Pollakiuria in a child can be either a natural phenomenon or a symptom of hormonal imbalance or pathological abnormalities in the urinary system. Frequent urination in children during the day is not a reason to panic, but it is also not a manifestation of the body’s activity that can be ignored. Parents often show their child to the doctor belatedly, when treating an already progressive disease is more difficult and longer.
Frequent urination in children during the day is not a reason to panic, but it is also not a manifestation of the body’s activity that can be ignored.
Norms of urination in children
Diuresis (amount of urine) depends on the age of the child. The formation of the urinary system is completed by the age of 14-15 years. Diuresis rates for girls and boys of the same age are somewhat different from each other.
The frequency of daytime urination in children of different age groups is as follows:
- a newborn urinates 4-5 times in the first week of his life;
- In an infant up to six months, there are much more acts of urination: up to 20-25 times;
- a one-year-old child already has them 15 times;
- at 2-3 years the bladder is emptied even less frequently: up to 10 times;
- in children from 3 to 6 years old - approximately 8 times;
- from 6 to 9 years and older - no more than 5-6 times.
Symptoms of problematic urination
A serious illness can be suspected if the following symptoms are present, which usually accompany infrequent urination in such cases:
- the urine stream is thin and has low pressure;
- urine is released in drops;
- this process becomes possible only with some specific, specific position of the body;
- burning, soreness;
- The urge to empty the bladder is felt, but is accompanied by pain and a feeling of strong pressure.
If such problems arise, it is recommended to immediately contact a pediatrician, who will be able to redirect parents to a more specialized specialist or independently identify and treat the underlying disease.
Why does a child have frequent urination?
The need for frequent bladder emptying can be caused by 2 reasons:
- influence of physiological factors;
- the presence of pathological disorders in the body.
If your baby doesn't get a lot of fluids before going to bed, he'll sleep well at night.
In the first case, the release of urine does not cause pain to the child. If his body doesn't get a lot of fluids before going to bed, he sleeps well at night and has a normal temperature. Sometimes frequent urination is a consequence of severe overstimulation. As soon as the provoking factors cease to affect children, the number of visits to the toilet becomes normal.
In the second case, children not only urinate frequently, but also experience pain when doing so. In addition, urine may flow out with difficulty and in small portions.
Often there is a painful, frequent urge to empty the bladder, which turns out to be false.
Physiological pollakiuria
Repeated daytime urination without pain, false urges and other signs of pathology can occur under the influence of the following factors:
- excess amount of water or other liquids entering the body;
- severe hypothermia;
- emotional stress;
- increased physical activity;
- treatment of the child with diuretics.
Small deviations from normal diuresis parameters associated with physiological processes are acceptable. For example, if yesterday a 7-year-old child urinated 5 times a day, and today – 8-9 times. It is necessary to check whether external factors or diet have changed. Daytime urination also progresses to nighttime urination, when the child drinks a lot of liquid before bed. Acts of urination also become more frequent if children eat large quantities of vegetables, fruits or berries that have a diuretic effect:
- lingonberries;
- cranberries;
- cherries;
- watermelon;
- melon;
- bananas;
- carrot;
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes, etc.
Pathological causes
Parents should consult a doctor if frequent urination in a child aged 4 or 5 years is accompanied by alarming symptoms.
If your child's urination is accompanied by alarming symptoms, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Pathological signs in older children, 7 or 8 years old, should be of even greater concern:
- pain in the lower abdomen or lumbar region, pain, false urges, which is a sign of cystitis;
- small portions of urine, typical for colds and neuroses;
- chills, high temperature, sweating, characteristic of kidney disease;
- swelling or bags under the eyes that appear with pyelonephritis;
- severe thirst or frequent urination at night, which occurs with diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus;
- a strong odor of urine, cloudiness, and the appearance of traces of blood, which may indicate the presence of tumors.
In some pathologies, urine leakage is not accompanied by pain or stinging. Among them:
- ARVI;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, neuroses;
- brain injury or tumor;
- small bladder volume, etc.
With a brain injury, urine leakage is not accompanied by pain or stinging.
What is physiological pollakiuria?
The causes of frequent urination may be harmless and not related to illness. In this case, physiological pollakiuria is usually meant. Its development is due to the following factors.
