Causes of purulent discharge
The pathological contents of the navel appear due to the entry of infectious agents into the soft tissues. The condition can develop under the influence of internal causes and external factors.
The reasons for the formation of pus in adults and children differ.
In newborns
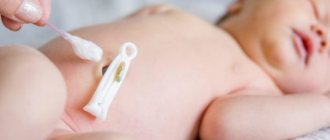
The baby's umbilical cord serves as a transport channel during the prenatal period. Through it, nutrients flow from the mother to the fetus through the bloodstream.
After birth, the connection is interrupted and the umbilical cord is cut off. In its place, a wound forms with a remnant of the navel, which under normal circumstances dries up, disappears without pus and pain in 4-7 days.
In case of pathology, the wound becomes wet, does not heal, hurts, and turns red. Omphalitis typically appears two weeks after the birth of the child.
Suppuration of the navel in a newborn occurs for the following reasons:
- Incorrect care. Pediatricians of the Soviet school recommend treating the wound with brilliant green and hydrogen peroxide. Modern family doctors insist on natural healing of the navel. Recommendations are individual for each situation. Failure to follow the doctor's advice may result in omphalitis.
- Diaper related overheating. The wound heals better in the fresh air. Diapers interfere with ventilation, creating favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms that cause inflammation with pus.
- Redness and suppuration of the navel can be caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are activated when the child’s immunity is reduced, usually in premature babies.
Typical signs of omphalitis are redness of the skin, increased body temperature, the child is constantly restless due to painful sensations, and a cloudy exudate appears inside the wound.
Pus in a baby's navel requires consultation with a pediatric neonatologist. Newborns with weak immune systems quickly develop dangerous complications.
In adults
Omphalitis is considered a childhood disease, but discharge from the navel can begin at any age.
Typically, inflammation develops due to damage to the skin in this area.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Possible causes of pus in an adult’s navel:
- Insufficient hygiene. Often the pit on the stomach is not given enough attention. It collects dirt, dust, sweat, and pieces of clothing. The components create favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms: fungi, viruses, bacteria, which causes inflammation.
- Pus from the navel in women can be a consequence of piercing. The puncture injures the skin; swelling, especially in the case of poor quality care, can develop into a pathological process.
- Abdominal injury. If after the injury the wound begins to get wet and does not begin to heal within a week, you need to consult a doctor.
Factors in the formation of exudate can be eliminated, preventing pathology.
Careful care of the navel at any age is an effective prevention of the appearance of pus.
Share this article
Inflammation of the navel is uncommon and can develop in both children and adults.
The medical name of this disease is omphalitis. Omphalitis (Greek omphalos - navel) is inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue in the navel area. Many people know that newborns have problems with the navel. But not everyone is aware that navel inflammation also occurs in adults. Let's try to fill this gap and tell you why the navel becomes inflamed in adults. Indeed, most often omphalitis is a disease of newborns in the first weeks of life, which occurs when the umbilical wound becomes infected and is manifested by redness of the skin around the navel, swelling, purulent discharge from the wound, abdominal pain, and fever. What about adults?
Causes of omphalitis.
The cause of inflammation is most often bacterial (streptococci, staphylococci, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) or fungal infection. But there are certain prerequisites for navel infection:
- The presence of a fistula at the umbilical ring. Fistulas, as a rule, are a congenital pathology caused by non-closure of the vitelline or urinary duct.
- In this case, an intestinal-umbilical fistula with intestinal discharge is formed in the navel area. In case of non-occlusion of the urinary duct, a vesico-umbilical fistula is formed, and then the discharge is most often urine.
- However, fistulas can also be acquired. This can occur after a long-term inflammatory process of the anterior abdominal wall, when a purulent abscess is opened through the navel.
- Inflammation of the navel may be associated with anatomical features. So if the skin umbilical canal is very narrow and deeply retracted, dying skin cells and sebaceous gland secretions can accumulate in it. In this case, if hygiene rules are not followed, an infection can occur and cause inflammation.
- Navel wounds, into which, if not properly cared for, pathogenic microorganisms easily enter and become the causative agents of the disease.
