhesive plaster,
- lubrication with a mixture of aloe and honey. You need to take a teaspoon of natural honey and mix it with the pulp obtained from fresh aloe leaves. Apply the resulting composition to the hematoma, hold for 15 minutes, then remove, wash the affected area thoroughly,
- use of badyagi gel or powder. This remedy speeds up the healing process several times. In pharmacies such drugs are presented by Lekar, Badyaga Forte.
If the tissue is severely cut, surgery is performed followed by suturing.
Possible complications
Possible complications from a bruise are:
- penetration of infection through the wound surface with subsequent formation of purulent masses. This condition threatens blood poisoning,
- deep damage, which can further cause lip deformation.
How to provide first aid for a bruise
A lip bruise usually does not have serious consequences
However, it is important to properly care for the injury to prevent infection. Also, after damage, you should undergo examinations to exclude the possibility of damage to other structures.
Wound treatment algorithm
What to do if your child falls, cuts or hits himself:
- Make sure you're safe: you've shooed the dog away, put away the knife, turned off the chainsaw, removed any broken glass.
- Usually, in a situation of injury, the child is frightened: by pain or by the fact of the cut. Reassure him and tell him that nothing bad happened. Make him feel protected.
- Before treating a wound, first wash your hands with soap.
- Remove clothing from the wound site: roll up your shirt sleeve, lift up your T-shirt or pant leg. Examine the wound. Try not to touch the wound with dirty hands.
- If the capillaries are damaged, bleeding is minor. Rinse the wound with warm water, apply hydrogen peroxide and bandage with gauze.
- Gently clean the wound of debris and dirt under warm water. To do this, use cotton swabs or gauze soaked in a disinfectant.
- Disinfect the wound. Usually at home there is always an alcohol solution of iodine, cologne, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol or strong drinks. Dilute alcohol with water so as not to burn the wound. If the wound is extensive, alcohol and iodine cannot be used, they will lead to a chemical burn and the wound will heal more slowly.
- Apply sterile material to the wound and bandage it. You need to bandage so that the bandage covers the wound site. It should not be tight or too soft.
What to do if your child is bleeding heavily:
- Assess the severity of bleeding. If the wound bleeds heavily with dark or scarlet blood, spurts out and the blood erupts synchronously with the heartbeat, the bleeding must be stopped at any cost.
- Call an ambulance. One person provides first aid, the second calls the team. Please note that if the wound is penetrating, that is, a screwdriver or knife is stuck into the body, you cannot remove the object yourself. Be sure to wait for an ambulance.
- Find a tissue or any other tissue in your bag or home medicine cabinet that can be applied to the wound.
- If the wound is on the extremities, place the child on his back and raise the injured limb above the level of the heart, bending them at the elbow or knee. This is temporarily uncomfortable but slows down blood flow.
- Apply a tourniquet. If you don't have one, use a belt, tie, suspender or wire. You need to place a napkin or cloth under the tourniquet so as not to injure the skin. For arterial bleeding, a tourniquet is applied above the wound site; for venous bleeding, a pressure bandage is applied to the wound. Note the time of application of the tourniquet, write it down with a pen or felt-tip pen (not red) on the skin near the tourniquet. Remember that in summer the maximum time for applying a tourniquet is 90 minutes, in winter – 60 minutes. If after this time the ambulance has not arrived, and you have not yet reached the hospital, carefully loosen the tourniquet so that the tissues of the limb receive blood, while pressing the bleeding site with gauze. If the bandage becomes saturated with blood, tighten the tourniquet again until the bleeding stops completely and record the new time on the skin.
It is not recommended to give your child painkillers. This is hampered by the fact that each drug has an expiration date and doctors need to recalculate the doses of a new painkiller or wait for the previous one to expire in order to avoid an overdose. But if you cannot do without pain relief, write down the time and name of the drug you gave your child. Save the empty vials of medication and give them to the ambulance crew so they know what you gave to the victim.