- Drinking large amounts of liquid. When a child drinks a lot, the urge to go to the toilet becomes more frequent. Parents should pay attention to the reasons for increased fluid intake. It’s one thing if a child in the family is accustomed to drinking mineral water every day or feels thirsty in hot weather, or after physical activity. If your baby constantly asks for water and pees a lot for no reason, this may indicate a disease such as diabetes.
- Taking medications with a pronounced diuretic effect. These include diuretics, antiemetics and antihistamines.
- Hypothermia. Frequent urination in a child without pain is accompanied by a reflex spasm of the kidney vessels. After warming, pollakiuria stops.
- Eating foods that have a diuretic effect (lingonberries, watermelon, cucumbers, green tea). Most of them contain a large amount of water, so the number of trips to the toilet increases.
- Frequent urination in a 4-year-old child is possible due to stress and overexcitement. Against their background, adrenaline is released in the body, which affects the excitability of the bladder and the excretion of the fluid itself. Therefore, the child often visits the toilet, but urinates in small portions. This is a temporary condition that goes away on its own.
Physiological pollakiuria is completely safe and does not require specific treatment. Urination returns to normal after the provoking factor is eliminated.
Parents are not always able to independently determine the cause of such a disorder. In some cases, frequent urination in a child without pain is a symptom of a serious illness. These may be psychosomatic disorders, pathologies of the endocrine and nervous systems. The disorder is usually accompanied by fever, excessive sweating and refusal to eat. Let's look at the main diseases that cause frequent urination in more detail.
- Your child suddenly begins to urinate every 10 to 30 minutes, and the total frequency of urination per day reaches 30 to 40 micturitions per day.
- Your child produces very little urine per urination.
- The child's urination is painless.
- Your child does not wet his panties or pee in his pants during the day.
- Your child does not drink excessive amounts of liquid.
- Your child was already toilet trained and tidy when the illness began.
- Frequent urination does not bother the child during sleep (an important distinguishing feature)
Diagnostics
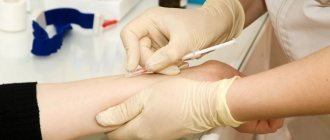
If a child's urination is very frequent and painful, it is necessary to do general, biochemical and bacteriological urine tests to determine its composition, the presence of sugar, protein, salts and infections.
A blood test with a large number of leukocytes and an increased ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) indicates an inflammatory process in the child’s body, especially if he complains that his stomach hurts.
Instrumental diagnostic methods help to make an accurate diagnosis if urination has become very frequent::
- Ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys, with the help of which the doctor receives information about their structure and size;
- radiography, which allows you to examine these organs in detail;
- cystoscopy and cystourethrography, which can help identify abnormal changes in the bladder;
- scintigraphy and renoangiography, which make it possible to assess renal function.
For diagnosis, an ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys is performed, with the help of which the doctor receives information about their structure and size.
What can parents do?
If urinary retention is not painful, you can try to provoke it with warm sitz baths and the sounds of flowing water.
If urination does not occur, you should call an ambulance to have the bladder catheterized.
If a child has urinary disorders, the first thing you need to pay attention to is nutrition and water consumption. Not every liquid is equal to water, so it is worth teaching your child to drink regular clean water regularly. Fatty and spicy foods, as well as fast carbohydrates and coffee, which tend to retain fluid in the body, should be excluded from the diet.
Urinary problems in children are not a cause for panic, but a cause for concern. Therefore, timely contact with a specialist is the main and first thing parents should do when such problems arise.
Author: Sukhorukova Anastasia Andreevna, pediatrician
Frequency of stool and urination in newborns
We recommend reading: What to do if your child feels pain, stinging and burning when urinating
source: mama66.ru
At different ages, children may experience rare urination, and parents begin to sound the alarm: what’s wrong with the baby? Most often, panic turns out to be completely in vain: a small organism can simply adapt to a new age regime, because it grows, its food becomes more solid - accordingly, the number of urinations per day becomes less.
But sometimes there are cases when the cause of this phenomenon is a serious pathology of the urinary system, which requires long-term treatment. Therefore, first of all, you need to find out what factor caused the decrease in urine output per day.
Treatment
If urination is painless, it is enough to eliminate the physiological factors that caused it, and the unpleasant phenomenon will disappear without treatment. But if the child urinates with pain, complex therapy will be required. Only cystitis and urethritis can be treated on an outpatient basis without complications. For all other diseases, hospitalization is necessary.
