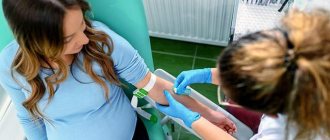
What is an in vitro fertilization program?
Thanks to the revolutionary development of assisted reproductive technologies, a method of treating infertility has emerged that has given great hope to infertile couples. This is a method of in vitro fertilization, embryo transfer, which today is the most effective method of treating infertility, helping even in the most seemingly hopeless situations. IVF, embryo implantation is used for absolute female infertility (in the absence or complete obstruction of both fallopian tubes), for male infertility, for infertility of unknown cause, as well as for ineffective conservative or surgical treatment of other forms of infertility. Therefore, doctors believe that it is impossible to continue treating infertility with other methods for more than 1.5–2 years if their ineffectiveness is obvious. The sooner a couple contacts an in vitro fertilization clinic, the higher their chances of success. During in vitro fertilization, after stimulation of the woman's ovaries, several follicles with eggs mature. Directly in vitro fertilization is carried out in this way: the doctor punctures the ovary, extracting eggs, which are then fertilized with the sperm of the husband or donor outside the mother’s body. If the quality of the spouse's sperm is reduced, a single sperm is injected using a microneedle (ICSI method). After a few days, embryo transfer takes place: the embryos obtained through IVF fertilization are transferred into the woman’s uterine cavity. Next, the embryo attaches and the embryo in the uterus continues to develop. After embryo transfer, one attempt at IVF fertilization, embryo implantation gives a chance of conception from 20% to 30%, which is even slightly higher than the average rate of pregnancy naturally. The likelihood of conception and successful development of the embryo during the procedure after embryo transfer depends on the age of the spouses, their state of health, the quality of the drugs used, the quality of the resulting embryos, as well as some other factors. The correct day for embryo implantation is determined by a specialist doctor. After embryo transfer, the days after embryo transfer should be supervised by a specialist. The failure of one attempt at IVF fertilization does not mean that this method - embryo transfer - was ineffective. Each subsequent IVF attempt and embryo implantation significantly increases the total chances of a successful pregnancy after embryo transfer. Within a year of treatment, in vitro fertilization after embryo transfer gives an almost ninety percent chance of getting pregnant. In the three decades since the birth of Englishwoman Louise Brown, the first child born from an egg fertilized in vitro (1978), more than three million children have been born using this method. Modern assisted reproductive technologies and embryo transfer have already helped millions of infertile couples around the world. We hope that they will help you too. If you do not have the funds to transfer embryos, then you can try to perform in vitro fertilization for free, or transfer embryos using a special state program. However, it should be remembered that free in vitro fertilization is much more difficult than a paid procedure - since if you fail, you will wait a long time for the next chance to get free in vitro fertilization. Good luck!
Program outline. Embryo implantation. Before and after embryo transfer
The IVF program consists of several stages. Each stage is important in its own way, so you need to treat it very responsibly, strictly following all the doctor’s recommendations.
Stage I Determination of the in vitro fertilization program, including treatment tactics after a preliminary examination.
Stage II Preparing spouses for such an important procedure as IVF fertilization: correction of hormonal abnormalities, including spermatogenesis disorders, treatment of infections
Stage III Stimulation of superovulation, ultrasound monitoring (10–30 days).
Stage IV Introduction of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) for the final maturation of eggs before in vitro fertilization (1 day).
Stage V Follicle puncture, egg collection, sperm donation. Fertilization of an egg with the sperm of a spouse or donor (1 day). Stage VI Cultivation of embryos, observation of embryo fragmentation (2–5 days).
Stage VII On the selected day of embryo transfer - transfer of embryos into the uterine cavity, after embryo transfer - freezing of the remaining embryos as necessary (1 day).
Stage VIII Days after embryo transfer - hormonal support for early pregnancy after embryo transfer. It is important that the implantation of the embryo is successful. (up to 10-14 weeks).
Stage IX Pregnancy test associated with the detection of the blood hormone hCG (2 weeks after embryo transfer, IVF fertilization).
