General information
Candidiasis in children is a common disease among children. Normally, small amounts of fungi are part of the opportunistic microflora and are constantly present in the body. If the child’s immunity is strong, microorganisms are safe for health. In weakened children, the fungus begins to multiply uncontrollably, affecting the mucous membranes, skin, and genitals. If candidiasis is left untreated, serious health problems can follow. The main task of parents in the fight against the disease is to establish good nutrition and strengthen the child’s immunity.
Treatment of intestinal candidiasis
This disease should be treated by a gastroenterologist. The doctor will be able to evaluate the symptoms, diagnostic results and prescribe correct and effective therapy. The principle of treating candidiasis is as follows:
- antimycotic therapy during the period of clinical manifestations;
- normalization of intestinal microflora;
- diet therapy - if you have candidiasis, you should not eat sweets, baked goods, sweet carbonated drinks, or alcohol;
- treatment of the underlying disease that caused the fungal infection.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Most often, candidiasis occurs in newborns and preschool children.
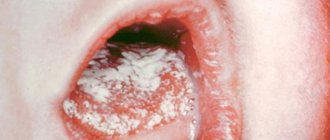
The older the child, the less often the disease is diagnosed. The favorite place for thrush to appear is the oral mucosa. A cheesy coating appears on the gums, palate, and inside the cheeks, and the baby feels pain and itching when eating. Along with these symptoms, candidiasis in children is also characterized by other signs:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- ulcers that open after removing the cheesy plaque;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness;
- white coating on the tongue.
The child does not eat well and is often capricious, since any touch to the mucous membrane causes pain.
In advanced cases, bleeding wounds open at the site of the removed plaque. There is another common form of candidiasis - fungal tonsillitis. It develops as a result of improper treatment of protracted sore throat. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are a cheesy coating on the tonsils and a burning sensation in the throat.
When the skin is infected with fungi, dense spots, redness, and blisters appear on it. In adolescents, thrush often affects the mucous membrane of the genital organs, and the disease is more typical for girls. Vaginal discharge becomes white and thick. In boys, the head of the genital organ turns red, and a discharge similar to sour cream appears in the area of the urethra. Cystitis and urethritis may develop.
If fungi infect the digestive tract, the child begins to suffer from colic, and food is difficult to digest. The baby suffers from constipation and pain in the lower abdomen. If fungi colonize the respiratory organs, the child often suffers from bronchitis, pneumonia, and ARVI. If internal organs are damaged, treatment should begin immediately, in consultation with a pediatrician.
Oral candidiasis
Oral candidiasis – stomatitis, glossitis, pharyngitis
.
Most have no complaints. Sometimes - burning, dullness of taste, pain when swallowing. White cheesy coating on the tongue. Clinically – “thrush” – multiple white plaques in the oral cavity, on the mucous membrane of the back of the tongue, mucous membrane of the cheeks, hard and soft palate, pharynx, different in shape, 1-2 mm in size. Atrophic candidiasis
- smooth red foci of epithelial atrophy in the oral cavity - on the hard and soft palate, buccal mucosa, dorsum of the tongue; hyperplastic candidiasis - white plaques that cannot be removed; with long-term treatment with antifungal agents, the plaques gradually resolve; jam - redness and cracks in the corners of the mouth.
Lip candidiasis – cheilitis
Vaginitis, vulvovaginitis
. They begin suddenly, about a week before menstruation. Itching of the vulva, burning and pain, especially when urinating, vaginal discharge, pain during intercourse. Clinically – white curdled vaginal discharge. Swelling, hyperemia and easily removable white plaques on the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix. Often combined with candidiasis of skin folds (perineum, inguinal folds).