- Nowadays, it is worth knowing that piercing in the navel area can also cause inflammation.
Symptoms of omphalitis.
The main symptoms are redness, swelling of the skin in the navel area and the appearance of serous discharge in the umbilical fossa. In more severe forms, the discharge becomes bloody and purulent, and as a result of intoxication of the body, the general condition suffers. The temperature can rise to 38-39°C. The navel changes its shape and becomes more protruding and hot to the touch. The area at the epicenter of inflammation will be especially hot. The wound area becomes covered with a thick crust, and pus collects under it. The inflammatory process can also spread to the surrounding tissues and umbilical vessels, resulting in the development of arteritis or phlebitis of the umbilical vessels. This is the most dangerous variant of the disease.
There are 3 forms of omphalitis , each of which is a consequence of the previous one, if appropriate treatment is not carried out.
- Simple form (wetting navel) . In this form, the general condition does not suffer, but in the navel area there is weeping with serous or purulent discharge, which, when dried, becomes covered with a thin crust. With a long-term process, pink granulations can form in excess at the bottom of the umbilical wound and form mushroom-shaped tumors.
- Phlegmonous form . This is a dangerous form of omphalitis, because. with it, the inflammatory process already spreads to the surrounding tissues. There is a gradual deterioration in general condition. If phlegmon of the anterior abdominal wall develops, the temperature can rise to 39 °C and higher. In this case, the umbilical fossa is an ulcer surrounded by a compacted skin ridge. If you press on the umbilical area, pus may come out of the umbilical wound. The tissue around the navel is noticeably inflamed and swollen, and palpation causes pain.
- Necrotic (gangrenous) form . This is the next very dangerous stage of omphalitis. It occurs very rarely in weakened individuals with impaired immunity. With it, inflammation spreads deeper into the internal organs. If the process affects all layers of the abdominal wall, peritonitis may develop. There is a death of the skin and subcutaneous tissue near the navel, and subsequently their detachment from the underlying tissues. The skin becomes dark, like a bruise after a strong blow. Ulcers of varying sizes may form. The infection can spread to the umbilical vessels and lead to the development of umbilical sepsis.
Treatment of omphalitis
It is difficult to independently determine the cause of navel inflammation. Therefore, consultation with a surgeon is necessary, and, if necessary, bacteriological culture of the discharge. The treatment method will depend on the cause of the inflammation. As a rule, omphalitis is treated conservatively, but in the presence of a fistula, surgery cannot be avoided. With timely treatment, omphalitis passes quickly enough and the risk of complications of the disease disappears.
A simple form of omphalitis. 1. Daily washing of the navel area with antiseptic agents - furatsilin solution or hydrogen peroxide, as well as lubricating it with a 5% solution of potassium permanganate, 1% solution of brilliant green or 70% alcohol. Ointments are also applied - 1% synthomycin emulsion or tetracycline ointment. When navel granulations form, the wound is washed with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, and the granulations are cauterized with a 10% solution of silver nitrate (lapis). 2. Ultraviolet irradiation is used locally as a physiotherapeutic procedure.
Phlegmonous and necrotic form of omphalitis . Treatment of these two forms of omphalitis requires hospital treatment. In severe cases and general intoxication, along with local intoxication, general treatment is carried out using broad-spectrum antibiotics and taking into account the sensitivity of microflora cultured from the umbilical discharge to these drugs.
Purulent inflammation of the navel often requires surgical intervention. To prevent the spread of infection to nearby organs and tissues, the wound is drained and pus is removed from the wound using a special probe.
Navel fistulas. In the presence of fistulas, rational treatment is possible only surgically with excision of the fistula and suturing of defects in the wall of the intestine or bladder.
879
Which doctor should I contact and how to treat the disease
Pediatricians, therapists, and surgeons treat pus in the navel area. The specialist’s profile and treatment tactics depend on the form of the pathology.
In medical practice, there are three types of omphalitis in adults and children. Downtime is manifested by local symptoms and does not affect the patient’s well-being. Serous discharge drains and dries to form a crust.