Stage X ultrasound – diagnosis of pregnancy (3 weeks after embryo transfer, in vitro fertilization procedure).
Stage XI Pregnancy management.
XII stage of Childbirth (maternity hospital).
How to increase the chances of pregnancy with a long protocol?
There are a number of recommendations that help increase the success of a long IVF protocol. In addition to using medications prescribed by a doctor, a woman should adhere to the following rules:
- Avoid drinking coffee and caffeine-containing products. It has been proven that drinking coffee every 5 days or more increases the likelihood of spontaneous miscarriage.
- Eat properly and balanced. The diet should be dominated by vegetables and herbs, lean meats, sea fish (heat-treated), cottage cheese, and eggs.
- Maintain sexual rest. Intimacy is prohibited for 2 weeks after embryo transfer, so as not to disrupt the implantation process by mechanical and chemical means.
- Do not visit baths and saunas, do not take a hot bath. High temperatures can damage the fertilized egg.
- You should spend more time outdoors. Bed rest, as it turned out, does not improve the outcome of conception, but on the contrary, it can even be harmful, for example, due to an increased risk of thrombosis.
- Try to avoid heavy physical activity and psycho-emotional shocks, because... they can disrupt the delicately regulated endocrine system.
Naturally, before entering the IVF program and at all stages of its implementation, as well as carrying a child, you should stop smoking and drinking alcohol. These factors have been proven to increase the frequency of miscarriages and the formation of placental insufficiency.
To realize your dream of happy motherhood, make an appointment with the fertility specialists of the SM-Clinic clinic. Our center has introduced the most advanced technologies for diagnosing the causes of infertility and the most advanced treatment methods that help cope with even the most severe fertility disorders. Doctors are available at convenient times by appointment.
Preparation for the procedure
Lifestyle for both spouses
In order for the body to be ready for such a procedure as embryo transfer and the upcoming pregnancy, it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle. The diet should be varied, rich in vitamins, proteins, containing a moderate amount of fats, as well as carbohydrates. No strict diets. When you need to donate blood for biochemical or hormonal studies, you can have breakfast only after drawing blood. It is recommended to take vitamin and mineral complexes intended for pregnant women. An alternative is to take folic acid, potassium iodide, and vitamin E in small doses a month before the start of the program. Avoid taking medications that are contraindicated during pregnancy. Smoking, even passive smoking, should be avoided. You should not drink more than two cups of coffee per day, and alcohol consumption should be kept to a minimum. Avoid hot baths, steam baths, saunas. Try to lead an active, mobile lifestyle. Try to ensure that the treatment has as little impact on your mood as possible. Avoid significant stress, as well as physical or psychological stress. After embryo transfer, the importance of a healthy lifestyle increases even more
Sexual contacts
The general nature of sexual activity during the in vitro fertilization procedure should not change. You can have sex with the same frequency as always. But you need to abstain from sexual intercourse for 3-4 days so that your husband can accumulate a sufficient amount of sperm. Also, the spouse should refrain from masturbation. Abstinence should continue for about seven days until the day of embryo transfer arrives. Sexual intercourse after embryo transfer should be avoided until pregnancy tests show that the embryo has been successfully implanted and the embryo is developing properly. Both spouses should try to avoid casual sex. Detected genital infections must be treated, so subsequent sexual intercourse should be carried out with a condom. When in vitro fertilization is performed, after embryo transfer, pain during sexual intercourse is possible due to enlarged ovaries.
Minimum preliminary examination
When you are indicated for an IVF procedure or embryo transfer, a number of studies can be done at your place of residence. Find out the required minimum examinations. Usually this is a spermogram of the spouse, a hormonal analysis, an image of the uterus, fallopian tubes, a blood test, and a vaginal smear analysis for the presence of infectious diseases. When you come to your initial appointment with a doctor, do not forget to take with you all the available results of previous examinations, extracts from medical records, etc. All this will be needed for the embryo implantation to be successful. Infections Before the procedure, it may be necessary to be examined for some infections that, after embryo transfer, pose a danger to the embryo and have a negative impact on its development, as well as on the pregnancy. These include, for example, herpes, cytomegalovirus, rubella, toxoplasmosis. These infections are widespread, but often occur hidden. The scope of diagnosis is determined by the attending physician.
