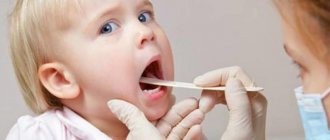
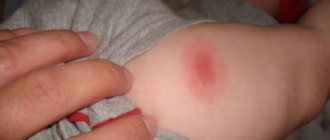
Atheromas are cysts of the sebaceous glands that are often found under the skin behind the ears and look like small whitish balls.
Atheromatous sebaceous cyst is not an oncological disease. Often atheromas go unnoticed, but sometimes they can be felt and cause discomfort upon palpation.
Rice. 1. Atheroma behind the ear
Atheromas that occur behind the ears can be located in other places: for example, on the head, back, face, chest, etc.
The most common location for atheromas is the face, neck and torso.
Atheromas can be of different sizes, large and small.
Very often, atheroma does not bother you at all, but sometimes, as a result of friction of atheroma on clothing, rupture due to pressure or injury, or infection, discomfort and pain appear. In this case, the atheroma must be removed.
Atheroma or cyst of the sebaceous gland in the postauricular area
Atheroma is a cyst filled with dead skin cells and sebum.
Behind the ears there are countless sebaceous glands, so it is in this area that atheromas are found very often. However, atheromas can often be found in the ear canal itself.
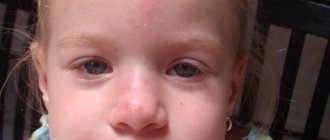
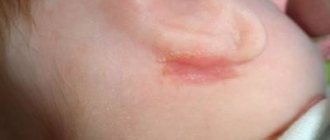
Rice. 2. Suppurating atheroma behind the ear
Although atheromas do not become malignant (such cases are described extremely rarely), they can become complicated. First of all, atheroma, in the absence of timely treatment, can become infected. When infected, the atheroma becomes inflamed.
If the atheroma is located in the genital area, then when it becomes inflamed, pain may occur during urination and sexual intercourse.
Causes of a lump behind the ear
The most common cause of a lump behind the ear in a child is enlargement or inflammation of the lymph nodes. It is necessary to understand the difference between these two concepts.
Against the background of decreased immunity, inflammation of the lymph nodes, or lymphadenitis, can occur. This is accompanied by the appearance of a lump behind the ear or on the jaw. The inflammatory process manifests itself due to infectious diseases, and the baby may feel pain near the ear, behind which the lump has formed.
In some cases, the inflammation is painless, the formation does not hurt or itch. The task of the lymph nodes is to protect the ENT organs from pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, compaction occurs due to the accumulation of cells in the organs that trap viruses and bacteria.
Diseases that provoke inflammation in the lymph nodes include:
- fungal diseases;
- Gaucher disease, Niemann-Pick disease;
- damage to the teeth and oral cavity (caries, pharyngitis, gumboil, tonsillitis);
- cat scratch disease;
- leukemia;
- mononucleosis;
- respiratory diseases (ARVI, influenza, laryngitis and tonsillitis);
- lymphangitis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- erysipelas of fatty tissue;
- measles;
- infections (tuberculosis, diphtheria, HIV, AIDS, toxoplasmosis);
- inflammation of the hearing organs (furuncle, eustachitis).
If the lump appears on one side, then this may also be a sign of an incipient inflammatory process in the middle ear cavity. Acute otitis media occurs against the background of a runny nose. In this case, along with the formation of a lump behind the ear, a slight tingling sensation is felt.
Lump behind the ears of a baby
One or two small bumps nearby indicate enlarged lymph nodes. This is caused by a previous infection or a weakened immune system. The resulting compaction is difficult to notice, and in a baby it is not visible, since the nodes are very difficult to palpate. This is often diagnosed not only in newborns, but also in one-year-old children. Enlarged lymph nodes at this age are a consequence of the body’s reaction to tooth growth. There is an outflow of lymph into the parotid lymph nodes, which then increase in size.
Read also: Effective methods of treating adenoids in children with folk remedies
Other reasons for the development of pathology include:
- infections (mumps, chicken pox);
- benign tumors (atheroma, lipoma, hemangioma);
- ear fistula
Infectious pathologies
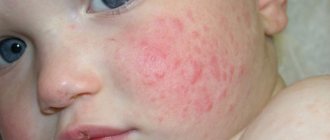
“Mumps”, or mumps, is an infectious disease that spreads through the air and through contact with objects (drops of mucus remain on toys, clothes, furniture). “Mumps” is known for dangerous health complications and is the cause of a lump under the ear on the neck. At an early stage, upon palpation, we will feel a ball near the auricle, which occurs due to damage to the parotid glands. Mumps is accompanied by inflammation and an increase in the size of the salivary glands.
The swelling spreads to other areas, causing swelling on one side of the face. Edema is formed:
- on the neck;
- on the earlobes;
- on the cheekbones;
- on the cheeks.
