Causes of blocked tear duct
Failure in the functionality of the lacrimal ducts has seven reasons:
- Congenital obstruction - the passage is narrow and small due to which it is clogged with a mucus plug. This failure often goes away with age.
- Deviations from the norm in the development of the eyelids, skull, face - along with these anomalies, the shape of the outflow changes.
- Infectious infections of the eyeball and inflammatory processes provoke the formation of adhesions in the nasolacrimal ducts.
- Mechanical injuries and eye surgeries - deformation of the tear drainage pathway is possible, resulting in tear stagnation and blockage of the duct.
- Neoplasms of the paranasal sinuses - sometimes tumors block the outflow.
- Dacryocystitis of the lacrimal sac is an inflammatory disease in which the outflow of tears is difficult or impossible.
- Medicinal cause - taking certain medications leads to blockage of the connective lacrimal duct.
Signs of the disease will tell you in more detail that a person has a problem with the patency of the lacrimal canal. At the appointment, the doctor asks the patient if there are any concomitant symptoms.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis in adults and children
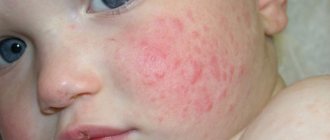
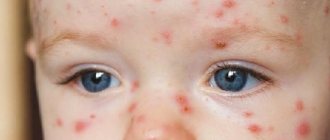
Signs of dacryocystitis are quite noticeably expressed externally. A swelling forms at the inner corner of the eye, and profuse lacrimation begins. Patients complain of a feeling of fullness from the inside. When pressing on the swollen area, purulent or mucous contents are released from the tubule, and moderate pain may be felt. With dacryocystitis, the eyelids turn red, swell, and the palpebral fissure narrows. After a few days, the swelling becomes softer and the skin turns yellow. As a rule, this process develops only in one eye.
Acute inflammation of the lacrimal canal can lead to dire consequences if treatment is not promptly addressed. In practice, there are cases where the tumor reached the size of a walnut. Chronic dacryocystitis can develop into empyema or phlegmon - purulent inflammation of the tissue around the lacrimal sac. The skin of the affected area becomes purplish-red, the nose becomes noticeably swollen, and the palpebral fissure becomes narrow or closes completely. In such cases, there is a danger that pus will break into the tissues, and further into the depths of the skull - such conditions can be fatal.
Symptoms
Obstruction of the lacrimal canal is the first stage of the disease.
Signs:
- suppuration of the corner of the eye, possible gluing of eyelashes with pus;
- profuse lacrimation for no reason.
If you do not consult an ophthalmologist in time, the disease develops and enters the second stage - blockage of the canal occurs (stenosis). In this case, the tears stagnate and harden. This phenomenon can occur in one eye or two. If further failure to seek medical help occurs, dacryocystitis occurs - a more dangerous pathology in which the canal is completely clogged. Causes loss of vision.
Signs:
- vision decreases;
- blood “strings” in the lacrimal sacs;
- purulent discharge;
- swelling and inflammation of the eye;
- redness and heat in the eye;
- painful sensations on palpation;
- profuse lacrimation;
- The density of the lacrimal sac increases and it increases in size.
Cellulitis of the lacrimal sac may develop - acute purulent inflammation followed by death of eye tissue.
Obstruction of the tear duct is easily confused with other ophthalmological diseases:
- Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye.
- A corneal ulcer is the destruction of corneal tissue.
- Eye stye is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash.
- Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelids.
- Demodectic mange is an infection of the eyeball by parasites.
- Allergic manifestations with whitish discharge from the eyes.
Therefore, at the first symptoms of a lack of patency in the tear duct, you need to contact an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination. Only a specialist will determine the disease and treatment method.
Nasolacrimal duct: the need for probing
Tear fluid plays an important role in protecting the anterior segment of the eyeball - it moisturizes, protects the eye, has the antibacterial effect of tears, and also washes away small dust particles and other foreign particles from the ocular surface with tears.
A little about the anatomy and physiology of this system.
The lacrimal gland produces tears (until the child is 2 months old, there are few tears; the lacrimal gland has not yet “started working”). Then the tear, washing the surface of the eye, flows down to the lower eyelid, forming a tear stream there.
In the eyelids there is a lacrimal punctum, which, like a pump, sucks in accumulated tears and collects them through the lacrimal canaliculus into the lacrimal sac, which serves as a tear reservoir. From it, the tear goes into the nasolacrimal canal and from there enters the nasopharynx.
Obstruction or insufficiency of the lacrimal ducts can be caused by various reasons, and the “block” can be located at any level of the lacrimal drainage system.