Causes of candidiasis
The main cause of candidiasis in children is a yeast fungus of the genus Candida, present in the human microflora. But to activate it and increase the number of microorganisms, a number of factors are required:
- weakened immune system;
- frequent viral and colds;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes;
- hypovitaminosis;
- taking hormonal drugs or antibiotics for a long time;
- chronic diseases;
- HIV infection;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
The disease often occurs in premature infants and weakened children. If the mother's birth canal has been affected by candida, the baby, passing through it, becomes infected. The risk of developing candidiasis in such a newborn is much higher.
Causes of intestinal candidiasis
The main cause of this disease is weakened immunity. A decrease in the body's defenses may occur due to the influence of the following factors:
- acute viral and bacterial diseases that affect the digestive system (rotavirus, enterovirus infection, salmonellosis, etc.);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), such as pancreatitis, gastritis, cholecystitis, etc.;
- taking certain medications, such as antibiotics;
- disturbance of intestinal microflora;
- improper and irregular nutrition;
- food allergies;
- enzyme deficiency;
- helminthic infestations;
- endocrine diseases with metabolic disorders;
- immunodeficiency states;
- periods of physiological decrease in immunity (pregnancy, old age, children in the first year of life);
- autoimmune diseases;
- oncological diseases and chemotherapy.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
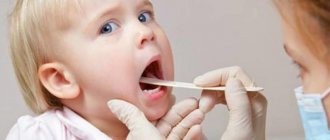
A pediatrician usually has no problems diagnosing thrush on the oral mucosa.
This is a common disease with characteristic symptoms, so an experienced specialist can easily identify it. In particularly difficult cases, when diagnosing a sore throat, sputum analysis may be required to identify the pathogen. The situation is more complicated with the diagnosis of candidiasis on the genital mucosa. In this case, you will have to take a smear for microflora, which will show the presence of inflammation and help identify the causative pathogen.
Thrush on internal organs is even more difficult to detect: external symptoms may be absent. Blood, urine, and stool tests may be required to detect mycosis.
Diagnosis of intestinal candidiasis
Intestinal candidiasis is often disguised as other gastrointestinal diseases and does not have obvious symptoms that would indicate a fungal infection. For this reason, it is quite difficult to identify the disease without laboratory and instrumental studies. For intestinal candidiasis, the doctor may prescribe the following diagnostic methods:
- stool analysis for dysbiosis;
- coprogram;
- cultural mycological examination of stool;
- serological diagnostics (for example, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with Candida);
- endoscopic examination of the intestine with biopsy.
The presence of a fungal infection in tests with no clinical picture may indicate candidiasis.
Treatment of candidiasis
The goal of treatment for candidiasis in children is to eliminate symptoms and prevent further proliferation of fungi in order to reduce their number. General recommendations for strengthening the baby’s body are as follows:
- reduce the consumption of sweet, salty and flour foods, which create a favorable environment for the growth of candida;
- take vitamin complexes, including folic and ascorbic acids, probiotics to normalize microflora;
- give the child drugs to strengthen the immune system;
- For newborns on artificial nutrition, switch to medicinal mixtures containing probiotics and vitamins.
If candidiasis has affected the oral cavity, treatment of the mucous membrane with antifungal agents is prescribed:
- a solution of baking soda, fucorcin or brilliant green;
- Miramistin (antiseptic);
- Clotrimazole (antifungal ointment);
- Nizoral, Pimafucin (antimycotic medications);
- spray for sore throat, stomatitis.
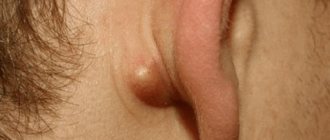
It is recommended to lubricate nails infected with fungus with iodine, antifungal ointments Clotrimazole, Decamine, Mikoseptin and varnishes. If the vagina is affected in girls, antifungal suppositories are recommended. You should not select medications yourself. It is better to consult a doctor and get examined. Self-medication can only worsen the baby’s condition. If thrush, despite the measures taken, does not go away, you may need to consult an immunologist, because This condition is usually associated with weak immunity.