With mumps, in addition to the lump behind the ear, swelling is observed in other places
With mumps, the formation hurts when swallowing, which is why the child loses weight because he refuses to eat. A lump behind the ear appears when vaccinated against mumps. In addition to external manifestations, pathology in a child can be determined by accompanying symptoms:
- orchitis (inflammation of the testicles in boys);
- pain when chewing and swallowing;
- dry mouth;
- chills and elevated body temperature;
- lack of appetite;
- headache and muscle pain.
Lumps behind a child's ears can form as a complication after chickenpox. This occurs because the lymphatic system spreads the pathogen through the blood. Viruses destroy the upper layers of the skin and produce blisters with fluid that is released during inflammation.
Viruses accumulate in the lymph nodes, and tissue swelling is observed. When touching the bumps near the ears, the child feels pain.
Benign tumors
If a hard lump appears, then this indicates an atheroma - a small cyst, similar to a ball, the skin over which turns blue. This benign tumor is located on the bone. The cyst provokes the appearance of a lump near the ear, which then becomes inflamed and festers. The seal is filled with contents.
Atheroma is formed due to blockage of the ducts, which interferes with the normal removal of sebaceous gland secretions. When bacteria penetrate this process, a purulent mass is formed. Pathology is often diagnosed in infants due to abnormalities in intrauterine development.
A fatty tumor, or lipoma, behind the ear is a benign tumor that is formed from adipose tissue. When you press on the seal that appears, you can feel its movement under the skin. If a mobile soft lump of an oval or round shape with clear boundaries appears, and the child does not feel pain upon palpation, then this is a lipoma.
Read also: Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of throat cancer
Other symptoms accompany an infected lipoma. With this type of disease the following are observed:
- swelling;
- suppuration;
- redness.
Lipoma
Infantile hemangioma is a type of tumor in infants, characterized by fusion of blood vessels. Pathology occurs from the first days of a child’s life and can develop into a malignant tumor. The lump has a red tint and can be hard or soft. Hemangioma is characterized by rapid growth and damage to nearby tissues.
Ear fistula
An infant may have an ear fistula. This pathological process develops due to improper development of the fetus in the womb. A fistula is a narrow canal that runs up to the neck from the cartilage near the ear. The disease becomes noticeable from the first days of the baby's birth.
Gradually increasing in size, the fistula does not cause discomfort. If a large red lump has formed near the ear, this indicates inflammation of the lump. Fistulas on the head next to the ear look like small formations; there should be no pain when pressing them.
Some diseases are typical for both infants and one-year-olds. The difference is that diseases caused by a congenital disorder of intrauterine development appear as a lump behind the ear immediately after birth.
Why do atheromas appear behind the ears?
Research into the mechanism of atheroma formation is still ongoing.
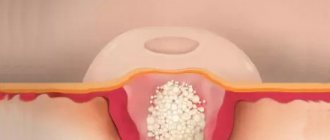
Today it is known that the epidermis (the surface layer of the skin) consists of layers of cells that constantly peel off from the surface during the process of growth. In the case when skin cells stop exfoliating and, accumulating and multiplying, begin to move into the tissues - a cyst wall is formed - atheroma. Inside the formed cavity, dead skin cells rich in proteins - keratin, and sebum accumulate. This is how atheroma is formed.
On the surface of the atheroma you can always find an enlarged pore through which the cyst can drain. In this case, we may notice yellowish masses with an unpleasant odor of decomposing sebum.
Other cysts, called epidermal, are very similar in appearance to atheromas. However, epidermal cysts are formed from sweat glands and their contents are very different in composition from the contents of atheromas.
Symptoms and signs of atheroma
Many patients, having atheromas behind the ears, do not even pay attention to them. However, sometimes atheromas become a serious concern.
It is worth paying attention to the following signs indicating the need to seek medical help:
- There is a small round ball under the skin;
- There is redness, swelling, thickening;
- There are signs of inflammation and infection;
- On the surface of the atheroma there is a small pinhole closed with a black plug;
- It is possible to extract thick yellow contents with an unpleasant odor from the atheroma.
You should consult a doctor immediately if the atheroma:
- Suddenly it began to grow quickly;
- Suddenly burst;
- Inflamed;
- It became sharply painful.
How does a lump appear behind a child's ear?
A lump behind the ear or lump is usually a round formation, which appears mainly due to an increase in the size of the lymph node in the neck. This phenomenon occurs as a result of inflammation, which has already spread throughout the body and begins to attack its most vulnerable systems.
As a rule, the lump that appears does not cause pain and is not dangerous to the baby’s health. Such a ball behind the ear should be dense, mobile, and should be clearly felt during palpation.
Most often, a lump behind the ear in babies occurs due to inflammation of the lymph node.
Important! If the formation does not go away or decrease in the child within several days, then you should definitely visit a doctor.
However, there are a number of other factors that provoke the occurrence of such a seal behind the ear, and in each individual situation the symptoms are strikingly different. Under any circumstances, parents should closely monitor the neoplasm.
