The first thing happy parents tell their family and friends is the gender, height and weight of the newborn. “A son was born, 52 cm, 3.5 kg”, or: “We have a girl, 3000 g, 50 cm” - these are the most common words spoken on the phone or written in SMS messages about their child. The doctor first enters the same parameters into the newborn’s health history. Why are the numbers of a child’s height and weight so important for doctors and parents?
Normal indicators for a newborn
Height, body weight, and head and chest circumference are the main indicators with which doctors evaluate the physical development of a newborn child. Low or, conversely, high weight, the ratio of head and chest circumference, and the baby’s height are not just dry numbers; they can be used to suggest or exclude some diseases of the newborn. Then, when the child grows up, based on these parameters, pediatricians will monitor his health, give advice on feeding, regimen, and make some prescriptions.
That is why, as soon as the child is born, he is immediately measured, weighed and this data is entered into the medical record. Then, in the first year of life, the child’s height, weight, chest and head circumference should be measured once a month, since the baby is growing very rapidly at this time.
The norm for a newborn is: Height: from 46 to 56 cm Weight: from 2600 to 4000 g Head circumference: 34–36 cm Chest circumference: 32–34 cm
Body length/newborn height
Body length is no less important an indicator of a child’s growth, as is weight. Determining body length in children - full-term and premature - is necessary not only to assess their growth, but also the proportionality of growth - the ratio of length and body weight [2]. Body length reflects the increase in lean mass [3].
Body length measurement
Measuring the body length of a newborn is difficult. In practice, body length is the most inaccurate indicator [4].
It is strongly recommended to measure body length in children using a stadiometer/infantometer using two people. The error when measuring body length using an infantometer is 0.5 cm, using a tape - 1.2-3.0 cm [5]. This difference is significant and can lead to an incorrect assessment of height - placing the child in the wrong percentile corridor - and , accordingly, incorrect tactics for managing the child.
Measuring height with an infantometer has minimal variability when measured by different people compared to a tape [2].
Using a measuring tape to measure body length is highly undesirable. This is an imprecise method [2]. However, if there is absolutely no choice, then when using a measuring tape, the measurement should be taken from the top of the head to the heels of the child while lying on his back on a flat and hard surface. The tape must be applied to the marks on the surface, and not to the baby’s body [6].
Estimation of body length is useful when it corresponds to reality, that is, measured in the most accurate way [7].
Increase in body length
The average body length of a full-term newborn baby is 46–56 cm.
Measuring body length in newborns can be delayed until 7–14 days of life [2,7].
The ideal increase in body length in newborns has not yet been determined [3]. On average, the desired increase in body length in full-term infants is 0.69–0.75 cm/week [6]. The increase in body length in premature infants is 0.8–1.0 cm/week [4,6].
Body length is usually measured weekly/twice monthly [8].
What affects a child's weight gain?
How a child will gain weight and grow in length depends on hereditary data, on his nutrition and on the quality of life in general. At the same time, heredity greatly affects the growth of the child - if mom and dad are tall, then the height of their son or daughter will most likely also be the same. But the main role in weight gain is played by the quality of nutrition - if the baby eats properly, this means that weight gain will be good. And, of course, the quality of a child’s life is of great importance: if he grows up in good living conditions, often spends time in the fresh air (sunbathing is especially important), if he gets a lot of exercise and pays attention to his health, then his growth and weight gain will be consistent normal for his age.
Child growth: increase by month
The height of full-term newborns is usually between 46–56 cm. Boys, as a rule, are longer than girls, but if the parents are tall, then a newborn girl can be significantly taller than the average newborn boy.
What happens to the growth of children in the first year of life? During this period, the child grows most rapidly - by as much as 20–25 cm! In the future there will no longer be such a significant increase in growth.
It is known that the growth of children increases unevenly, in leaps and bounds. For example, there are seasonal and daily dynamics. Many parents notice that during the summer the child stretches out more than at other times of the year. It has also been established that children grow faster at night than during the day.
An interesting fact: those parts of the body that are farthest from the head grow faster (that is, the baby’s foot grows faster than the lower leg, and the lower leg, in turn, faster than the thigh), this is associated with age-related changes in the proportions of the child’s body.
In addition to growth, doctors evaluate other parameters of the newborn. Be sure to measure the circumference of his head and chest. A newly born baby has an average head circumference of 34–36 cm, and a chest circumference of 32–34 cm. The chest and head circumferences, as a rule, become the same by 4 months of life. After this, the chest increases in circumference faster than the head. A one-year-old child has a chest circumference of approximately 48 cm, and a head circumference of approximately 46–47 cm. But these are only average figures: after all, children, just like adults, have different body types and different head shapes - so a slight deviation from the average is possible numbers
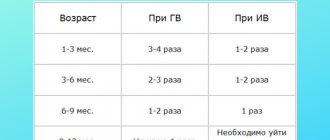
Height gain by month: 1–3 months: 3–3.5 cm monthly (total 9–10.5 cm) 3–6 months: 2.5 cm monthly (total about 7.5 cm) 6–9 months : 1.5–2 cm monthly (total 4.5–6 cm) 9–12 months: 1 cm monthly (total 3 cm)
Child's weight: increase by month
The weight of a newborn can be 2.6–4 kg. Babies born weighing more than 4 kg are considered large. This can be either a feature of the constitution (large parents will have a large child) or evidence of a carbohydrate metabolism disorder in the mother.