Complex therapy uses:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- traditional medicine.
Frequent urination is treated conservatively with the use of drugs that relax the bladder muscles, antibiotics, and sedatives. Their choice is determined by the etiology (origin) of pathological disorders in the urinary system or kidneys.
Surgical interventions are performed in extreme cases if stones or tumors are detected in children.
Surgical interventions are performed in extreme cases if stones or tumors are detected in children. Urination of an inflammatory nature responds well to physiotherapeutic treatment. Procedures are prescribed when the acute stage of the disease has passed.
Speed up recovery:
- electrophoresis;
- amplipulse;
- diadynamic currents;
- ultrasonic influence;
- laser radiation;
- hyperbaric oxygenation (saturation of the body with oxygen).
Who to contact
If your child is urinating more frequently, you should first go for an initial examination with a pediatrician. He will make a preliminary diagnosis and refer you for consultation to a urologist, nephrologist, neurologist or endocrinologist. After examination and diagnosis, the child will be treated by the doctor whose specialization covers the identified disease.
The pediatrician will make a preliminary diagnosis and refer you for consultation to a urologist, nephrologist, neurologist or endocrinologist.
Drugs
Their purpose depends on what causes frequent urination. The following groups of medications are used:
- anticholinergic drugs (Oxybutynin, Vesicare, Urotol, etc.) - for an overactive bladder;
- antispasmodics (Driptan), m-anticholinergics (Atropine, Ubretide), nootropics (Picamilon) - for a lazy bladder;
- uroseptics (Canephron N), antibiotics (Amoxiclav, Sumamed, Monural) - if urination is caused by inflammatory processes;
- sedatives, nootropics, antidepressants (Pantogam, Picamilon, Melipramin) - for neuroses;
- hormonal drugs (Insulin, Minirin, Prednisolone), cytostatics (Chlorobutin, Leukeran, etc.) - for diabetes, glomerulonephritis, enuresis (urinary incontinence).
An experienced physician may prescribe anticholinergic medications for your child. For example, Vesicare.
Folk remedies
Popular recipes to help normalize urination:
- Pour 1 tsp with a glass of boiling water. birch buds, leave for 2-3 hours. Give your child half a glass 3 times a day before meals.
- Grind thin cherry stems, brew and drink as tea. Alternate with dried corn silk.
- Take 4-5 tbsp. l. dry crushed mint, pour 1.5 liters of boiling water, boil for 8-10 minutes. Drink a glass of decoction before meals 3 times a day.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you experience abnormalities in the process of urination (little urine and rare urination), even if this situation is not accompanied by additional alarming symptoms, you should still contact a urologist and undergo a diagnostic procedure.
The examination will determine the cause and nature of the pathology related to the problem, explain why infrequent urination occurred, and the doctor will be able to determine the optimal treatment path.
Diagnosis in our women's and men's health clinic is carried out comprehensively.
The first and mandatory stage of diagnosis is a medical appointment, which involves a conversation with the patient and a physical examination. During communication with the patient, the doctor finds out how long the symptom has been onset, the presence of additional pathologies, in particular, chronic diseases of the genitourinary organs, what operations the patient has undergone and what medications he has taken recently.
The further diagnostic process includes a number of laboratory and instrumental methods for examining the patient:
- conducting a general clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- bacteriological examination of smears from the genitourinary system;
- ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system;
- X-ray of the pelvic and abdominal organs (general and excretory contrast urography).
If necessary, additional methods can also be used in the form of biochemical and hormonal analyzes of relevant biological media, as well as instrumental research methods (tomography, urocystoscopy, MRI and others).
In our center, diagnostics are performed using the latest generation equipment, and the examination results are guaranteed to be accurate.
All doctors undergo strict selection. They are professionals, polite and attentive to their patients.
The results of the treatment are felt after the first visit. We guarantee you a solution to any problems
We carry out diagnostics using modern European devices. Diagnostic reliability - 99%
Our doctors treat everyone with care and understanding. Appointment with a doctor is completely confidential
Complications and consequences
The presence of problems with urination often leads to the development of pyelonephritis, especially with anatomical defects of the urinary tract or kidneys.