Hormonal examination Often, infertility is accompanied by hormonal abnormalities. Their timely detection, as well as correction, can increase not only the likelihood of pregnancy after embryo transfer, but also the chances of its favorable course. Most hormones are tested from days 1 to 5 of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, the first visit should occur during this period. Blood is donated from a vein, usually in the morning, on an empty stomach.
Visit to an andrologist, sperm examination
Treatment of infertility with IVF involves a mandatory examination by an andrologist, including sperm testing. Before a sperm analysis, the spouse must follow some rules: abstain from sexual activity for 3 to 7 days (optimally 5), do not drink alcohol, do not take steam, no hot baths, do not urinate for two hours before visiting the doctor, eat only low-fat, non-spicy foods.
Planning visits to the doctor Treatment with IVF and embryo transfer takes place on an outpatient basis, but requires discipline and punctuality from patients. Before starting the program, plan your activities so that you do not have night shifts so that you can undergo ovulation stimulation (for 2-4 weeks), and then come for puncture and embryo transfer on the day of embryo implantation. The presence of the husband is required for a preliminary examination and sperm donation during follicle puncture. After the embryo transfer, you will be issued a sick leave certificate.
Agreements If you are planning to start treatment with IVF or other methods of assisted reproduction, which include ICSI, artificial insemination, fertilization with donor sperm, egg donation, surrogacy, then first decide with your doctor all the ethical and legal issues that concern you. For each type of treatment, a legal agreement is concluded with the clinic, which must be signed by both spouses.
Assessment of folliculogenesis
To determine the violation of folliculogenesis by the type of lack of follicle maturation, a special study is performed - folliculometry. What it is? Folliculometry is a routine ultrasound that is performed starting from days 4-7 of the menstrual cycle. The purpose of the study is folliculogenesis, which means that the number of maturing follicles, the size of the follicle at ovulation, the presence of ovulation and its day are determined.
Preparation for the procedure includes a gas-reducing diet to improve ultrasound imaging. The study is carried out daily or every other day. The normal growth rate of the follicle is 20-23 mm; upon reaching this size, it must burst to release the egg. If this does not happen, then you need to look for the cause, which is usually associated with hormonal disorders.
In case of infertility, it is necessary to study folliculogenesis, the results of which will allow you to exclude some factors and continue the examination to identify the true causes. If abnormalities are detected, hormonal treatment and adjustment of the balance of hormones in the blood is required.
Mechanisms of folliculogenesis disorders
Impaired folliculogenesis is a common cause of infertility. Follicles in the ovaries may not grow for several reasons. The main ones:
- There are no hormones that ensure follicle growth. This function is mainly performed by FSH. There are situations when its production is insufficient. Most often this happens after childbirth. The blood supply to the pituitary gland is disrupted and the part of it responsible for the formation of FSH ceases to function. As a result, there are not enough hormones. This disrupts folliculogenesis, which leads to infertility.
- There are hormones, but the ovaries “do not see” them. This is called resistant ovarian syndrome. The reasons for it are unknown. An autoimmune origin is suspected. Your own immunity destroys receptors that respond to FSH. This results in a violation of folliculogenesis, despite the fact that there are enough hormones in the blood.
- The ovaries are exhausted. They simply can no longer form follicles because there is no longer a supply of eggs. At the same time, the level of hormones responsible for folliculogenesis increases significantly - this is due to the fact that the pituitary gland “sees” the insufficient function of the ovaries and “tries” to strengthen it. Ovarian depletion normally occurs in all women; this phenomenon is called menopause. Sometimes this happens prematurely due to diseases, operations or genetic characteristics of the functioning of the reproductive system.
Stimulation of superovulation
In order for the likelihood of pregnancy to be higher after one IVF attempt, after embryo transfer, it is necessary to obtain several eggs suitable for fertilization. For this purpose, before the procedure, the so-called stimulation of superovulation is carried out, when the woman is prescribed medications that cause the simultaneous maturation of several follicles. Various drugs can be used to stimulate superovulation. Before stimulation begins, the doctor discusses with you the most appropriate treatment option, selects medications, and determines the sequence of their use, which is called the “stimulation protocol.”
