What is the norm?
Phimosis in boys is considered physiological (age variant of the norm) if:
- 1Impaired opening of the head occurs during the first 16 years of life (congenital disorder).
- 2Phimosis is associated with congenital narrowing of the opening of the skin of the foreskin, adhesion of the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the skin flap with the head of the penis, short frenulum of the penis.
- 3There are no pathological conditions that could lead to the formation of phimosis (trauma, inflammation of the head of the penis).
- 4Phimosis in a child is not accompanied by complications such as infections of the head of the penis (balanitis, balanoposthitis), urination disorders and other complaints.
When the head of the penis opens with difficulty or does not open at all, we are talking about phimosis.
About three percent of adults of the stronger sex have encountered a condition that is characterized by the narrowness of the epidermal structures of the foreskin of the penis and has the medical name phimosis . We are talking specifically about adult men, since the vast majority of newborn boys are born with physiological phimosis of the foreskin, which resolves itself during the first years of the child’s life, without requiring the use of special therapeutic techniques.
If this disease manifests itself in adulthood, they speak of pathological phimosis , which most often implies the need for medical supervision.
Learn more about phimosis (symptoms, causes, treatment and cost)
When is phimosis a disease in a child?
Phimosis is considered pathological when a violation of skin abduction is combined with local symptoms (redness, inflammation of the head of the penis and the covering layer of skin, cicatricial deformation of the foreskin ring, slowdown of the stream during diuresis), and/or with symptoms of damage to the organs of the urinary excretory system (infections of the urethra, bladder ).
Until now, doctors often cannot accurately distinguish pathological phimosis from physiological one. Insufficient experience of the doctor, his inability to distinguish physiological phimosis, and explain important information about the disease to parents can lead to excessive anxiety in parents, which will lead to unnecessary and unnecessary repeat visits to the urologist.
To this day, the operation of circumcision (popularly known as circumcision) remains the gold standard in the treatment of pathological phimosis.
However, new treatment methods are emerging and developing, which can somewhat displace the usual surgical intervention. Most of the new techniques can achieve certain positive results with less trauma to the patient.
It is important to understand that physiological phimosis does not require surgical treatment and often goes away on its own with proper adherence to measures to prevent infectious and inflammatory lesions of the head of the penis and the skin above it.
Phimosis is the inability to retract the narrowed foreskin beyond the base of the head of the penis. The disease occurs quite often among boys under 16 years of age and accounts for a large proportion of parents' visits to a pediatrician.
As a rule, parents are alarmed and overly concerned about the inability to retract the skin from the head of their child's penis. Most of these requests end with a planned circumcision operation.
Analysis of medical records carried out in England and the West. Australia, indicated that the incidence of circumcision for medical reasons was seven times higher than the incidence of phimosis in children under the age of 15 years.
Considering the above facts, we can talk about a high frequency of unnecessary circumcision. The circumcision operation itself is not without side effects and can cause psychological trauma in the child.
To reduce the frequency of circumcision without sufficient grounds, it is necessary to learn to distinguish between physiological and pathological phimosis, to know about the availability of modern non-invasive techniques that require less cost and are accompanied by a lower likelihood of complications.
Do I need to open the head?
You should not do anything without studying the situation. In medicine, narrowing of the foreskin on the penis is called phimosis. However, in childhood, this is not a pathology. Confusion exists at the age up to which the phenomenon is considered normal - physiological. This happened due to the serious development of medicine. Science has made great strides forward and opinions have changed. Just two decades ago, doctors would have sounded the alarm and insisted on studying ways to open the head yourself.
Now mothers are being made to understand that nature approached the creation of men intelligently. They are protected. It is the foreskin, an instrument that protects an important organ from infection. In 99% of boys it opens naturally, without outside intervention. The discovery occurs purely individually; all you have to do is observe and prevent negative manifestations.
Why is the skin from the head of the penis not retracted in children?