Symptoms of intestinal candidiasis
Clinical signs of the disease depend on the cause of its occurrence and severity. The following symptoms may occur with candidiasis:
- general condition disturbance: weakness, lethargy, adynamia;
- decreased appetite;
- pain in the abdominal area (pain can be aching or cramping);
- flatulence;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- stool disorders - the discharge is most often liquid, mixed with mucus, blood (optional) and white inclusions, of a cheesy nature.
Prevention of candidiasis
To avoid thrush, follow the disease prevention measures:
- Mothers in labor are advised to sanitize the birth canal before giving birth. To do this, the woman takes a smear, based on the results of which the doctor determines the need for treatment. If candidiasis is diagnosed, vaginal suppositories with antiseptics are prescribed. This measure will prevent the baby from becoming infected with fungi.
- Follow the rules of hygiene in the maternity hospital.
- Breastfeed your baby only unless there are medical indications for bottle feeding. In the latter case, you need to choose the right mixture together with your pediatrician.
- Limit the consumption of sweets and sugar in children over one year of age. Try to keep your diet varied, healthy and nutritious.
- If the baby is weakened, strengthen the immune system with hardening procedures, proper nutrition, physical exercise, etc.
Candidiasis is an unpleasant but treatable disease. Timely consultation with a pediatrician, the correct course of therapy and compliance with preventive measures will allow you to forget about thrush for a long time. SM-Doctor specialists are always ready to help your child in the fight against candidiasis.
Candidiasis
Cervical cancer
Diabetes
HIV
Thrush
14268 27 July
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Candidiasis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Candidiasis is an infectious disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. It is caused by the active proliferation of fungus on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, genital and internal organs and on the skin.
All representatives of the genus Candida belong to opportunistic microorganisms, that is, they are constantly present in the normal microflora. But with a decrease in immunity, changes in hormonal levels and for a number of other reasons, these fungi can begin to actively colonize the mucous membranes and skin.
The most common members of the genus are Candida albicans and C. tropicalis. In 90-95% of cases of urogenital candidiasis, C. albicans is the dominant pathogen.
The first contact with fungi of the genus Candida occurs during the passage of the child through the birth canal. However, the medical literature describes cases of detection of these microorganisms in amniotic fluid, which indicates the possibility of a vertical (transplacental) transmission route. Transmission of the fungus of the genus Candida also occurs through breastfeeding, skin contact between the child and the mother, and through household and food routes.
These microorganisms produce endotoxins and enzymes that cause cell death and tissue necrosis, which enhances the adhesive (attachment to cells of the mucous membranes or skin) ability of the fungus and ensures penetration into tissue.
Overproduction of these and a number of other substances determines the pathogenicity of representatives of the Candida family.
Causes of candidiasis
- Exogenous (external) factors facilitating the penetration of fungi into the body:
- occupational hazards leading to frequent skin damage;
- prolonged exposure to a warm and humid environment;
- violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes.
- Factors leading to a decrease in the body's resistance:
- presence of chronic diseases;
- long-term use of drugs that disrupt the natural microflora;
- unbalanced diet;
- frequent stress, disturbances in sleep and rest patterns.
Risk factors for developing candidiasis
- Metabolic disorders (hypovitaminosis), diseases of the immune system (HIV infection), endocrine pathologies (diabetes mellitus, etc.).
- Long-term use of certain drugs: hormonal contraceptives, systemic glucocorticosteroids, broad-spectrum antibiotics, cytostatics.
- Long stay or living in an area with high humidity and temperature, comfortable for the circulation of fungal spores in the environment.
Classification of the disease
Based on the localization of the process, the following are distinguished:
- Urogenital candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of the oral mucosa.
- Superficial candidiasis.
- Interdigital candidiasis.
- Candidiasis of periungual ridges and nails.
- Candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Urogenital candidiasis (UGC)
– a widespread disease: according to medical statistics, about 75% of women of reproductive age have registered symptoms of UGC at least once.