The simple form is treated by daily washing the affected area with antiseptics: Furacilin, hydrogen peroxide. The use of disinfectant solutions alternates with the application of antibacterial ointments. These include drugs based on tetracycline and erythromycin. The cavity with pus is treated with brilliant green and potassium permanganate.
Dr. Komarovsky advises not to forget about the hypertrophic form of the pathology. Sometimes pink granulations grow in the wound on the navel, which will stick out on the skin. Cones are cauterized in a hospital setting with silver nitrate.
Phlegmonous and necrotic forms of omphalitis are advanced conditions, accompanied by high body temperature, chills, discharge of pus from the wound, and an unpleasant odor. Gangrene develops in the inflamed area. Both forms require inpatient monitoring. Treatment includes conservative and surgical methods.
A patient with complaints of omphalitis undergoes examination. They do a bacteriological examination of pus, general clinical tests of blood and urine. Laboratory diagnostic methods will help select pathogenetic treatment for the disease.
An abscess on the navel in the phlegmonous and necrotic stages is treated surgically. The doctor uses local anesthesia, cuts the outer wall of the formation, and evacuates the pus. Drainage is placed in the wound to prevent the accumulation of exudate. The surgeon performs the procedure for 15-30 minutes.
In women, men, and children, the healing time of the postoperative area varies. The speed of recovery depends on the person’s immunity, the severity of the condition, and complications.
From the moment the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient is prescribed penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics. The drugs are administered by injection or orally.
The prognosis of the disease is favorable. After the evacuation of pus and healing of the wound on the navel, the patient returns to the normal rhythm of life.
Features of treatment of discharge
A treatment regimen for a weeping navel in adults should be developed by a doctor, based on the established cause of the pathology and concomitant diseases. For the treatment of omphalitis, antiseptic drugs must be used:
- 10% alcohol solution of iodine;
- 2% solution of brilliant green;
- 5% solution of potassium permanganate;
- silver nitrate solution 2%.
Before applying the antiseptic, wash the umbilical area with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
For a weeping navel associated with purulent and acute inflammatory processes, ointments are prescribed:
- Polymyxin-m sulfate. Use to lubricate the affected area 1-2 times a day, immediately after removing the pus. A thin layer should be applied to the umbilical fossa, as well as to the surrounding tissue.
- Synthomycin liniment. Apply the ointment 3-4 times a day in a thin layer, always using a sterile bandage.
- Bactroban. The cream is used 3 times a day for 10 days, can be combined with a bandage.
- Baneocin. Apply 2-4 times a day, but if the skin is dry, it is better to choose another product.
With the development of phlegmonous and necrotic forms of omphalitis, it is not enough to treat the navel, if it is oozing, with ointments. It is necessary to use antibiotics and undergo therapy in a hospital setting.
Often, to eliminate purulent discharge, a surgical operation is performed, during which a drain is installed in the navel to drain the fluid. If the inflammation is associated with a fistula, the affected area must be excised and sutured.
Antibacterial therapy is used in most cases for inflammation, excluding the simple form of omphalitis. During the consultation, the doctor will tell you whether surgery is necessary. You cannot prescribe medications or other methods of therapy on your own.
Features of physiotherapy for a weeping navel
Physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out after antibacterial and surgical treatment. Microwave and UHF heating methods are highly effective. Other technologies should be discussed with the doctor. It is important to remember that a physiotherapeutic course cannot last less than 5-7 procedures.
Complications of the disease
If you do not consult a doctor in the early stages of the disease that caused pus from the navel, complications may develop.
Common consequences of untreated omphalitis:
- development of sepsis;
- spread of infection from the navel to the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and neighboring tissues;
- the appearance of a fistula.
Complicated conditions require long-term treatment, cleansing of blood vessels and organs from bacterial agents and their metabolic products.
If your navel turns red or starts to hurt, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Pathology, accompanied by the release of pus, quickly turns into a systemic process.
Complications can be suspected by the deterioration of the patient’s condition, prolonged fever, the spread of inflammation to surrounding tissues, and the appearance of holes from which pus is released.