The embryonic development of the penis begins in the seventh week of intrauterine life and is completely completed by the seventeenth week. The covering of the penis forms a fold that gives rise to the foreskin, which covers the head of the penis and performs protective functions (mechanical, immune protection), and an erogenous function [1].
The inner lining of the skin of the head is formed by mucous membrane, which is adjacent to the head and fixed to the lower surface of the head of the penis by a frenulum.
The foreskin (preputium) has pronounced innervation and is well supplied with blood. On its surface there are tactile receptors for point touches.
The circumcision operation is accompanied by the removal of most of the sensitive areas. Unlike the foreskin, the glans contains pressure receptors and does not have tactile receptors.
On the surface of the preputium and head there are glands that produce secretions (the secretion includes lysozyme, which has a bactericidal effect, cathepsin B, chymotrypsin, elastase, cytokines, pheromones - androsterone).
The secretion of the glands acts as a lubricant and protects tissues from infection. The skin of the foreskin contains Langerhans cells (tissue macrophages), which perform the functions of innate immunity.
Approximately 96 out of 100 boys are diagnosed with a violation of glans exposure at birth. In this case we are talking about physiological phimosis, which is associated with:
- 1A narrow ring of skin covering the head (prepuce).
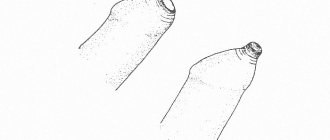
- 2Natural adhesion of the preputium and the head of the penis. From birth and during the first few years of life, the inner surface of the preputium is tightly adjacent to the head of the penis and cannot be retracted (abducted). With age, the balano-preputial plate (BPL in the figure) is reabsorbed, which makes it difficult to expose the head.
- 3Short frenulum of the penis.
Rice. 1 - Diagram of the formation of the foreskin. Source-https://circumcisiondecisionmaker.com/foreskin-facts/development/
Over time (from birth to 16-18 years), the mobility of the skin of the head gradually increases as a result of erections and keratinization of the epithelial lining. As a result of these physiological processes, the degree of exposure of the head of the penis increases.
So, when does the glans penis open in boys? For the most part, the opening occurs by the age of 12, but under the supervision of a urologist you can wait until 14-16 years.
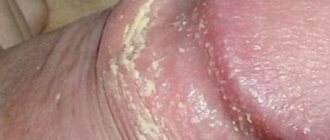
With physiological phimosis, the foreskin is not changed, has a normal color, the skin does not contain scar tissue (whitish stripes, spots), or signs of inflammation. The narrowing is determined at the very tip of the foreskin, and not along its entire length .
Rice. 2 – A – physiological phimosis, B – pathological phimosis. Source - Medscape
What is the danger of untimely opening?
If a boy’s head does not open at 2, 3, 4, 5 years old, then there is nothing to worry about yet. Due to male physiological characteristics, the foreskin can be completely retracted in the majority of such children. But in some cases this process is protracted. That is, the head does not open in a boy of 9, 10, 11, 12 years old. If this feature is not accompanied by inflammation, suppuration, or change in color of the genital organ, then there is also no cause for concern.
The process of urination should also not cause discomfort. Therefore, when the head of a boy’s penis should open is determined individually.
If a boy’s head does not open well, this condition is accompanied by painful urination and other unpleasant symptoms, a specialist will tell you what to do. Most often, this condition requires surgical intervention. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, this can lead to the following dangerous consequences:
- Balanoposthitis. This pathology is chronic infectious in nature. When treating balanoposthitis in a boy, it is extremely important to strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene. Effective antibacterial therapy is also carried out.
- Obstruction of the urethra. The narrowing of the foreskin prevents the normal excretion of urine. The process of urination causes severe pain and a burning sensation. In this condition, the child requires only surgical intervention. The boy's foreskin will open after the operation.
- Accumulation of urine and natural secretions under the foreskin. This usually occurs as a result of insufficient penile hygiene when the boy’s head does not open. The discharge turns into a thick, hard mass, which interferes with the normal development of the penis in the future.
