Kinds
First you need to figure out what kind of “beast” this is? Birthmarks are usually called formations on the skin that are brighter or darker than the rest of the skin.
There are two main types: vascular (angiomas) and pigmented (nevi). In the first case, the blood vessels change the color of the skin, in the second, it is colored by melanin.
And they can look completely different! Depending on size, color, shape and other characteristics, they can be divided into several groups:
Vascular
- Stork bite (patch, salmon cartridges). These are flat red and pink birthmarks on newborns. They occur in almost half of babies and, as a rule, disappear after a few months. Moreover, the same mark on the forehead or back of the neck goes away much later. When a child cries, it becomes much more noticeable and brighter.
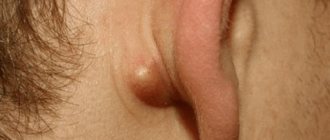
- Strawberry (infantile) hemangioma. It is quite easy to recognize - it is always a raised bright purple or red mole. Where does it come from? During development, material can be separated from the developing circulatory system inside the mother - this is what appears after birth. Statistics say that this type occurs in 1 in 10 newborns.
- Capillary malformation (port, port-wine stain, flaming nevus). Red or purple moles of irregular shape that grow with the child.
Private children's clinics in Krasnoyarsk
Do you need a consultation with a pediatric specialist? Take a look at our catalog!
Go to catalog
Nevi
- Lentigo. Small brown spots, most often characteristic of people with fair or sensitive skin. Juvenile lentigo is distinguished separately.
- Mongolian spot. Its appearance is somewhat similar to a bruise on the back, legs or butt. They can appear both at an early and late age. As a rule, they are found in children of Mongoloid and Asian origin (Khakas, Tuvinians, Yakuts, Koreans, Chinese, etc.)
- Coffee stain. It is a light brown lesion that often appears several months after birth.
Types of birthmarks
Many babies are born with skin without defects. But this does not mean that there are no spots on the body. It happens that they are faintly colored and difficult to detect when examining the skin.
Moles in newborns are clearly visible in only one baby out of a hundred. In the rest, the formations are not detected; only by the age of 2–5 years do they acquire their color and become noticeable. There are two types of nevi in newborns:
- pigmented moles of brown or black with blue color;
- red spots (angiomas, hemangiomas) of bright pink, red color.
The color of spots is influenced by the cells that form them. If the mark is formed from actively producing melanocytes, the color of the moles is brown or black. And the nevus from the vascular cells will have a red color.
Most often, pigmented formations occur in infants. A factor influencing the formation of such marks is a large amount of melanin in a small area of skin. Melanin is a pigment produced by pigment cells - melanocytes. It is what affects the color of a person’s eyes, hair and skin tone. The degree of melanin production in the body directly depends on the functioning of the endocrine system. There are several types of formations, the structure of which contains pigment cells:
- Mongolian spot. Occurs in babies with Mongoloid genes. A formation appears in the sacrum area. Outwardly it looks like a large bruise, which then spontaneously disappears by the age of five. It does not have a negative effect on the baby's health.
- Dysplastic marks. They have irregular outlines, different sizes and degrees of color. It happens that formations look like single elements.
- Moles. The formations look like dots of different colors and appear on all parts of the body: stomach, back, limbs, head.
- There is another type of birthmark - this is a congenital nevus, formed from pigment cells. In this case, the lesions are characterized by their extensive size.
Each child has an individual outline of this formation; the color can be light yellow, coffee, or black with blue. Hair is noticeable on the surface, which is the main diagnostic sign.
Reasons for appearance
Previously, it was believed that moles were special marks that could tell about a person’s fate. Of course, we couldn’t do without superstitions either. For example, if a mother darned old things during pregnancy, then her baby was born with a “patch.” The same applied to those women who used obscene language in conversation.
Modern experts hold slightly different views. One point of view is that birthmarks are inherited. And if parents have a lot of moles, most likely the child will also have them. In addition, they can also appear from ultraviolet radiation, so if you do not want your baby to acquire pigments, think about protection. At the same time, some doctors believe that their appearance may be caused by injuries, viruses or a hormonal surge.