Another serious complication is reflux (reflux of urine from the bladder into the ureter). Urination accompanied by pain is a manifestation of an infectious disease of the genitourinary tract.
Urination accompanied by pain is a manifestation of an infectious disease of the genitourinary tract.
Partial necrosis of kidney tissue occurs in 20% of children who were not treated, and only in 1% of those who were treated. The death of the cells of this organ of the urinary system leads to its chronic failure.
General principles of therapy
In cases where a child urinates little, treatment depends on the cause of the disorder. Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the factors that caused the pathology.
If the cause of rare urination is bladder disease, the following methods are used:
- sitz baths. Initially, the water temperature should be 26 degrees. It should be gradually increased to 30 degrees. A sitz bath can be done for 15 minutes once a day;
- often during inflammatory processes, soothing compresses are prescribed to the area where the bladder is located;
- for rare urination, a therapeutic diet is also important. It is necessary to feed the child food with a low salt content. You also need to give your baby plenty of fluids to drink;
- if rare urination is accompanied by pain and discomfort, the doctor may prescribe douching;
- in severe cases, a catheter is used to remove urine.
If these methods of therapy are ineffective, and the child’s well-being does not improve, then surgical intervention may be required.
To confirm the need for surgery, the patient needs to undergo an examination, namely, take all tests and have an ultrasound.
If no pathologies from the urinary system are detected, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- The baby should be allowed to drink as much as possible, especially in the hot season and during active physical activity;
- exclude salty foods from the diet;
Only a pediatric urologist should treat diseases of the urinary system. Timely contact with a specialist will prevent the development of complications and the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Prevention
To prevent urination problems in a child, doctors advise:
- Extend breastfeeding as much as possible to strengthen the baby’s immunity;
- dress the child according to the weather, so that the clothes protect him from both overheating and hypothermia;
- do not allow him to sit on wet ground, cold benches, stones, steps, etc.;
- Periodically monitor the frequency of urination.
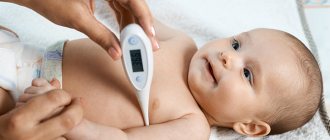
Regular examinations by a pediatrician are important, even if the child appears healthy. Children under one year of age require a monthly medical examination. A child aged 1 and 2 years should be taken for examination quarterly, and over 3 years old – every six months.
Prevention of urinary retention
There are no targeted measures to prevent pathology.
A healthy and active lifestyle, proper nutrition, and avoidance of injuries will help you avoid the disorder. Monitor your body's water balance; in case of a cold or other illness accompanied by fever, drink more fluids.
If a symptom first appears, contact a specialist, do not self-medicate! Call the phone number listed on our website and make an appointment. Our urologists will definitely help you!
Symptoms of genitourinary diseases
Having received the results of examinations in the presence of frequent urges and a high temperature that lasts for several days, the specialist diagnoses one of the diseases:
- processes with inflammation in the bladder cavity, cystitis;
- inflammatory activity in the renal pelvis, pyelonephritis;
- inflammation of the surfaces of the urethral canal, urethritis;
- inflammatory activity in the patient's prostate, prostatitis.
Symptoms of cystitis
The inflammatory process in the bladder is called cystitis. It is accompanied by the most striking symptoms in the form of high fever, a sharp and sudden urge to urinate, as well as pollakiuria. This condition is characterized by acute pain, especially in the later stages of the disease, when the walls of the organ begin to shrink.
More on the topic: What can cause urine to become transparent?
Symptoms of urethritis
With urethritis, inflammation affects the cavity of the urethra and manifests itself in a late stage with severe pain during deurination. In addition, the patient experiences frequent urges (pollakiuria) to defecate, high body temperature, and discharge of blood clots or pink sediment in the urine. Pain when urinating in men occurs when surfaces are damaged due to stones passing through it or when there is inflammation on the walls of the canal.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis
With inflammation in the pelvis areas of the renal system, the symptoms resemble cystitis and urethritis, but in addition to high fever and discomfort during deurination, the patient notes an unusual color of urine and an unusually small amount excreted at one time.
Symptoms of prostatitis
With prostatitis, the tissue in the prostate gland becomes inflamed. This pathology most often affects men over 40 years of age. The entire urinary system is affected, resulting in difficulty and pain when urinating.