Not Recommended Actions
What not to do if a child has a cut lip:
- Use alcohol solutions. Some parents, even knowing the rules of first aid after a cut lip, use alcohol solutions to speed up wound healing. However, they do not know what the consequences may be after such actions. If you do make this mistake, then urgently treat the damaged area with anti-burn products;
- Use iodine or its derivatives (Betadine) or brilliant green to treat the wound. Many parents are not familiar with the rules of first aid after a cut lip, so they use medications that can harm the child. For example, iodine or its derivatives (Betadine) or brilliant green are often used to disinfect a wound. These solutions, even in minimal concentrations, can damage the delicate skin of the lips and cause chemical burns. In addition, after treating the lips with brilliant green or iodine, a scar may remain on the damaged area;
- Apply ice without a protective coating. Other moms and dads apply ice without a protective coating, which can cause additional tissue damage or hypothermia. The ice must be wrapped in a cloth and kept for no longer than 15 minutes;
- Touch the wound with unwashed hands. Many parents panic so much at the sight of a child with blood on his lips that they completely forget to wash their hands before treating the wound. Then the risk of infection in the damaged area increases, especially if the wound is located on the inner surface of the lip.
Treatment of abrasions in children
How to properly treat abrasions in children:
- Wash your hands.
- Clean the skin around the wound from dirt, dust, debris and other objects.
- Disinfect the wound: the abrasion can be treated with the following products: zinc oxide ointment, benzalkonium chloride cream, dexpanthenol cream, chlorhexidine, methyl blue, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green and 5% iodine solution.
- Usually, mild capillary bleeding occurs with abrasions. It is enough to apply a dry cloth or gauze to the damaged skin.
What to do with a broken lip and its swelling from the inside: first aid and wound treatment
A split lip is an injury to the soft tissues and mucous membranes of the mouth, which causes a lot of discomfort.
It is important that the consequences of the cut are minimal
Processing agents
A split lip requires mandatory treatment with antiseptic drugs.
The first place is occupied by hydrogen peroxide - a solution for external use of 3%. The medicine is effective when the baby has broken his lip from the inside.
The main advantage is that (unlike iodine and brilliant green) peroxide can be anointed on open wound surfaces and will not cause burn damage to the skin.
The effect of the drug becomes noticeable: bubbles and hissing appear. The disinfection process occurs through the release of atomic oxygen.
It is forbidden to remove dried bandages and compresses so that the healing wound does not begin to fester. Peroxide is not applied to damaged mucous membranes.
Another broad-spectrum agent is chlorhexidine.
Available in the form of a solution, adhesive plaster, gel and cream. The substance disinfects the wound surface and removes pus. The price of the medicine is affordable for everyone.
The antiseptic is intended for healing ruptures and is capable of treating fungal diseases, sexually transmitted infections, and pathologies of the oral cavity.
A modern disinfectant medicine is Miramistin. The main advantage of the drug is the complete absence of side effects. A solution for external use helps damaged areas heal without burning them.
The medicine kills harmful microorganisms, blocking the inflammatory process. Miramistin is used to treat burned skin areas, for candidal and gynecological diseases, and ENT pathologies.
Potassium permanganate solution is a home method for washing festering wounds. You can prepare weak potassium permanganate by adding a few crystals of permanganate to a glass of warm water. The cut should be treated several times a day, diluting a new mixture.
An alternative option is a dry bandage applied to the torn corner of the lip. It is easy to remove and change. The prepared solution can be used for no more than 2 weeks.
Store in a dark glass container at a temperature not exceeding 15 degrees.
Traumeel ointment will help your lip heal - a homeopathic medicine that helps relieve swelling and eliminate inflammation. The product should be applied to the skin in a thin layer 2-3 times a day for 2-3 weeks. You can use gauze bandages.
If the frenulum is torn, Panthenol cream will help. It promotes rapid healing of damaged areas without scar formation. Before applying the medicine, you need to disinfect the wound. The drug has no side effects, with the exception of intolerance to the components. Apply the cream twice a day until the wound surface heals and the swelling and thickening disappear.
How to remove swelling after a blow
The affected lip may darken and swell. The following types of damage to the labial border are distinguished:
- Bruise (can be caused by being hit by an object, resulting in internal swelling). The bruise or hematoma will go away within a few weeks.
- An abrasion is a minor tissue injury that does not need to be stitched.
- The wounds appear when the labial border is bitten or cut. The main symptom is a violation of the integrity of the skin. The wound surface may be damaged through and through.
Treatment provides assistance in restoring normal shape and allows the natural color to return. If the lip is swollen from the inside, lotions based on bee honey are useful. The mass is applied to cotton wool and applied to the lower or upper swollen area for 30 minutes.
It is forbidden to apply warm compresses to the wound; the area will swell and swell even more.
Wound care
In order for the wound surface to heal quickly, proper care is necessary. There are several recommendations:
- The painful area should be treated regularly and treated with recommended remedies.