Medical classification of melanomas
To determine the stage of melanoma, the Unified Staging System is quite informative, which distinguishes 4 stages - according to the thickness of the tumor and the depth of its invasion according to Clark:
- 1 – tumor thickness up to 1.5 mm with invasion level 2-3;
- 2 – tumor thickness up to 4 mm and invasion level 4-5;
- 3 – regional presence of metastases about 3 centimeters in diameter;
- 4 – distant metastases.
Melanoma can occur in both cutaneous and extracutaneous forms (10-20%) - with localization on the mucous membrane of the esophagus, rectum, genitals, eye mucosa, etc. The proportion of cutaneous forms is incomparably greater - 70-80%, but poses no less a threat for a large number of people around the world.
Treatment
Of course, the main desire to get rid of a birthmark on a child’s body is associated with the cosmetic defects that the neoplasm brings with it. Fortunately, modern cosmetology and medicine can offer various procedures for removing age spots: surgery, cryotherapy, electrocoagulation, laser therapy, hormonal therapy.
But the problem is that not all spots can be treated. Many neoplasms are not recommended to be touched at all: interfering with this area of your child’s nature can lead to sad consequences (from the growth of spots and changes in their color to malignant tumors - melanomas). That is why it is imperative to consult a doctor and assess all the risks before starting therapy.
For the treatment and removal of birthmarks in Krasnoyarsk, you can contact the following centers:
- Medical and cosmetology, st. Vzlyotnaya, 26g, t. 275-55-11
- Center for Medical Cosmetology OK, Metallurgov Ave., 36, t. 224-91-26
- Center for Aesthetic Medicine "Renovatsio", st. Vesny, 7d, t. 277-52-52
What are hemangiomas in children
Nevi from vascular tissue (hemangiomas) are 2-3 times more common in girls than in boys.
Hemangiomas are formed from a deeper layer of skin than pigmented birthmarks, so their formation sometimes involves not only blood vessels, but also nerve endings. In this regard, there may be some pain or increased sensitivity of certain types of hemangiomas. Hemangiomas form in a child inside the womb. Their size can range from a few square millimeters (the size of a pinhead) to 100 cm2 or more. The color of hemangiomas can vary from pink to dark red or burgundy. There are a large number of their varieties; We will list just a few. Flat hemangiomas are slightly elevated superficial spots, consisting of the smallest vessels (capillaries) and ranging in color from pink to red-violet. These hemangiomas account for up to 96% of all hemangiomas. Their size and shape can be very different.
Stellate angioma is often observed in children on the skin of the face and neck in the form of a central ruby point, from which small arterial vessels spread in the form of star rays. May disappear spontaneously by 2 years of age.
Tuberous-cavernous, or cavernous, hemangioma is elastic, bluish-red in color with a brownish tint, sometimes lukewarm to the touch. It rises above the surface of the skin and has an uneven, bumpy surface. It can be located deep in the skin and therefore have the color of normal skin. This hemangioma consists of blood-filled cavities delimited by connective tissue septa. Usually it is of considerable size, most often located on the face, scalp, less often on the limbs, buttocks, and sometimes on the mucous membrane of the mouth. It may be painful when pressed and gives a sensation of pulsation. Some tuberous-cavernous hemangiomas regress (gradually decrease and sometimes disappear) throughout life, but some require therapeutic or surgical treatment.
Strawberry hemangioma is a flat, bright red formation with clear boundaries, most often found on the face. 70% of them resolve spontaneously by age 7.
When to see a doctor?
As soon as you notice that there is a birthmark on the baby’s body (this can happen in the maternity hospital or a little later), be sure to contact your pediatrician. The doctor should pay attention to changes in the skin and make sure that the neoplasm is not dangerous.
If a mole did not manifest itself in any way, but suddenly changed its structure, color, increased or decreased in size, this is also a reason to visit a specialist. It is necessary to visit a specialist to make sure that the behavior of the neoplasm fluctuates within normal limits. The same goes for inflammation.
Protect moles from sunlight and mechanical irritation (tight clothing that can rub) to avoid infection and cause the mole to grow.
Effective Treatments
Most pediatricians and dermatologists believe that pigmented formations do not harm the health of children, but it is difficult to say why children are born with marks. Moles are not accompanied by symptoms such as itching, burning, pain or other discomfort. But parents should carefully monitor such formations.