So, at an early stage, the lump may not manifest itself in any way and may not bother you. However, some signs are still present even in a non-dangerous form. These include:
- visual appearance of a bump;
- clear delineation of boundaries;
- pain when touched is not observed;
- no discomfort.
You should visit a doctor if the lump becomes painful
In some cases, the process takes on a negative course, in which suppuration may begin. In this case, the following symptoms are noted:
- Redness of the neoplasm.
- Development of swelling.
- Increase in size of the bump.
- Soreness when touched.
- Burning and itching in the parotid area.
- Fluid accumulation in the seal.
- Headache.
- Increased body temperature.
Attention! If you do not take the child to the doctor in time, the lump may change, and the accompanying symptoms also change: the lump becomes hard and its mobility disappears.
Removal of atheromas behind the ears.
Atheroma behind the ear can be removed in two ways:
- Laser;
- With a scalpel.
With traditional removal with a scalpel, after injection anesthesia, a skin incision is made to expose the atheroma. Then the cyst is removed along with its contents. The skin wound is sutured.
Rice. 3. Bursting atheroma behind the ear
It is clear that when working with a scalpel, a scar is left on the skin, comparable in size to the atheroma itself, and sometimes larger.
Laser technologies make it possible to remove atheroma entirely without a single drop of blood from a small puncture in the skin, which allows for the best possible cosmetic result.
Advantages of laser removal of atheroma behind the ear:
- Speed (removal is possible on the day of treatment in just 15-20 minutes);
- Atheromas of any size and in any condition can be removed (even festering atheromas can be removed, since the laser has a sterilizing effect on tissue);
- Bloodlessness (the laser seals the vessels that feed atheromas and removal takes place in a dry field);
- Fast recovery;
- Almost complete absence of relapses and complications in the postoperative period.
If you have atheroma, we suggest seeking help from laser medicine specialists at the ATLANTIC Laser Surgery Center.
Treatment for a lump behind the ear
Enlarged lymph nodes do not require special treatment. A lump behind a child’s ear goes away on its own after 1-2 months. If inflammation of the lymph nodes occurs, then it is necessary to take antibacterial drugs to relieve pain from the group:
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides;
- penicillins.
The lump that appears as a result of inflammation of the lymph nodes will go away after the disease is eliminated. If the cause of the pathology is mumps, then to eliminate it it is necessary to limit contact with others for 9 days. There is no treatment for mumps; bed rest and a special diet are indicated. The lump will go away after recovery.
With chickenpox, the lymph nodes located behind the ears, on the neck and head are the first to be affected. The disease in children disappears after 10 days. After consultation with a doctor, the child may be prescribed drugs from the following pharmacological groups:
Read also: Is it possible to warm the nose and paranasal sinuses at home if you have sinusitis?
- immunomodulators (Viferon, Cycloferon);
- antiviral drugs (Miramistin, Acyclovir);
- solutions of essential oils (tea tree, calendula, celandine);
- antiallergenic agents (Fenistil, zinc ointment, Calamine and Tsindol).
Getting rid of a lump behind the ear caused by a tumor:
- Formations such as atheroma do not tolerate self-medication. This leads to tissue abscess in the child. Atheroma is removed by radio waves at the initial stage of development or by laser. The cyst can open on its own after suppuration if the baby has a strong immune system.
- Parents should be concerned if the lipoma begins to increase in size and the child complains of discomfort. Subsequently, the bump becomes a cosmetic problem, which is removed with a laser. Infected lipomas require emergency medical attention.
- Hemangioma is treated with Propranolol, a drug that acts as a beta-blocker. Before using the drug, you should read the list of contraindications for children.
Therapy for ear fistula
The doctor opens the ear fistula to release the accumulated pus. To alleviate the patient's condition, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Antiseptics: Furacilin, Miramistin.
- Antimicrobial ointments: Levomekol.
- Treatment solutions: Chlorhexidine.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
The discharge of pus is suspended until the next period of exacerbation. To avoid relapse, galvanocaustic surgery and laser treatment are performed.
Folk remedies
The most effective folk remedies for getting rid of a fistula behind the ear are:
- St. John's wort compresses . You need 2 tbsp. l of raw materials, pour 1.5 glasses of water and boil. Let it brew, then take a clean bandage or cotton wool, moisten it in the prepared broth and apply it to the fistula.
- Lotions made from mumiyo and aloe. You need to get juice from aloe, and soak the mummy in water until it darkens. Mix the resulting liquids. Soak a bandage in the solution and apply to the ear fistula.
- Ointment made from oil, pine resin, tar and aloe. Take the ingredients in equal proportions, mix and place in a water bath. Heat the product until smooth. The prepared ointment is applied to the affected area, wrapped in film and secured with a band-aid.
![shutterstock_1111315238 [converted].jpg](https://dou10ugansk.ru/wp-content/uploads/shutterstock_1111315238-preobrazovannyj-jpg-330x140.jpg)