Painful and frequent urge (pollakiuria) to defecate is accompanied by problems with pushing the stream through the urethral canal, sometimes even acute urinary retention is possible. The pain affects the lower back, genitals and intestines, as well as all organs in the pelvis. These are the most striking signs of prostatitis, as well as pain, problems with bowel movements, high temperature and the presence of fluid discharge from the urethral canal. All this indicates possible inflammation.
In some cases, the combination of high fever and pain when urinating may be due to other factors of different etiologies, but only a specialist can determine the cause and prescribe effective treatment. Of all the doctors, men need to turn to a urologist as a specialized specialist to solve their problems.
The daily amount of urine during pregnancy is normal
In order to draw conclusions about possible violations, you need to have a good idea of what is called normal, in this case, the standard volume of urination. Medical practice considers this standard to be 1500 ml of urine per day. This volume will depend on the amount of liquid you drink per day, as well as on a number of other factors. Approximately ¾ of what you drink can be excreted in the urine; if this ratio is significantly less, then we are talking about urinary retention during pregnancy.
If there is too much urine, more than two liters per day, this can also be caused by natural reasons: in the second half of pregnancy, the bladder feels the pressure of the growing uterus. The second probable cause is inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs. Finally, we can talk about polyuria - exceeding the daily norm, or even urinary incontinence during pregnancy. It is caused by a lack of protein foods, as well as diseases such as diabetes mellitus, nutritional dystrophy, renal failure, epilepsy, and a number of diagnoses associated with dysfunction of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
How to treat pollakiuria at elevated temperatures?
Regardless of the type of reason that provoked the discomfort and difficulty with urination, in order to combat elevated temperature due to frequent visits to the toilet, it is necessary to undergo a full course of treatment for the disease. For urethritis and cystitis, the attending physician prescribes antibiotics, usually broad-spectrum.
If it is possible to identify the pathogen, then the active substance of the drugs is directed specifically against such bacteria. Antibiotics can relieve the main symptoms of the disease. The doctor also prescribes antispasmodics and analgesics, antipyretic drugs and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as immunomodulators.
Treatment of cystitis and urethritis
If a patient is diagnosed with urethritis or cystitis, it is usually enough to normalize the urination rhythm and eliminate signs of the inflammatory process so that the patient’s body temperature drops to normal levels. If the prescribed medication regimen does not bring the expected result, the doctor prescribes washing the urethra or bladder with antiseptic solutions. This helps to destroy pathogenic microflora inside the organs and relieve inflammation as quickly as possible.
The patient can help himself by taking enough water, about 3 liters per day. It is also important to exclude sour, spicy and salty foods, choose a complex preparation with vitamins, take herbal diuretics and other herbal remedies that can quickly expel harmful bacteria from the body. Since urethritis and cystitis most often occur as a background to other diseases, sometimes transmitted through sexual contact, it is also necessary to treat concomitant diseases.
Treatment of pyelonephritis
With pyelonephritis, especially in its acute form, most often there is an elevated temperature with frequent urges; treatment requires antibacterial agents and antibiotics that relieve inflammatory processes in the kidneys and prevent destructive lesions and the release of pus into the organ. Experts prescribe comprehensive therapy with medications that increase the body’s immune defense.
More on the topic: Methods of treating tuberculosis of the genitourinary system
When the disease becomes chronic, it is necessary to use surgical interventions that can eliminate problems with the outflow of urine. With any treatment regimen, first of all, the inflammatory process is relieved and urination is normalized; against the background of such an improvement in the condition, the temperature drops to normal levels on its own.
Treatment of prostatitis
For prostatitis in men, to treat troubling symptoms, it is necessary to restore and normalize the functioning of the genitourinary system. To do this, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics, antispasmodics, agents that reduce fever and inflammation, as well as analgesics. The patient is prescribed additional physiotherapeutic treatment and prostate massage. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is not excluded.
General recommendations for treatment
Frequent urination in men is treated conservatively and involves normalizing the diet, from which all pickled, canned, salty, spicy and fried foods should be removed, alcohol and tobacco should be limited. The patient should increase physical activity and avoid physical inactivity.
It is necessary to treat concomitant diseases that aggravate the situation:
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | colds and others accompanied by inflammation |
| 2 | long-term stressful situations |
| 3 | passive lifestyle |
| 4 | prolonged regular hypothermia |
Once proper bladder emptying is normalized, the patient's temperature will decrease with treatment.