A special form of obstruction of the lacrimal ducts is the closure of the nasolacrimal duct in newborns, as previously said, the nasolacrimal duct is the final part of the lacrimal system of the organ of vision and ends in the nasal mucosa.
During intrauterine development, the nasolacrimal canal is closed by a membrane or glandular “plug”; at the first cry of the child, this barrier is “removed”, but there are times when this “plug” is denser or there are some anatomical features in the nasolacrimal canal (narrowing, tortuosity, etc.) .p.) and, as a result, tears are poorly drained from the lacrimal sac. It stagnates, a bacterial component joins and so-called dacryocystitis of the newborn occurs. It can be one-sided or two-sided.
A typical complaint in newborns with obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct is persistent mucopurulent discharge from the eye from birth or from the first days of the child’s life, which does not go away with the use of antibacterial drops. Later, lacrimation occurs (the eye is “wet”). If bacterial contamination continues to increase, the lacrimal sac is involved in the process and dacryocystitis occurs. This condition can already pose a danger to the health and even life of the child and requires emergency medical attention.
Prevention
From the birth of a child, you need to carefully treat the baby's eyes. Several times a day, especially after sleep, wipe the eyelids with warm boiled water from the outer corner of the eye to the inner corner; in no case, if there are purulent crusts, should you scrub them with force. A child's skin is much more delicate than an adult's skin and even a small force can injure it. The crusts are soaked, then the eyelids are wiped very carefully. If purulent discharge is present, then after toileting the eyelids you need to instill an antiseptic drug. For this, it is good to use Vitabact eye drops, you can also use Albucid (Sodium Sulfacyl 10-20%) - 3-4 times a day for a week.
Sometimes, if there is very copious discharge, an antibiotic is added, which cannot be used without the supervision of a pediatrician or ophthalmologist!
Before and after the drops, you should do a jerky massage of the projection area of the lacrimal sac and the nasolacrimal canal (this is the inner corner of the eye and the side surface of the nose to the wing of the nose), and massage should also be done during feeding. When sucking, the osmotic pressure in the nasopharynx increases and the massage effect increases.
Diving in the pool is not recommended. You can swim, you can swim. Diving - no!
If, after following these recommendations, complaints persist, it is important to contact an ophthalmologist or ENT doctor. A special feature of young children is narrow nasal passages and any swelling of the nasal mucosa, even the slightest, can affect lacrimal drainage.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, then probing of the lacrimal ducts is performed. This procedure is performed for children under 6 months of age without anesthesia. After 6 months (to avoid injury), the baby is given light anesthesia.
Probing is carried out in a special treatment room in complete sterility.
Something to remember! Dacryocystitis of newborns is a complication of obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct. If the above measures do not relieve the complaints, and especially if swelling of the eyelids, hyperemia around the eye and in the face, or a rise in temperature occurs, then you should immediately consult a doctor for emergency medical help!
Currently, thanks to the high awareness of parents, as well as the presence of a nursing service for newborns, obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct rarely turns into dacryocystitis, but if the problem cannot be solved on its own, there is no need to delay and be afraid of probing the lacrimal ducts. This procedure allows you to avoid very serious problems in the future.
May your children be healthy!
about the author
- Medvedeva Inna Gennadievna
- Ophthalmologist of the highest category
- All publications by the author
Symptoms of tear duct obstruction in infants
Signs of pathology in infants are the same as in adults.
The very first symptoms that are important not to miss:
- causeless lacrimation in the baby;
- redness of the area around the eyes (one or both);
- purulent discharge, more abundant at night.
Pus sticks together the newborn's eyelashes, making it impossible for him to open his eyes. Subsequently, dacryocystitis develops with symptoms similar to those of an adult.
Diagnostics
The initial examination is carried out by a therapist. An ophthalmologist diagnoses such diseases.
In adults
First, the symptoms of the disease are determined and the patient’s medical history is examined. To make an accurate diagnosis, he conducts laboratory tests:
- Instills collargol solution into the eyes to determine the source of inflammation.
- Takes a sample of the lacrimal canal to determine the degree of obstruction.
- Conducts a culture of pus that comes out during palpation - identifying an infectious disease.
- Prescribes eye x-rays - if the cause of obstruction is mechanical damage.
Important!
The main thing is to determine what kind of disease has affected the patient’s eyes - dacryocystitis or conjunctivitis. These are different pathologies caused by different pathogens.
In children
Diagnosis of blockage of the nasolacrimal duct in newborns is carried out on the basis of the mother’s story about the child’s well-being. Carry out:
- ophthalmological examination;
- tubular test;
- bacteriological examination;
- endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity;
- general blood and urine analysis.
Additionally, parents and their child visit related doctors:
- ENT;
- Pediatrician.