Drugs to stimulate superovulation
Preparations containing follicle-stimulating hormone Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is responsible for the maturation of follicles, therefore, when stimulating superovulation, drugs containing FSH are used. Recombinant drugs are now considered the most effective. They increase the pregnancy rate and reduce treatment costs. One such recombinant FSH is the drug Puregon, created through genetic engineering. Nowadays, for maximum convenience of women, the Puregon Pen injector pen is used. The Puregon Pen injector pen is intended for self-administration of Puregon subcutaneously by patients. The pen is designed for reusable use using a cartridge with a ready-made Puregon solution.
Puregon-Pen reduces the pain of manipulation thanks to microneedling - this is a new method of administering FSH - Puregon, which provides the following advantages:
- maximum accuracy of administration of the dose of Puregon prescribed by the doctor,
- maximum possibilities for dose adjustment based on the individual characteristics of the patient,
- maximum ease of use,
- reduce additional stress associated with the treatment process itself, and therefore your confidence increases.
Drugs that suppress the production of the pituitary gland's own hormones (hormone agonists, antagonists) To prevent a woman's own pituitary gland hormones from interfering with the stimulation of superovulation, their production is blocked by antagonists. Orgalutran is a new antagonist that allows you to instantly block the pituitary gland and then quickly restore its function, which reduces the duration of treatment by almost half compared to traditional drugs (agonists). Agonists (triptorelin, goserelin, leuprorelin, buserelin) require fairly long-term administration. They need to be administered daily for 20–30 days, or once, but in a large dose, which dissolves in about a month.
Preparations containing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) Follicular puncture is carried out 36 hours after the injection of hCG, which initiates ovulation of mature follicles. The use of hCG allows you to obtain a mature egg ready for fertilization. One of the drugs containing hCG is Pregnil.
Superovulation stimulation protocols
During in vitro fertilization, different types of protocols are used. It should be remembered that there are no strict treatment regimens; individual variations are possible for each of the protocols below.
"Clean Protocol"
Some women use stimulation regimens without blocking the pituitary gland. For this purpose, only drugs containing FSH are used, for example Puregon Pan. This scheme is called “pure”. Its disadvantage is the likelihood of premature ovulation (rupture) of the follicle even before puncture, which makes it impossible to obtain eggs. With this protocol, the administration of stimulant drugs begins on the 2nd–3rd day of menstruation and continues for 9–14 days. The daily dose is adjusted by the doctor depending on the ultrasound data, which is usually performed 4-5 times during the entire stimulation period. For the final maturation of the follicles, hCG, for example Pregnil, is injected, and after 35–36 hours the follicles are punctured.
"Long Protocol"
The protocol is called “long” because, as a rule, it begins on the 21st–23rd (rarely from the 2nd–3rd) day of the menstrual cycle preceding stimulation. To block the pituitary gland, only an agonist is taken for the first 5 days from the start of treatment. After blockade of the pituitary gland is achieved, menstruation begins, and from the second to third day from its onset, stimulation is carried out with drugs containing FSH, in the same way as with the “pure” regimen, but together with the continued administration of the agonist.
"Optimal Protocol"
When using the new antagonist Orgalutran, the stimulation protocol is significantly shortened, although a pronounced, easily reversible blockade of the pituitary gland remains. Stimulation begins, as with the “pure” regimen, from 2–3 days of the menstrual cycle by daily administration of a drug containing FSH. Then, from the 5th or 6th day of stimulation, daily injections of Orgalutran are given, but stimulation continues. Thus, the “Optimal Protocol” becomes short and therefore effective. The combination of the new generation drug Puregon with Orgalutran (antagonist) is: - reduction of treatment time; - better tolerance of injections; - proven effectiveness. Thanks to this, the combined use of Puregon with Orgalutran can be called “Two components of hope in the treatment of infertility.”
Why choose a long IVF protocol?