When should parents contact a urologist?
- 1You should definitely visit a urologist once a year for regular follow-up, even if the child has no problems.
- 2The appearance of redness, swelling, inflammation, pain, bleeding in the area of the glans penis is an indication for consultation with a pediatric urologist.
- 3Consultation with a urologist is also indicated in the presence of cicatricial deformation of the skin above the head (see Figure 2), weakening of the child’s flow as a result of a narrowed foreskin, difficulty urinating, and recurrence of urinary tract infections.
- 4If, after removing the skin from the head, it is impossible to return it to its original place, the foreskin forms a tight ring that compresses the base of the head, you must urgently contact a urologist or surgeon!
- 5According to statistics, only 8-14.4% of requests from parents with complaints about problems with skin retraction from the head of the penis in a child are caused by pathological phimosis, requiring surgical intervention.
With pathological phimosis, an attempt to retract the skin is accompanied by the formation of a cone, with a narrowed, scarred part of the foreskin.
Risk factors for pathological phimosis are:
- Excessive efforts to remove the skin from the head with physiological phimosis lead to the formation of microcracks, infection of the skin and head, bleeding followed by scarring, the process becomes pathological.
- Failure to comply with hygienic prevention measures for infections, repeated balanitis (inflammation of the head of the penis), posthitis (inflammation of the foreskin) lead to the formation of cicatricial deformation of the skin of the head and the development of pathological phimosis.
- Diabetes mellitus leads to an increased likelihood of the addition of pathological bacterial flora due to increased glycemia in the blood and the appearance of glucose in the urine (sugar is a good nutrient medium for bacteria, promoting their proliferation).
- Pathological phimosis can develop as a result of xerotic balanitis obliterans. The exact cause of the disease has not been established. It is believed that the disease may be based on a combination of infectious, inflammatory, hormonal and autoimmune factors.
- Repeated catheterizations of the bladder can lead to the development of phimosis.
The presence of physiological phimosis in a child requires observation, but pathological phimosis is treated promptly.
The nature of the structure of the penis of boys
While in the mother's belly, the baby's foreskin is fused to the head. At birth, it is impossible to see what an open head looks like. There are statistics on the age at which phimosis goes away on its own:
- Up to 1 year - 50%.
- Up to 3 years - 90%.
- Seven years of age - 92%.
- By age 13 - 97%.
- At the age of 17 years - 99%.
There is no need to worry when the boy is healthy. It is important to contact a specialist if inflammation and other troubles appear. Often, undesirable consequences occur precisely because of illiterate doctors and parents. There is no hurry here.
Main symptoms
The incidence of the pathological form of phimosis is 0.4 per thousand boys per year; by the age of 15, 6 boys out of a thousand suffer from the pathological form of phimosis [1].
The data presented are significantly lower than the prevalence of physiological phimosis, the frequency of which is higher among young children and decreases with age.
Symptoms of physiological phimosis in a child:
- 1Inability to open the head of the penis.
- 2Swelling of the foreskin at the beginning of urination.
- 3In the physiological form of phimosis, there is no pain, difficulty urinating, dysuria, local signs of inflammation, or recurrent infections of the organs of the urine separation system.
- 4With careful retraction, wrinkles form on the skin of the foreskin, the skin itself is pink, without pathological changes (scar tissue, inflammation).
Symptoms of pathological phimosis in children:
- 1The boy is unable to open the head of the penis.
- 2 There is fibrous narrowing of the foreskin and scar tissue. The foreskin forms a kind of cone, a proboscis.
- 3 Pain is observed in the area of the head and foreskin.
- 4Pain may appear during an erection.
- 5Inflammatory changes are often observed in the area of the head and the skin covering it.
- 6Bleeding from cracks in the skin of the preputium.
- 7Impaired urine output. With severe phimosis, the stream during urination becomes sluggish.
- 8The appearance of blood in the urine (as a result of microcracks that form during urination, unchanged red blood cells enter the urine).