This measure is necessary in order to exclude concomitant diseases.
Massage
The first step is to prescribe the so-called conservative method of treating tear obstruction - drops and massage. The main thing is to massage the tubule correctly.
For adults
Regardless of whether a person massages himself or someone else, he needs to follow the rules of hygiene:
- Wash your hands thoroughly.
- Trim your nails.
- Wear sterile gloves.
Prepare:
- cotton pads;
- wet wipes;
- antiseptic.
As an antiseptic you can use:
- Tea leaves are a natural disinfectant.
- Chamomile infusion – removes inflammation. One teaspoon of infusion per glass of warm water. Strain the chamomile flowers well through cheesecloth.
- Furacilin solution - one tablet per glass of warm water.
If a person himself stimulates the passage of tears, then it is convenient to use the index finger. For some, a thumbs up.
Massage stages:
- Place your finger slightly above the upper corner of the inner side of the eye.
- Using a little pressure, insert your finger from the wing of the nose to the edge of the area under the eye (from the outside).
- Carry out the procedure at least five times during one massage.
- Wipe off the pus that came out during the process with a cotton pad.
- Rinse the eye with the selected disinfectant and wipe with a sterile napkin.
After the massage, eye drops are applied. The doctor selects the drops. Repeat the massage five times a day.
Newborns
If pathology is detected in a newborn, the only way to restore the patency of the lacrimal canal is massage and drops. At an advanced stage - surgery.
The massage regimen is similar to the treatment of blockage in adults:
- Run a clean finger from top to bottom from the inside to the outside edge along the nasal sinus, then move up from bottom to top - repeat five or more times.
- Remove the released pus using a cotton pad soaked in an antiseptic solution.
- Rinse the eye with chamomile infusion, tea leaves or liquid containing furatsilin.
- Apply drops to both eyes, even if one is damaged - for prevention.
For children you can use eye drops:
- Tobrazon;
- Tobradex;
- Tobrex;
- Oftaquix;
- Vitabact.
Drops are prescribed to infants by a pediatric ophthalmologist.
You should press lightly so as not to damage the not yet fully formed nasolacrimal duct. If your child's eye is stuck with pus, first clean it with a disinfectant solution and a cotton pad.
It is important to know!
Never put breast milk in the eyes of a newborn. The healing properties of this drink in this case are a myth.
Repeat the procedure at least five times a day, before feeding. With intensive stimulation, the obstruction of the lacrimal lumen will disappear in an average of two weeks. Do not use ointments, creams or oils during massage.
In case of prolonged illness, you should contact an ophthalmologist for a second consultation.
Treatment
Treatment therapy may vary depending on various factors. To ensure that treatment is as effective as possible, specialists use a set of measures. Such therapy should contain not only drug treatment, but also massage, which accelerates the process of restoring normal functioning of the tear ducts. In cases where therapy does not produce the expected results, surgery may be used to eliminate the pathology.
Drug therapy
Most often, drug treatment is used after surgery, since such drugs can speed up the recovery process. It should be noted that the main task of medical products is to stop the manifestation of symptoms of pathology and prevent re-inflammation.
The most effective medications for treating blocked tear ducts are:
- Paracetamol;
- Tobrex;
- Vigamox;
- Oftaquix;
- Gentamicin.
Massotherapy
One of the additional methods of treating blocked tear ducts is a special massage. As a rule, this procedure is an addition to drug therapy. Before starting the procedure, you should thoroughly wash your hands and disinfect them. The procedure is performed with fingers with short nails.
This point is one of the most important. Before starting, you should clean the lacrimal opening; for this, use a cotton swab soaked in a weak solution of furatsilin. The use of gauze swabs should be avoided as they may leave behind small lint that is difficult to remove.
The duration of the massage should be no more than 10 minutes. The entire procedure includes jerky movements of the fingers without much effort, which are moved along the small tubercles that appear in the inner corner of the eye. During such a massage, the lacrimal sacs should be filled with purulent discharge from the lacrimal canals. It becomes necessary to clean the eye with a cotton swab. At the end, the affected eye must be instilled with eye drops prescribed by a specialist. On the recommendation of an ophthalmologist, massage can be done at least 5 times a day. The duration of the treatment course is 1-2 weeks.
Operation
Surgical intervention is prescribed in cases where medications do not give the expected result. Also indications for surgery are tumors and congenital obstruction of the lacrimal canals.
The main direction of the operation is to restore the normal functioning of underdeveloped and damaged tear ducts. Most often, dacryocystorhinostomy is prescribed, during which the normal outflow of tear fluid is restored.