The long protocol is the most tested and most researched, because... appeared one of the first in reproductology. It allows you to achieve good results, having many advantages:
- good control over the process of growth and maturation of follicles;
- absence of unplanned pre-ovulatory hormone surges that can cause premature ovulation;
- better quality of mature eggs and obtaining them in sufficient quantity.
However, like any medical intervention, the long protocol has some disadvantages:
- a woman has to take hormonal medications for a longer period of time, so at the preparatory stage an assessment of the functional activity of these organs is required;
- at the first stage of the protocol, the cyclic activity of the female body is completely blocked, that is, the patient is put into a short-term drug-induced menopause, so symptoms of estrogen deficiency may appear (headache, hot flashes, increased sweating, etc.);
- a long protocol uses large doses of tropic hormones, which can lead to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. This condition is manifested by the release of fluid from the vascular bed into the intercellular space. As a rule, in most cases, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is mild and responds well to drug therapy. According to statistics, only 1-4% of women with this complication require hospitalization.
At SM-Clinic, reproductive specialists carefully assess the gynecological and somatic status of the patient in order to minimize the risk of undesirable consequences and achieve the best therapeutic result.
We do the injections ourselves
Before you start injections, carefully read the storage conditions of the drugs. Some of them require storage at temperatures close to 0°C. Others can be stored at room temperature. Puregon Pen, Orgalutran, Pregnil are stored at temperatures from 3°C to 25–30°C. Freezing of drugs, as well as direct sunlight, can change their activity.
How to give injections?
Using the Puregon Pen injector pen, patients inject themselves themselves, without additional assistance from medical personnel. It's simple, and most importantly, convenient. If a woman uses drugs that are administered with a syringe, you can seek help either in the treatment room of the clinic, or in the clinic at your place of residence, or involve someone familiar with injection skills. Puregon or Orgalutran are administered subcutaneously, Pregnil - intramuscularly. Injections should be done at one time, for example, in the afternoon, and the environment should be as calm as possible. Drugs must be administered slowly. Each administered dose is of great importance, so errors during administration can significantly affect the outcome of the entire treatment. If you forget to administer the drug, do not administer a double dose to make up for the missed injection, but consult your doctor immediately. Some drugs, for example Pregnil, are available in powder form, with solvent ampoules attached separately. Read the instructions carefully. Drugs can only be dissolved using a sterile syringe. The substance dissolves instantly, without foreign impurities.
Monitoring
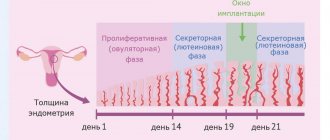
During stimulation of superovulation, ultrasound monitoring of the growth of ovarian follicles, as well as the maturation of the endometrium, is carried out. This is necessary to adjust the dose of administered drugs, which can be increased or decreased. It all depends on the condition of these organs. On the one hand, it is necessary to obtain a sufficient number of mature eggs, but on the other hand, excessive stimulation can lead to complications. A follicle with a diameter of 17–20 mm is considered mature, with a thickness of the uterine mucosa (endometrium) greater than 8 mm.
Ultrasound monitoring
Monitoring is done by your healthcare provider, usually on days 2–3 of your menstrual cycle. At the same time, stimulant drugs are prescribed. The next follicular growth study is repeated after approximately 5 days. Further studies are carried out more often, almost daily, until the follicles reach sizes close to ovulatory. The study is carried out with an ultrasound sensor, which is inserted into the vagina. This procedure is painless. Do it safely. To ensure sterility, a disposable condom is placed on the sensor. The thickness of the endometrium is assessed, as well as the number and diameter of follicles, and the doctor decides whether to change the dose of drugs. When certain criteria are reached, usually on the 10th–14th day of the cycle, a decision is made to end stimulation. After this, hCG drugs are prescribed, the exact time of their administration is reported, as well as the date of the upcoming puncture.
What should you do?
If you are scheduled for an ultrasound monitoring day, you should not do any injections in the morning without your doctor's advice. An ultrasound through the vagina is performed with an empty bladder, otherwise the doctor will not be able to see the ovaries on the monitor. You will have to undress as if for a gynecological examination.