Let's go to the doctor
So, you suspect something is wrong when you notice any of the listed symptoms in your child. The first step is to consult a pediatrician. After listening to complaints, finding out the necessary details, examining the child, the pediatrician will make a decision - either conduct an initial examination in a clinic, or immediately refer the mother and baby to the appropriate specialist: nephrologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, urologist, gynecologist.
What examinations can be ordered?
General urine analysis. The glass jar for analysis should be washed with a brush in the evening and sterilized by steam. In addition, pharmacies sell sterile plastic containers for urine, which greatly simplifies the process of finding a suitable jar and sterilizing it. If you are going to donate urine at a commercial center, you can go in advance and ask for such a container. The children's potty should also be washed clean and rinsed with boiling water (this can be done in the morning). It is advisable to wash the baby's external genitalia with soapy water.
An older child can be asked to urinate a little (in the potty or directly into the bath), and use a jar for the rest of the urine.
Morning urine is needed for analysis. There is no point in collecting it in the evening, since storage (even in the refrigerator) distorts the results of the study. In the resulting urine test, the doctor will be able to evaluate indicators such as the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes (blood cells). An increase in the number of leukocytes (leukocyturia) may be a sign of inflammatory diseases such as pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis; a large number of red blood cells (hematuria) - with glomerulonephritis, the release of large crystals of salts or stones and some other diseases. The presence of protein in the urine may indicate glomerulonephritis, etc.
Urine culture. To detect bacteriuria (the presence of bacteria in the urine), the doctor may order a urine culture, i.e. a small portion of urine is placed on a nutrient medium (special broth). If there are bacteria in the urine, after some time the growth of their colonies on the nutrient medium is noticeable. Usually, before this test, the mother is given a special sterile container or tube for urine. After collection, urine should not be stored; if possible, the container should be immediately taken to the laboratory (short-term storage in the refrigerator is acceptable, but no more than 2 hours).
If a certain number of microbes are found in the urine, the laboratory will conduct an antibiotic sensitivity test, which can serve as a guide when prescribing antibacterial agents.
Collection of daily urine for protein, glucose or salts. If a child urinates in a potty, you will not have any problems with collecting daily urine (except for the night portion, especially if the baby sleeps in a diaper). Each portion of urine should be poured into a large jar. Of course, all the urine will not be needed in the laboratory; they will measure the daily volume of urine excreted and take a small part.
A study of the daily amount of protein is carried out for glomerulonephritis, congenital and hereditary kidney diseases. An increase in the amount of protein in daily urine can also be observed in any disease accompanied by fever (body temperature above 38°C), with increased kidney mobility, as well as in some children after intense physical activity.
An increase in the amount of glucose (or, more simply, sugar) in daily urine can be a sign of diabetes mellitus and hereditary kidney diseases.
If the daily excretion of salts (oxalates, urates, phosphates) exceeds certain figures, then they speak of crystalluria. Against the background of increased salt secretion, other diseases (for example, cystitis) may occur.
Rhythm of spontaneous urination. Not every mother will be able to give a more or less accurate answer to the question “how many times a day does a child urinate,” and it is completely unrealistic to estimate the volume of each portion by eye. Therefore, at home (with a normal drinking regimen), you should count the number of urinations per day, and also measure the volume of each portion of urine (not approximately, but using a measuring cup). It is advisable to conduct the study within two to three days. On a piece of paper prepared in advance, you will record the time of urination and the volume of urine excreted. There is no need to collect urine; you will only bring to the doctor a piece of paper with notes that can be used to identify frequent urination in small portions or rare urination in large portions. In the first case, we are talking about such a pathological condition as a hyper-reflex bladder (having accumulated a very small amount of urine, the bladder gives a signal about the need to urinate), in the second - about a hypo-reflex (even when a large amount of urine accumulates in the bladder, the urge to urinate is weak or absent). The reasons may be different: impaired regulation of urination on the part of the nervous system, insufficient development (maturation) of the structures responsible for the act of urination, pathology in the bladder itself.
Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder (ultrasound). This study, if possible, is best carried out as planned, that is, by applying on your own, even without any suspicious symptoms indicating diseases of the urinary system. An ultrasound will show whether there are any malformations of the kidneys (such as doubling of the kidney, reduction of the kidney - hypoplasia, absence of the kidney - aplasia, low-lying kidney - nephroptosis, etc.), signs of inflammatory diseases, the presence of stones or large crystals, urinary disorders .
Bring a diaper with you (although some institutions use their own). You can also use it to wipe off the gel from the baby’s skin at the end of the study.
Do I need to come for an ultrasound examination with a full bladder? If the baby can, then yes. Then the specialist will examine the full bladder, then send the child to urinate and repeat the examination of the bladder to find out if there is residual urine (the part of the urine that remains in the bladder after urination with pathology).
It is better to carry out dynamic observation by the same specialist using the same device. And one more thing: if you were sent for an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder with suspected pathology, try to get examined at a specialized nephrology center.
Advertising
X-ray examination. Intravenous (excretory) urography. Despite the widespread use of ultrasound devices, X-ray examination has not lost its relevance. This method allows you to evaluate the location and structure of the kidneys and urinary tract, the preservation of kidney function, the process of urination, possible formations or stones. The child is given an intravenous contrast agent. Since the kidneys are involved in the process of purifying the blood from foreign substances, after about 5 minutes the contrast agent appears in the kidneys and then, as part of the urine, “descends” through the ureters into the bladder. At this time, several X-ray images are taken.
Of course, everything related to injections, especially intravenous ones, is very unpleasant for the child, so it is advisable to have a conversation with him at home about the upcoming examination.
Before this study, preparation is required. Since the intestines, which are loaded with gases and feces, can complicate the assessment of x-rays, the child is prescribed a cleansing enema 12 hours and 1-2 hours before the examination (children under the age of 3-5 years can limit themselves to only one - 12 hours before the examination). 2-3 days before the test, reduce foods such as raw vegetables, juices, brown bread, and milk in the child’s diet. On the day of the study, children under the age of one year are allowed to be given breast milk or formula (1 - 1.5 hours before), older ones - a bun with tea without sugar.
In addition to a negative psychological reaction to the study, others are possible (in approximately 4-5% of children): nausea, vomiting, decreased blood pressure, facial swelling, chills. Severe reactions occur quite rarely (the X-ray room must have the necessary medications for this case).
Victory cystourethrography. This method is also based on the introduction of a contrast agent, but through the urethra into the bladder.
Immediately before the examination, the child is asked to urinate, then a contrast agent is injected into the bladder through a catheter (thin tube) (before the urge to urinate) and two photographs are taken (before and at the time of urination). Some clinics limit themselves to only one image at the time of urination, which reduces radiation exposure, but practically does not reduce the information content of the study.
This method will help in identifying abnormalities in the development of the bladder and urethra, the presence of vesicoureteral reflux and its severity.
Radioisotope research. Renoangiography. The research technique consists of intravenous administration of a radiodiagnostic substance and recording the passage of this compound through the renal vascular system. The curve obtained as a result of the study is called an indirect radioisotope renoangiogram. This method allows you to evaluate renal blood flow, kidney function, and the process of urination in the ureters. Compared to x-ray methods, the radiation exposure is minimal.
Dynamic and static scintigraphy (scanning) of the kidneys. The patient is intravenously injected with a radiodiagnostic drug, which causes radioactive radiation from the organ being examined, and special devices - gamma cameras or scanners graphically record it. The received data undergoes special processing on a computer and is displayed in the form of a static or dynamic image. The method allows you to evaluate the size, shape, location of the kidneys, as well as identify formations in the kidney (for example, cysts or tumors). The radiation dose is almost the same as during intravenous urography, that is, quite high. You don’t have to prepare in advance for radioisotope research methods, but some clinics recommend taking iodine supplements 3 days before the examination (to “protect” the thyroid gland).
Cystoscopy. Using an optical device (cystoscope) inserted through the urethra, the doctor examines the bladder from the inside to evaluate the mucous membrane, examine the openings (ostia) of the ureters and assess some other points (including the presence of stones, tumors, foreign bodies). Special preparation is usually not required, except in cases where the examination is carried out under general anesthesia (anesthesia) for boys and very young children.
Your child may need other tests. Do not be shy and always check with your doctor for what purpose and how exactly the necessary research is carried out.