If the operation is successful, the patient should undergo a long course of medication aimed at restoring the normal functions of the tear ducts. At this stage, sprays are prescribed to help eliminate swelling of the mucous membranes. Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial eye drops are also required.
Rules for massage
For a massage to be effective, it must be done according to the following rules:
- Movements should be fast, but not strong. There is no need to put pressure on your eyes.
- A single movement takes about five seconds.
- Stimulation should end with a crunch – a breakthrough of the membrane membrane. It is this breakthrough that releases pus from the canal and clears the way for tears.
Attention!
It is necessary to remember the rules of personal hygiene. Never reach into your eyes with dirty hands - this will only make the situation worse.
If you self-medicate for a long time and do not visit an ophthalmologist, you can end up with severe eye complications, including loss of vision. Therefore, the first and most important rule is to begin treatment only after examination by an ophthalmologist.
If massage doesn't help
There are rare cases when simple classical treatment for blocked tear ducts does not help. This happens with advanced dacryocystitis (when tears harden in the lumen, which leads to complete blockage of the passage).
Cancer of the lacrimal sac projection, a malignant tumor of the lacrimal glands, is treated exclusively by surgery.
For adults
The doctor prescribes surgery. The operation is simple, under local anesthesia. The procedure itself takes 5-7 minutes. There are three current intervention methods:
- Laser - use an endoscope with a laser. A small hole is made in the nasal cavity and connected to the lacrimal sac.
- Endoscopic - a thin tube with a camera at the end is inserted. An incision is made in the blocked tear duct, which helps create a new tear duct.
- Balloon - allows you to avoid making incisions on the face. A tube with a small balloon at the end is inserted. Inside the passage, the device expands and enlarges the channel.
Surgical intervention for children
Operations are performed on children from the age of seven months. Under general or local anesthesia. Surgical intervention occurs only within the walls of the hospital. Carrying out surgery at home is strictly prohibited.
They use small umbrellas that look like many small needles with blunt ends. They carefully expand the baby's connecting canal and relieve it of pus - that is, they carry out probing. The whole procedure takes five minutes and is completely harmless.
Children also undergo bougienage of the lacrimal canal - they expand the lumen of the canal using a thin long rod (bougie).
The essence of all methods is to expand the tear drainage path and rid the child of purulent discharge. Sometimes the probing or bougienage procedure needs to be repeated several months later to consolidate the effect.
How to properly massage the eyes of a newborn baby
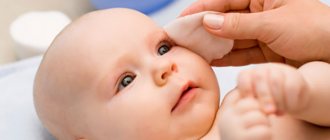
The massage must be carried out in compliance with hygiene and safety requirements so as not to accidentally damage the child’s eyes or cause an infection. Be sure to cut long nails to avoid scratching your baby's skin. Before starting the procedure, wash your hands thoroughly and dry them. It is better to start a massage after feeding, when the baby is in a calm, relaxed state. It is not recommended to do this if he is feeling anxious for any reason or has a fever. First, you should rinse, clearing your eyes of traces of purulent discharge. Weak antiseptic solutions are suitable for this - for example, boric acid, furatsilin, chamomile, etc. A cotton pad is moistened in the solution and traces of purulent fluid are carefully removed by moving from the outer corner of the eye to the inner. Use a separate disk each time.
Next, you should place your index finger on the point in the inner corner of the eye where the two canaliculi meet before entering the lacrimal sac. Ask your doctor to show you this place, and also feel it yourself to better understand where the desired point is. Next, start moving your finger from top to bottom towards the baby’s nose, while applying gentle pressure. It is necessary to repeat such movements 6-10 times. If during the procedure pus is released from the lacrimal sac, it means that the eye massage is carried out correctly. The contents of the ducts are removed using a cotton swab.
It is recommended to eliminate purulent discharge in this way 5-6 times a day. Upon completion of the procedure, you need to rinse the eye with antiseptic solutions, and then administer antibacterial ointments or drops. This could be a solution of Levomycetin 0.25%, Vitabact or other medications. Doctors recommend eye massage in newborns with obstruction of the lacrimal canal for two weeks, and then see a specialist. Usually during this time the process normalizes and the tear begins to flow normally. As a rule, the doctor’s prescription looks like this:
- eye massage - 4-6 times a day, 6-10 repetitions;
- washing the lacrimal canals with an antiseptic solution;
- "Levomycetin" 0.25%, 1 drop 4-5 times a day.
Under no circumstances should you treat your child based on advice from online forums. Incorrect therapy will lead to dacryocystitis taking an acute form, and it will be difficult to cope with it. In general, in 80% of cases, the measures taken act favorably and the film breaks, ensuring normal patency of the tear duct. If this does not happen, surgical treatment is prescribed.