Administration of hCG
hCG drugs (Pregnil) are administered for the final maturation of the egg. The doctor will tell you the exact time of administration of the drug, which usually occurs in the evening hours. It is very important to strictly observe the time of drug administration. The route of administration is intramuscular. The rules of administration are the same as those described earlier for intramuscular agents. Check the dose of the drug carefully, as the ampoule may contain 1,500, 5,000 IU (International Units). Sexual intercourse should be stopped. It is very important not to be late, to arrive at the puncture on time, 35–36 hours after the hCG injection. It is advisable to take a robe, slippers, nightgown or long T-shirt with you to the puncture, and bring socks. When you have a puncture, your spouse will need to be present.
Indications for a long protocol
As a rule, the long protocol is preferred in cases where short stimulation failed to obtain the required number of good quality eggs. However, there are also categories of women who are recommended to begin the ART program with long-term stimulation. We are talking about patients with the following diseases and conditions:
- uterine fibroids;
- endometrioid disease;
- poor egg quality;
- cystic formations of the ovaries;
- overweight and obesity;
- elevated levels of luteinizing hormone according to hormonal screening.
Depends on the characteristics of the clinical case, ovarian reserve and general level of health. The optimal ART program will be selected by a reproductologist after a detailed examination of the female body.
Puncture
Puncture of the ovarian follicles is performed to obtain eggs. During the puncture, the doctor, under ultrasound guidance, empties the follicles through the vagina using a needle connected to a vacuum device. As a rule, the puncture is performed in the morning, strictly on an empty stomach, under intravenous anesthesia. There is no reason to be afraid, this procedure is painless, quick, and the thin needle will not cause any serious damage.
Before puncture
You can’t eat anything the night before, or even drink anything after midnight. You can shave the hair around the vaginal opening. You cannot use decorative cosmetics. Immediately before the puncture, already at the IVF clinic, you need to empty your bladder and put on a clean shirt. If you are allergic to any medications, be sure to notify the anesthesiologist about this.
After the puncture
You will wake up in 5-10 minutes, and 40-60 minutes after the puncture you will be able to get up. The doctor will tell you about the results of the puncture, how many eggs were obtained, and then determine the date of the next visit for embryo transfer. The next procedure is embryo implantation; your doctor will tell you on what day to schedule it. The doctor will also give you prescriptions for the next two weeks aimed at maintaining sufficient levels of pregnancy hormones after embryo transfer (hCG injections or progesterone preparations). It is better to have someone accompany you after the puncture. After the puncture, it is strictly forbidden to drive. If you feel pain in the lower abdomen, you can take a painkiller tablet after consulting your doctor. You can only obtain information about the quality of eggs, sperm, success of fertilization, fragmentation, and number of embryos from your attending physician.
When to carry out
In each specific situation, the doctor determines individually on which day of the cycle it is necessary to do folliculometry. But most often this is a minimum of 4 - 5 studies per cycle, and sometimes more. On average, the graph might look like this:
It is better to do the first study immediately after the end of menstruation, approximately on the fifth to seventh day. This will give the doctor a general idea of the structure and possible disorders in the reproductive system. At this time, there may already be a “suspicion” of one or more follicles ready to grow.
The second study must be carried out 3 - 5 days from the first (8 - 10 days), it all depends on the result of the previous one. On the 8th - 10th day of the cycle, it becomes finally clear whether there will be ovulation this month. The dominant follicle already reaches 10 - 12 mm, which clearly distinguishes it from the total mass of ovarian tissue. If the doctor does not find anything similar these days, the study can be completed in this cycle. The exception is situations when a girl has very long breaks between periods, then an ultrasound scan can be performed every 5 to 7 days before the start of her critical days.
USEFUL INFORMATION: Why the dominant follicle does not mature
The third study should fall on ovulation or the closest time before/after it - 12 - 16 days of the menstrual cycle. Special tests help doctors and women in this matter. By doing them regularly, you can choose the most suitable day. Ovulation tests are easy to perform and available to everyone. Based on the results of the ultrasound at this time, the doctor makes recommendations, for example, for collecting eggs for IVF or simply for an active sex life.