- You need to be careful not to accidentally tear the scabs near the wound.
- To avoid injury to the labial border, it is recommended to lubricate it with protective agents.
In most cases, the wound will go away on its own. Such injuries heal on their own with proper care. But if pimples or pus appear on your lip, the pain does not go away and prevents you from living fully, you need to consult a doctor.
The article has been verified by the editors
What to do if the wound does not heal for a long time
The wound may not heal for a long time. This occurs due to several factors: the skin is not cleaned after injury, blood flow is complicated due to inflammation, or the regeneration mechanism is disrupted. Because of this, complications arise:
- Seroma is an accumulation of inflammatory fluid (exudate) in the wound cavity. Seromas most often occur when dirt, microorganisms, or foreign bodies remain in the wound;
- wound hematoma. It appears due to the fact that after the wound the bleeding did not stop completely, and drops of blood gradually soaked the surrounding tissue. Hematomas also occur as a result of diseases in which blood clotting is impaired;
- necrosis of soft tissues. Occurs due to severe and massive tissue damage or cutting of blood vessels. Early signs of necrosis: in the first days after injury, the skin is pale, has a bluish tint and is cold to the touch;
- malignancy is a process when tissue cells acquire the characteristics of a tumor. Malignization occurs when a chronically non-healing wound.
In addition, the wound may not heal for a long time with poor immunity, diabetes, long-term use of glucocorticoids and vitamin deficiency. The only correct option is to consult a surgeon: at home it is impossible to assess the condition of the wound and provide proper medical care.
What to do if your child has a broken lip
If your child falls or hits an object and breaks his lip, then you need to act according to the following plan:
- First of all , parents must calm down themselves, because they need to act clearly and confidently. Then calm the child down, explain that you will help him now,
- Before touching your sore lip , be sure to wash your hands with antibacterial soap. Then wash your baby’s hands, because most likely he will touch the wound, which can cause infection. If you are outside, use antiseptic spray or wipes. Such things should always be with you on a walk,
- Rinse the damaged area with warm boiled water. Try to visually assess how deep the wound is. If it seems deep, then seek medical help, if not, continue treatment at home,
- Now you need to disinfect the damaged area to protect it from the penetration of pathogenic microbes. To do this, use a weak solution of potassium permanganate or hydrogen peroxide (3%). Moisten a cotton wool or disk with antiseptic liquid and apply to the lip,
- If a child has broken the inside of his lip , then it can be treated with a solution of Miramistin or Chlorhexidine. These antiseptics are effective against bacteria and viruses. It is enough to apply a cotton wool soaked in liquid to the wound. If the child is already old enough, then suggest that he rinse his mouth with a solution,
- Swelling appears at the site of injury ; to reduce it, apply a cold compress. To do this, take a piece of ice from the freezer, wrap it with gauze and a clean cotton napkin. You can also use a chilled spoon.
After this, carefully examine the wound again; if it is deep, then go to the doctor. You may need to get stitches to prevent a scar from remaining on your lip.
When to see a doctor
To protect your child from complications, you need to know in what situations to consult a doctor:
- if after 15 minutes the wound has not stopped bleeding even when applying a pressure bandage;
- if outside the wound the skin begins to become numb, cool, and acquire a pale or bluish tint;
- if you are not sure that the wound is completely cleaned of splinters, rust, dirt and other foreign objects;
- if the injury occurred on the neck;
- if the child was bitten by an animal;
- the wound does not heal within 10 days.
Warning signs also include: an increase in the child’s body temperature, increased swelling, increased pain, a burning sensation and severe redness of the wound.
A wound is tissue damage that requires first aid. However, if you treat the wound according to the algorithm, after 10–15 minutes the bleeding stops, and by the end of the day or the next day the pain goes away. The main thing when a child is injured is not to give in to emotions, calm the child, act quickly and call an ambulance or see a doctor.
2
1
0
Article rating:
4.29 out of 5 based on 7 ratings
Author: Popov Evgeniy Vladimirovich
Orthopedist-traumatologist, pediatric orthopedist-traumatologist. Highest category. Work experience 11 years.
The child tore the frenulum on the upper lip
The mouth has 2 frenulums that connect the upper and lower lips to the oral cavity. If a child falls and breaks this jumper, then he needs help:
- The mouth is washed with cooled boiled water;
- Then the affected area is treated with hydrogen peroxide;
- After this, the wound is treated with antiseptics: Furacilin solution, Chlorophyllipt oil, Miramistin spray;
- A cold compress is applied to the affected area to help relieve pain and stop bleeding.