How to treat odor and discharge from the navel
Therapy directly depends on what factor caused the unpleasant phenomena. Each disease has its own treatment mechanism:
- If an umbilical fistula is detected, surgery is prescribed. This is the only way to protect yourself from complications.
- To cure omphalitis caused by a fungal or bacterial infection, you should definitely consult a dermatologist or surgeon. Therapy prescribed by a doctor usually includes frequent washing of the affected area with antiseptic and antibacterial agents, maintaining good hygiene, wiping the folder dry with a clean towel or napkin after each shower. An antibacterial cream will help get rid of purulent discharge.
- In case of diabetes, diet is adjusted and the percentage of blood sugar is reduced with the help of medications.
- If you are overweight, you should lose weight and carefully follow hygiene recommendations.
Unusual smell, pain, discharge from the navel are symptoms of pathology. Do not neglect them and begin treatment immediately.
Prevention in children
To prevent the appearance of pus in the navel area in a newborn or omphalitis in adults:
- The baby's wound should be treated with clean hands.
- The diaper is wrapped inward in the abdominal area. To prevent the appearance of pus, the skin must be in contact with air.
- If the remaining umbilical cord is contaminated, rinse it with distilled or boiled water, then dry it with a clean towel.
- Adults need to pay attention to hygiene. Daily washing of the navel prevents pathogenic flora from multiplying.
- After the piercing procedure, you need to monitor the condition of the wound and regularly treat it with antiseptics. Itching, pain, redness are typical symptoms of infection.
- If pus appears, do not self-medicate, consult a doctor.
- A strong immune system prevents the development of inflammation. A balanced diet rich in vitamins improves the body's protective functions.
Pus in the navel area responds well to treatment, but it is better to prevent the appearance of pathology and monitor the condition of the skin to prevent omphalitis.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Symptoms of pathology
Purulent discharge from the navel is a sign of infection.
The inflammatory process is characterized by the appearance of several characteristic symptoms:
- Redness (hyperemia) of the tissues around the navel, they become hot to the touch (local increase in temperature).
- Tissue swelling, developing as a result of local release of plasma from the vascular bed into the tissue against the background of increased permeability of the capillary walls. In this case, the navel often protrudes.
- Feelings of discomfort in the navel area in the form of pain.
- Pathological discharge - mucus streaked with blood may appear, pus is a sign that the tissue has begun to rot.
- Superficial violation of the integrity of tissues in the form of erosions or ulcerations - as the pathological process progresses, they become covered with a crust. Then pus (suppuration) can accumulate under it, which can periodically break out and come out.
- General intoxication - a purulent process is almost always accompanied by an increase in temperature from +38 ° C, body aches, headaches, loss of appetite, up to its complete absence. The severity of intoxication depends on the severity of the purulent process.
If the inflammation is of fungal origin, the skin around the navel begins to itch and peel, but there is no pus. If the itching is very severe, scratches appear on the skin, which are an entry point for bacterial infection.
A weeping navel is a simple form of omphalitis.
Depending on the severity of the course, the nature of the pathological process and the predominant symptoms, several clinical forms of omphalitis are distinguished:
- Weeping navel or a simple form - the inflammatory reaction is accompanied by small erosions, serous discharge, and a crust may form. The general condition of the child or adult does not suffer.
- The phlegmonous form is a severe form of inflammation that spreads to the tissues surrounding the navel. There is an accumulation of pus in the intercellular substance, and there is no clear limitation of the pathological process. A crust forms on the surface, from under which pus periodically oozes (mostly when pressed). The general condition suffers, severe intoxication develops with an increase in temperature to +39 ° C, aches, and general weakness.
- The gangrenous (necrotic) form develops in the absence of therapeutic measures, tissue death occurs, and the navel festers with the smell of rot. The general condition of a person worsens significantly, and exhaustion (cachexia) develops against the background of intoxication.
In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease gradually progresses. In this case, the inflammatory process begins with weeping, then the area begins to fester, phlegmon develops, and then gangrene. After the death of a section of tissue, a pathological canal (fistula) can form, connecting to the abdominal cavity. This increases the risk of developing peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum, which is often purulent) and death due to intoxication and decompensation of the functional activity of all organs.