It is necessary to ensure that the newborn is not exposed to direct sunlight for a long time and does not scratch or injure the mole. Also, parents should not use alternative medicine methods to eliminate pigmentation.
If the spot changes color or size, begins to peel, crack, bleed, fill with liquid or pus, you must urgently seek medical help to eliminate it. There are several treatment methods:
- Medication. Medicines are injected into the cavity of the affected area of skin, after which the cells gradually die.
- Surgical intervention. Surgical excision is performed only for large tumors. The operation is accompanied by pain and long healing.
- Laser procedure. A popular method for removing nevi in infants: it is painless and does not leave defects on the skin in the form of scars.
- Radio wave method. Hemangioma is removed using radio waves. The method is highly effective and low-traumatic.
- Cryodestruction. An event using liquid nitrogen, when the hemangioma can be frozen, and after a certain time dies on its own.
The choice of treatment method depends on many reasons: the type of nevus, the age of the child, and research results are taken into account. If, for example, the doctor does not suspect the presence of malignant processes, laser treatment is preferable.
But if there are symptoms of the transformation of a mole into a malignant formation, the affected area is removed using the traditional surgical method. Only excision of the tumor with a scalpel can completely neutralize the pathology. And the biological material taken will be sent for histological examination.
Birthmarks in infants should not worry parents, as they are not dangerous to the health of babies. Moreover, age spots usually disappear spontaneously, without the use of any therapeutic treatment.
Popular questions from parents
You are being advised by dermatologist Anastasia Georgievna Popova.
Can birthmarks appear after birth?
“If a birthmark appears later, but does not change at all, then it is not dangerous. Birthmarks rarely degenerate and become malignant. If changes occur, you should consult a doctor."
Is it possible to confuse birthmarks with other neoplasms?
“For some babies, a light brown or pink birthmark on the chest or belly may actually be an extra nipple. In order to determine whether this is really the case, show it to a dermatologist. Currently, additional nipples are considered not dangerous. If they do not bother the child, they do not need to be removed.”
Are birthmarks inherited?
“Some types of birthmarks (such as port-wine stains) can be inherited.”
Follow your doctor’s recommendations, if you have any concerns, contact a specialist and monitor your baby’s health. A birthmark on a child’s body or face is not an attack or a nuisance if you treat it correctly.
Vascular spots
Hemangiomas appear on the skin of a baby from birth; they can be distinguished already in the first month of life. Factors that provoke their formation: active division of vascular cells, as well as the accumulation of pathologically altered small capillaries. The red spot is characterized by constant growth. Hemangiomas usually occur in premature infants. These marks may form under or on the skin. They are externally unpleasant to look at, so parents often want to remove them. Doctors say that they are harmless and will disappear on their own over time, so there is no need to worry about the health of the baby. There are such types of hemangiomas:
- Stork trail. The birthmark is localized on the head of a newborn, starting from the back of the head and up to the forehead, moving to the bridge of the nose. It has a bright pink color. The surface can be formed from small individual elements.
- Kiss of an angel. The skin of the face is covered with a solid yellow-pink spot. When a baby cries a lot, the intensity of the color increases.
- Flaming nevus. It appears on the head and face and is brightly colored.
- Strawberry stain. A red mole with a convex shape. The outline is similar to a strawberry. In the first few months, it actively progresses in development and growth. By the age of 3, growth begins to decline. In adolescence, when hormonal changes occur in the body, it completely disappears, leaving behind a scar.
- Cavernous hemangiomas. Distributed to different parts of the body. Spots without clear outlines are characterized by active growth and increase in size, dense to the touch. There is a noticeable temperature difference between the hemangioma and a healthy area of skin. The temperature of the vascular formation is several degrees higher.
- Spider spot. Hemangioma resembles a star, therefore it is also called “star nevus”. Completely disappears from the surface of the skin by the time of puberty.
Parents should constantly monitor the development of vascular spots and prevent injury to the formations. If a red nevus forms in the area of the eyes, ears, nose and does not show signs of involution by the age of two, you should definitely consult a doctor.
What to do if red moles appear on the body?
If red moles appear on the body in large numbers, single angiomas increase in size, or trauma to the red mole occurs, you should consult a dermatologist. Diagnosis of angiomas that are located on the surface of the skin is usually done by visual examination and palpation.