The fourth study is ordered based on previous data. This can be either the next day or a day or three after the previous ultrasound, usually on days 14–21 of the menstrual cycle. This is necessary to track ovulation if it has not occurred previously, or to assess the formation of the corpus luteum.
The last study must be done on days 21 - 26. Later it is carried out when a woman has a long cycle. For example, folliculometry with a 45-day cycle will be carried out on days 36 - 39
Around this time, implantation of the fertilized egg into the endometrium occurs, so it is important to evaluate all the parameters of this inner layer of the uterus. The area of the corpus luteum is also examined and the indicators are compared.
Artificial insemination
When the day of the puncture arrives, the spouse must donate sperm to the laboratory assistant. The sperm is cleaned of excess plasma and prepared for fertilization, checking the quantity, quality, and motility of sperm. The follicular fluid filled with eggs obtained after puncture of the ovaries is examined under a microscope, the eggs are found, they are selected and washed. Each egg is carefully placed in a separate well in a special cup filled with a nutrient medium. Cups containing sperm are always signed immediately. Then, if there are enough sperm and they are motile, some of the sperm is added to the eggs, after which the incubator is left for approximately 12 hours. The sperm themselves must swim to the eggs and fertilize them. Then they check whether fertilization has occurred. Fertilized eggs, or rather embryos, continue to be cultivated for 2 to 5 days.
ICSI
If there are too few sperm, then the ICSI procedure is performed, that is, the injection of a single sperm using a microneedle. Under the control of a microscope, using micromanipulators, the embryologist selects only high-quality sperm and injects them into the egg.
Embryo transfer
When the embryo will be implanted and on what day to schedule the embryo transfer procedure is determined by the doctor. As a rule, this occurs 2–5 days after the puncture. Embryos can be transferred both at the stage of several cells - blastomeres, and at a later stage - blastocysts. The embryo transfer procedure is painless, although slight discomfort is sometimes possible. Speculums are inserted into the vagina, and a flexible catheter is inserted into the cervical canal. Embryos are transferred through this catheter, the number of which is determined by the doctor. It is usually recommended to transfer two embryos, since transferring a larger number is undesirable due to the risk of developing multiple pregnancies. After embryo transfer, the remaining high-quality embryos can be frozen so that they can be used in subsequent attempts.
What should you do when transferring embryos?
During insertion of the catheter, try to relax as much as possible without straining your lower abdomen. Try to be positive. After embryo transfer, you can remain horizontal for some time. It is better to return home with an escort. At home you should also relax and try to distract yourself from obsessive worries.
What to do next?
At this stage - after embryo transfer - the program ends. If there are no complications, the embryo has settled in the uterus and is developing successfully, then you will not be hospitalized. But if you wish, after embryo transfer, you can apply for a hospital stay. The doctor gives clear recommendations on further supportive hormonal treatment, which must be strictly followed. You may be prescribed drugs for hormonal support of pregnancy - progesterone or hCG. Try to spare yourself physically and psychologically in the first weeks after embryo transfer. Try to drink more. After embryo transfer, it is advisable to measure body weight, monitor urination, abdominal volume, and pulse rate. If you have any concerns, please contact the clinic immediately. There you will be issued a sick leave certificate for 10–14 days. If pregnancy occurs after embryo transfer, sick leave can be issued by the antenatal clinic at the place of residence.
Pregnancy - yes or no?