The degree of phimosis in children can vary greatly in severity. Depending on the degree of skin retraction from the surface of the head of the penis, phimosis is divided into 5 stages (degrees), which are discussed in detail in another article. Compare the two pictures below (photo source: Medscape.com).
Rice. 3 - Physiological phimosis in a child (Source - Medscape)
Rice. 4 - Pathological phimosis in a 3-year-old boy (Source - Medscape)
Symptoms and stages of the disease
The main manifestation of phimosis in men is the occurrence of difficulties in releasing the head of the penis or the absolute impossibility of stretching the foreskin. In this case, one should take into account the complex structure of the epidermal structures covering the body of the genital organ.
On the outside, the foreskin is represented by a skin fold, while its inner surface is lined with a mucous membrane, allowing the skin to slide freely relative to the surface of the head. With phimosis, the movement of the foreskin is limited or impossible at all. Experts distinguish four stages of this disease, the severity of which will determine the treatment strategy for phimosis.
- Phimosis I degree. The mildest degree of severity of the pathological process, in which exposure of the head of the penis in a calm state is carried out without effort and discomfort. Minor problems with the release of the head from the foreskin arise only during an erection, when an increase in the size of the penis is observed. This stage of phimosis usually does not cause significant discomfort to a man and requires treatment only if complications or concomitant diseases develop. Phimosis of the first degree is usually called relative;
- Phimosis II degree. The condition is characterized by difficulty in releasing the head of the penis, even in a relaxed state. During an erection, it is possible to expose only a small part of the head, which may be accompanied by pain of varying intensity. The second degree of phimosis is considered an indication for contacting a specialist;
- Phimosis III degree. This stage of the disease is accompanied by the inability to remove the head of the genital organ from the preputial cavity. Phimosis of the third degree, in the absence of timely treatment, can affect the sexual function of a man and can lead to the development of acute inflammatory and traumatic complications;
- Phimosis IV degree. The most complicated condition in which the inability to expose the head of the foreskin is accompanied by difficult painful urination and accumulation of seminal fluid in the preputial space.
Determining the severity of the disease is especially important when deciding how to treat phimosis.
Diagnostics
- 1The diagnosis of “phimosis” is established during examination and manual examination by the attending urologist [1].
- 2To diagnose phimosis, there is no need to resort to additional laboratory and instrumental studies.
- 3During the examination, the doctor collects information from the parents about the presence of concomitant pathology in the child, checks from the outpatient card and from the parents whether inflammatory processes in this area, injuries, or attempts on the part of the parents to fully open the head of the penis have been noted.
- 4During examination and palpation, the doctor pays attention to the condition of the skin above the head, the presence of scar changes, signs of inflammation, and cracks.
- 5During the examination, it is important for the doctor to make a differential diagnosis between pathological and physiological phimosis, since in the latter case, phimosis in a child is considered a normal variant and is managed conservatively.
- 6Examination and collection of information about the course of the disease can help in establishing the cause of the development of phimosis in a particular child.
Features of treatment in childhood
The option of therapeutic intervention depends on the age of the child, the type of phimosis, the severity of its course, the reasons that led to it and the presence of pathological conditions resulting from phimosis [1,3].
If you are sure that the boy’s phimosis is physiological, the attending physician explains to the parents that this condition is the norm for the child, typical for most male children.
Also, the attending physician should familiarize parents with the necessary techniques for preventing infections in this area.
For pathological phimosis, the following types of treatment are used:
- Local application of ointments and gels based on corticosteroids. The exact mechanism underlying the therapeutic effect of these dosage forms has not been established.
Perhaps the therapeutic effect is due to the local anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of the drugs. A positive effect from the use of steroid ointments/gels is observed in 6-9 cases out of 10.
Only a small part of the drug is resorbed and reaches the bloodstream, so taking these drugs is rarely accompanied by systemic side effects.