If there is a suspicion of the presence of red moles in the internal organs, additional research will be required to detect them. Skeletal angiomas are determined using x-rays of the spine, ribs, pelvis, bones and skull. Angiography (contrast X-ray examination of blood vessels) allows identifying red moles in the lungs, kidneys, brain and other internal organs. The structure of the angioma and the features of its location are determined by ultrasound examination.
After the diagnosis, the dermatologist will determine whether it is necessary to treat the red mole. So, the absolute indication for removing red moles is their rapid growth.
In addition, indications for treatment of angiomas are:
- localization in the neck and head;
- disruption of the functioning of the internal organ in which the angioma is located;
- extensive tissue damage around the red mole.
Treatment of red moles involves their removal, which can be done in various ways. Treatment methods for angiomas include:
- laser therapy;
- radio wave method;
- cryotherapy (removal of angiomas using liquid nitrogen);
- diathermoelectrocoagulation (cauterization with electric current);
- hormone therapy;
- ligation of the arteries that feed the angioma;
- surgery.
Effective therapy for red moles can only be prescribed by a dermatologist. Treatment of angioma with folk remedies is not recommended.
Where do nevi come from?
There is no clear answer to the question of why moles appear on a child’s body. The causes of moles on the body of young children are varied. The following predisposing factors are most likely to lead to this process
- Genetics. There are often cases when a child “inherits” the same mole as one of the parents - similar in location, shape and size. This is the case when moles appear in newborn children.
- Hormonal background. This reason is no less common. However, it is not so relevant for infants. Fluctuations in the concentration of hormones in the blood cause the formation of moles at a later age - during puberty, which occurs on average at 11-14 years.
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays. For young children, this factor is also not relevant, since people acquire the habit of sunbathing a little later.
At what age a child will develop moles under the influence of hormones can be guessed by the formation of signs of puberty. And the occurrence of neoplasms as a result of exposure to ultraviolet rays can be counteracted by protecting the baby from direct sunlight on its skin.
In addition, categories of children in whom nevi occur with greater probability and frequency have been identified:
- children with light skin color;
- female gender (girls have moles 4 to 5 times more often than boys);
- premature babies.
However, even speaking about these infants, who are most predisposed to the appearance of nevi, experts cannot unambiguously answer the question at what time moles appear in these children. This phenomenon is individual and has a direct dependence on several factors:
- rates and characteristics of growth, development and maturation of the organism;
- frequency and duration of sun exposure;
- genetic predisposition.
The family factor cannot be excluded, since a pattern has been established according to which it is heredity that determines at what age moles appear on the baby’s body. For example, if the parents began to develop moles late, then the child’s early years pass without them, and spots appear in the grown-up baby.
The number of birthmarks can also be inherited: if the parents have a lot of them, you should expect the same in the baby. Most often, the first spots, caused by the influence of a genetic factor, begin to appear on the skin between the ages of 1 and 2 years.
Birthmark on the back of a newborn's head
The appearance of any neoplasms on the body of a newborn, including a red spot on the back of the head, should alert parents. Despite their harmlessness, at first glance, it is still necessary to consult a pediatrician. What treatment is required depends on the shape of the spots, color and size. You may not need it, and the stains will go away on their own.
The spot on the back of the head is popularly called the “kiss of an angel” or “stork bite”, and in the medical community – nevus of Unna, or telangiectasia. Birthmarks can be of two types - multiple and single (but large in size). Their surface is not convex and smooth. In the future, the spots become smaller in size and pale in color. When a child reaches the age of 1-2 years, formations on the skin may not be observed.
If the spots are red and have a bluish tint, this is a hematoma. It is rarely observed on the occipital part and is accompanied by swelling. They do not pose a danger to the child, because After a couple of days they disappear.
Consultation with a doctor cannot be avoided in case of hemangioma and gngiodysplasia. In the first case, spots are purple, blue or red, gradually increasing in size. With angiodysplasia, the neoplasms are light pink and sometimes purple in color. They may become darker and also enlarge over time.
![shutterstock_1111315238 [converted].jpg](https://dou10ugansk.ru/wp-content/uploads/shutterstock_1111315238-preobrazovannyj-jpg-330x140.jpg)