Whether pregnancy has occurred or not will be known no earlier than the 14th day after embryo transfer. Do not try to independently determine pregnancy using tests until this moment, since at this stage the embryo cannot yet produce sufficient amounts of the hCG hormone. The answer may also be incorrect due to the use of certain hormonal medications. In addition, rapid test strips often give false results. Two weeks after embryo transfer, go for a blood test for the beta subunit of hCG, which is an indicator of pregnancy. If the test result is positive, it means pregnancy has occurred. Almost every one and a half to two days the amount of hCG will double. Pregnancy after embryo transfer, determined by hCG, is called “biochemical pregnancy”. She still needs ultrasound confirmation, which allows you to see the fertilized egg only starting from the 3rd week after embryo transfer. Therefore, after embryo transfer, you will need to come for an ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy. If pregnancy occurs, you should be under constant supervision of obstetricians and gynecologists, since after embryo transfer you still have to carry a pregnancy that was achieved in such a difficult way. If you experience pain, bleeding or other worrying symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. The appearance of menstruation, a negative test result, and the absence of a fertilized egg according to ultrasound data indicate that pregnancy did not occur after embryo transfer. However, a negative result does not mean that the IVF method was ineffective. Subsequent attempts may be successful. As already mentioned, the probability of pregnancy after embryo transfer per attempt ranges from 20 to 30%, and with each subsequent attempt, the total chances of becoming pregnant increase over the course of a year of treatment to 90%. You can leave an interval of about 2 months between attempts. If you are unable to visit the center to diagnose pregnancy, then determination of hCG in the blood after embryo transfer and ultrasound can be carried out in clinics at your place of residence. But in any case, please inform your doctor at the IVF center about the diagnostic results and discuss further actions.
When to test folliculogenesis
You need to undergo an ultrasound examination on special days. Usually one ultrasound examination of the follicle is not enough (normally the number of sessions should be about 3). You also need to remember that the menstrual cycle lasts differently for different women. Depending on the type of menstrual cycle, an ultrasound examination is carried out as follows:
- Regular standard cycle. Typically, female ovulation lasts 28 days (the first day of the last menstruation is considered the start of ovulation). In this case, the first ultrasound examination should be performed 10 days after the end of ovulation. Additional sessions can be performed on days 15 and 20 after the onset of ovulation.
- Regular non-standard cycle. For some women, ovulation lasts shorter or longer. In such cases, an ultrasound examination should be performed 5 days before the start of menstruation. All additional sessions are prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis.
- Irregular non-standard cycle. For some women, menstruation occurs irregularly, and its duration can be 28, 23 or even 35 days. In this case, folliculogenesis should be examined 5 days after the end of menstruation. All additional sessions are prescribed by the doctor on an individual basis.
Possible complications
Ovarian hyperstimulation
As a result of stimulation of the ovaries after puncture, many so-called corpora lutea are formed at the site of the follicles. Some women do not tolerate excess hormones produced by the corpus luteum. In approximately 10% of cases, a mild form of hyperstimulation syndrome develops. This is indicated by pain in the lower abdomen, nausea, and abdominal enlargement. In more serious cases, weakness, decreased urine output, and severe bloating are observed. In rare, severe forms, breathing may become difficult and blood pressure may drop. Treatment for hyperstimulation syndrome usually involves drinking plenty of fluids and taking special medications, which can sometimes be administered intravenously. For mild forms of hyperstimulation, you can stay at home, but be sure to keep your doctor informed of your condition. More severe disease requires hospitalization.
Multiple pregnancy
To increase the likelihood of pregnancy using the IVF method, several embryos (no more than three) are usually transferred into a woman's uterus. Sometimes, after embryo transfer, this can lead to the development of multiple pregnancies. If more than two fetuses develop in the uterus, then carrying such a pregnancy can be quite difficult. There are methods to stop the development of one embryo without affecting the others. This operation is called fetal reduction and is performed under ultrasound guidance. Usually, after embryo transfer, two embryos are left. The likelihood of successfully carrying a pregnancy to term after embryo reduction is higher than if you leave triplets.
Ectopic pregnancy
If, after embryo transfer, weakness, dizziness, early signs of pregnancy, vague or sharp pain appear, then perhaps this is an ectopic pregnancy, in which the fetus develops not in the uterus, but outside it. Seek immediate medical attention as this condition is life-threatening as a ruptured pipe can cause severe bleeding. Ectopic pregnancy is usually treated with gentle laparoscopic surgery. If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, contact your doctor immediately. Write down the clinic's phone number, as well as the doctor's name. Also find out emergency phone numbers. By following all the doctor’s recommendations, you will reduce the risk of complications and at the same time the chances of a happy conception.