More often, local adverse reactions are recorded in the form of swelling of the foreskin, its redness, and local pain. Local use of steroids is the basis of the first line of treatment for pathological phimosis in children.
Despite the high effectiveness of local use of steroids, a few months after the end of the course (the course lasts 4-6 weeks), a relapse of phimosis is possible. In this case, a second course of steroids may be prescribed.
- Surgical treatment is divided into minimally invasive methods of foreskin plastic surgery and circumcision (circumcision).
With plastic surgery of the foreskin, the effect is achieved by eliminating the narrowing of the foreskin without completely removing it.
With plastic surgery in the postoperative period, pain and bleeding are less pronounced, and the risk of infectious complications is lower. In addition, normal sensitivity of this area remains, but there is a possibility of relapse of the disease.
What is prohibited for phimosis in a child?
- 1You cannot neglect genital hygiene. There is a high chance that phimosis will resolve on its own, but the aspect of preventing infections should not be skipped. It is necessary to regularly, while bathing the child in the bath/showering, wash the head of the penis and foreskin with mild detergents, followed by rinsing with water. When bathing, the foreskin moves exactly as much as this process does not cause discomfort and pain in the child.
- 2To wash the genitals, do not use concentrated soap solutions, which can lead to irritation, dry skin and increase its vulnerability. It is advisable to use children's hypoallergenic shower gels.
- 3You cannot try to forcefully help the child retract the foreskin. With such exposure, microcracks may occur, which heal with the formation of scars that reduce the extensibility of the skin in the future.
- 4You cannot self-medicate and wait for the problem to resolve itself. If you have questions or doubts, it is better to contact your pediatrician. If necessary, the pediatrician will refer the child to a urologist.
9. Prevention of pathology
To prevent the transition of a physiological process to a pathological one, it is necessary to teach parents the following rules:
- 1It is important to prevent infection of the foreskin and glans penis. To do this, it is necessary to regularly carry out hygienic treatment of this area, especially while bathing the child.
- 2Hygienic treatment is carried out using non-concentrated soap solutions, mild detergents (for example, Mustela, Weleda, Avene, etc.).
- 3 During bathing, showering, and urination, boys’ foreskin is retracted to the usual distance. It is important not to cause pain/unpleasant sensations.
- 4In no case should the foreskin be retracted with force, causing pain or discomfort in the boy. You need to stop before they happen.
- 5 It is recommended to teach your child to independently remove the skin from the head of the penis during shower/bath/urination.
- 6After washing, the soap solution is washed off with water at body temperature. The skin dries out. The foreskin returns to its place, covering the head of the penis. [2]
Video Photo Tables
The danger of pathological phimosis for the health of an adult man
Typically, questions about how to get rid of phimosis are of interest to patients who feel a certain discomfort and experience inconvenience caused by this condition. The asymptomatic course of the disease often leads to a long-term lack of rational treatment for phimosis in men, and as a consequence, the development of complications and concomitant pathologies.
First of all, abnormal narrowing of the foreskin significantly increases the risk of developing infectious diseases and inflammatory processes. This is due to the gradual accumulation in the preputial space (the cavity between the foreskin and the head of the penis), the natural biological fluid of smegma, which is a product produced by special glands located on the inner mucous surface of the foreskin.
This substance is a natural lubricant of the genital organ, which not only protects the head from drying out, but also simplifies sexual intercourse. The chemical composition of smegma is an extremely favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which leads to the development of complex inflammatory conditions such as balanitis and balanoposthitis.
In addition, it has been proven that the inability to provide complete hygienic care for the genitals, which is observed in men with severe forms of phimosis, can lead to the accumulation of carcinogens in the preputial cavity. These substances contribute to the development of cancer, such as penile cancer.
One of the most unpleasant and acute complications of pathological phimosis in an adult man can be paraphimosis, which is manifested by clamping of the head of the penis with a tight ring of the epidermis of the foreskin. Typically, infringement occurs during sexual intercourse or masturbation. This condition requires immediate contact with a medical institution for phimosis surgery.