After this, you need to urgently show the child to the doctor. This is a serious injury that requires qualified medical care.
Otherwise, the risk of infection increases. If the frenulum does not heal properly, speech defects, facial deformities, and problems with chewing may appear. To avoid complications, you need to put self-absorbing sutures on it.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia for 30 minutes. After it, swelling appears, which with proper care will disappear after 2 days. Tissue regeneration in this area usually occurs quite quickly. You need to take care of sutures after surgery using antimicrobial agents. In addition, it is necessary to rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions after each meal.
Steps
First aid
Wash your hands.
Before touching your face or sore lip, lather your hands with antimicrobial soap and wash them under warm running water. If you don't currently have access to water, use alcohol wipes to clean your hands. This will reduce the number of germs that can enter the wound from your fingertips.
Wash the wound with mild soap and water. Lean over a sink and run running water over the wound to clean it of dirt and debris.
Apply a little antimicrobial soap to a cotton swab or piece of cotton wool and gently treat the wound with it. Rinse off the soap with water
Do not rub the wound to avoid causing further damage.
Apply a cold compress to the crack.
If there is swelling or bruising in your mouth or lip, apply a small ice pack to the wound until the swelling goes down. If you don't have an ice pack, use a bag of frozen vegetables or a clean towel soaked in cold water instead. You can give your child popsicles to relieve pain and minimize bleeding.
Assess the severity of the wound.
Now that you can clearly see the wound, stand in front of a mirror and try to assess the depth and severity of the wound. If the cut is very deep and may not heal properly, or if it is affecting your ability to speak, seek help from a doctor. If you decide to treat the wound yourself, be sure to check it every day.
If the wound is severe, consider contacting your doctor or plastic surgeon immediately. When the crack heals, and this will happen quite quickly, it will be extremely difficult to get rid of the scar.
Apply topical numbing ointment.
Protect the cleaned wound from infection by applying some numbing or antibiotic ointment. Apply a pea-sized amount of ointment to a cotton swab and then spread it over the wound. Next, follow the instructions for use of the drug.
Apply medical adhesive or cover the wound with a bandage.
If the wound is superficial enough that you can heal it yourself, buy medical glue or a special sterile plaster for the wound surface. Both are designed to bring the edges of the wound together. If you decide to use medical glue, shake the bottle and apply a thin layer of glue to the wound. When the first layer of glue has dried, apply a second layer. Medical glue will ensure the wound heals, and it should last about a week.
- Keep the layers thin so they don't peel off.
- While all of these products generally work well for treating a cracked lip, they can be quite difficult to apply yourself.
- If you want to protect yourself from getting a scar, consult a doctor for help.
Seek medical attention immediately.
If the cut depth does not allow the lip to close, you will most likely need stitches. If you think that a foreign object or debris may have gotten into the wound, or the crack is located in the corner of the mouth and continues to bleed even 10 minutes after applying pressure, it should definitely be examined by a doctor.
Avoid touching the wound with your fingers and tongue.
The more you lick the wound, the more it will dry out and crack, which can lead to a cold sore in or near the crack. Also try to resist the urge to touch or feel the wound with your fingers, so as not to enlarge the wound even further and introduce harmful bacteria into it.
Consult your doctor or dentist.
If after the first stage of treatment the cut begins to become red or more painful, consult a doctor immediately as this may indicate the presence of an infection. If your teeth start to hurt, see your dentist as this may indicate dental damage. Medical help may also be helpful if you suffer from persistent dry mouth and cracked lips.
Lip protection
Apply zinc-based ointment to your lips.
For many people, chapped lips are a result of overexposure to the sun. When gardening, construction, or other work in the sun, be sure to apply a zinc-based lip protectant to your lips.
Diaper cream has a similar effect.
Apply lip balm.
Once your lip has healed, buy a natural, unscented beeswax lip balm and apply it to your lips regularly. It’s even better if the balm contains lanolin or petroleum jelly. Some lip balms even have an SPF level and can protect your lips from drying out from the sun's rays.
Drink more water.
To maintain normal fluid balance in your body and prevent chapped lips, drink at least eight glasses of water a day. To speed up the healing of a wound on your lip, add a couple more glasses to this amount.