There are acute and chronic forms of urogenital candidiasis, candidiasis of the vulva, vagina and other urogenital localizations.
In some cases, when diagnosing, a clarification is used: complicated or uncomplicated UGC, which reflects the number of exacerbations per year and the severity of the disease. Symptoms of female urogenital candidiasis
- The appearance of white-yellow cheesy or creamy discharge from the genital tract. The intensity of discharge may increase before menstruation, which is associated with changes in hormonal levels.
- Unpleasant sensations, itching in the genital area, often aggravated by sexual intercourse or urination.
- Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina, the presence of damage to the skin of the genital organs (cracks, microtraumas).
- In the chronic course of UGC, dryness of the mucous membranes of the genital tract develops.
Symptoms of male urogenital candidiasis
- Redness, swelling, discomfort in the genital area.
- Whitish discharge of a cheesy structure from the genital tract.
- Pain and burning during sexual intercourse and urination.
Superficial candidiasis
can be erythematous (the main symptom is reddened areas of the skin with a weeping surface) and vesicular (the formation of papules, vesicles and pustules in the affected area - inflammatory elements located in the superficial layers of the skin). The lesion begins with large folds of skin, gradually spreading to other areas of the body. In the depths of the folds, weeping occurs (separation of serous exudate through the smallest defects of the epidermis), a violation of the integrity of the skin contributes to the addition of a secondary infection.
Interdigital candidiasis
localized in the space between the fingers. In this case, redness of the skin is noted, followed by the appearance of bubbles in transparent contents. The disease spreads quickly in close groups (in kindergartens, schools, etc.).
Oral mucosal candidiasis (OCOR)
Oral candidiasis causes discomfort, especially when eating - burning, pain, dryness. Depending on the location of the process, several forms of oral candidiasis are distinguished.
Often, CSOPR and the gastrointestinal tract accompanies immunodeficiency conditions: HIV infection, acquired human immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) or congenital immunodeficiency (for example, with T-lymphocyte pathology). In the presence of these diseases, candidiasis occurs with the most severe symptoms, is difficult to treat, and is aggressive in nature.
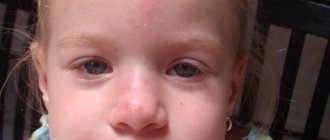
The most common manifestation of CSOPR is candidal stomatitis, which mainly affects infants and adults with weakened immune systems.
With this pathology, the oral mucosa turns red, swells, and whitish films with a cheesy consistency appear on it. In the initial stages of the disease, plaque is easily removed. As the disease progresses, the films become denser, are difficult to separate, and when removed, the bleeding mucous membrane is exposed.
With candidal stomatitis, the tongue may be affected, which is manifested by redness of the back of the tongue, the appearance of plaque and desquamation of the epithelium. These symptoms are accompanied by severe pain in the affected area when talking, eating, and palpating the tongue.
Smokers, more often than other types of CSOPR, develop chronic hyperplastic candidiasis, accompanied by the formation of white, merging plaques that rise above the surface of the hyperemic mucosa.
With this pathology, the consistency of saliva changes: it becomes viscous and foaming; there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, a gray or white coating on the mucous membrane. In 10-40% of cases, this clinical form of candidiasis becomes malignant (i.e., becomes malignant).
Older people most often develop a chronic atrophic form of oral candidiasis. The mucous membrane turns red and swells. The lesion is often localized under dentures, which causes pain.
Candidal cheilitis and candidiasis of the corners of the mouth mainly occur in children and the elderly. The lesion is usually bilateral, with the formation of red, painful cracks in the corners of the mouth, covered with an easily removable white coating or scales. With a long course of the disease, a bacterial infection may occur.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
The diagnostic search algorithm for candidiasis of any localization includes taking material from the affected area, followed by microscopy and culture to determine the type of fungus and its sensitivity to antimycotic (antifungal) drugs.
In order to diagnose conditions that lead to a decrease in immunity, a general blood test is used;