An important fact: a child’s body weight upon discharge from the maternity hospital is usually less than that with which he was born - both indicators are recorded in the documents issued to the mother. You should not be afraid of such “weight loss” - this is a natural process called physiological weight loss. It occurs due to the loss of water through the lungs and skin, drying out of the umbilical cord remnant, and the release of urine and meconium (original feces).
Maximum weight loss in most newborns occurs by days 3–5 and normally amounts to no more than 6–8% of the initial weight. And by the 7th–10th day of life, healthy children weigh the same as immediately after birth. If a child loses more than the specified norm or cannot regain the lost grams for a long time, this may indicate an infection or congenital pathology.
In the first year of life, the baby's weight increases the most. There are several ways to calculate weight gain.
For example, in the first half of the year the child should gain at least 600–800 g per month. By 6 months his weight normally doubles. In the second half of life, the rate of weight gain decreases somewhat - it increases by 300–550 g per month. This happens due to the fact that the child becomes more mobile: he no longer just lies in the crib, but actively turns over, crawls, sits down, stands up and begins to walk. By the age of one year, the child's weight should triple compared to the original.
Some mothers are very careful about how their baby gains weight. They are ready to weigh their child daily, almost after every feeding, believing that the weight should increase with each meal. You should not waste time on this - the child’s weight, like his height, increases unevenly. It does not happen that every day the baby gains the average grams: over time, the mother will notice that there are periods when the weight is stable or increases slightly, and then suddenly there is a sharp jump.
To control, it is enough to weigh the child once a week, preferably in the same clothes. There are two types of scales for weighing children: mechanical and electronic. Today, electronic scales are more convenient to use - they are lightweight, compact, and mobile. Some models automatically take into account and subtract the weight of the diaper, “remember” previous weighings, can show the dynamics of weight changes and even measure height. If it is not possible to purchase scales, you can get by with a monthly weight measurement at a children's clinic.
After the first year of life, the rate of weight gain (as well as growth) decreases significantly. In ordinary life, a child, and even an adult, will never be able to double or even triple their weight in one year.
Average height and weight at 1 year: Height 75 cm Weight 10.5 kg Chest circumference 48 cm Head circumference 46–47 cm
Advertising
Newborn weight gain and growth
First week - weight loss and first gains
The weight of newborn babies is very unstable in the first week and may decrease - this is a manifestation of a healthy norm.
In the first days of life, the young body intensively rids itself of excess fluid. For this reason, the baby can lose up to 7-10% of its original weight. For example, with an initial weight of 3500 g, a child can lose weight by almost 350 grams (up to 3150 g) in 3-4 days.
As a rule, such a drop in weight is clearly visible during natural breastfeeding, because the mother’s production of breast milk usually begins only 2-4 days after birth. Until then, the child eats only colostrum, which is produced by the mammary glands only in small quantities, which cannot have any effect on weight.
If the child is kept on artificial or mixed feeding, then the initial weight loss will be insignificant or will not appear at all.
Infant weight gain in the first week
| Gain, g | Average | Minimum |
| boy | 150 ±150 | -200 … -300 |
| girl | 100 ±100 | -150 … -250 |
* Gain is calculated from the initial weight with which the child was born
So, in the first week of life, boys gain an average of 150 grams, girls - 100 g. However, a significant percentage of children (about 25%) may show zero or negative gain (weight loss), and this is also normal for them. There will be enough time in the following weeks to compensate for the initial weight loss. But, in this case, the baby’s weight must be regularly monitored: after the first week, the weight must increase steadily, otherwise it is necessary to look for and solve a problem with feeding or health with the help of a doctor.
If on any day of the first week it turns out that the baby has lost more than 7% of its original weight, it is recommended to consult a specialist. If you have lost more than 10%, medical intervention is mandatory.
Gain and gain in the first month
The following table shows the approximate norms of weight gain and growth of infants in the first month of life (30-31 days).
So, it is advisable for a boy to gain 0.77–1.45 kg, for a girl 0.67–1.27 kg. Norms of newborn weight gain in the first month
| Weight gain, kg | Short | Average | Big |
| boy | 0,38 – 0,76 | 0,77 – 1,45 | 1,46 – 1,76 |
| girl | 0,40 – 0,66 | 0,67 – 1,27 | 1,28 – 1,58 |
* The table shows weight gain from birth to 30-31 days from birth
Low and high weight gain usually indicate that the feeding intensity can be increased or decreased accordingly. If the baby’s weight gain goes beyond the proposed ranges, then this is a reason for the local pediatrician to intervene. He must find the cause of too low or excessive weight gain (incorrect feeding, temporary illness of the child or mother, etc.). Then, depending on the child’s current growth and health indicators, the doctor develops feeding recommendations so that all indicators gradually return to normal.
Please note that many doctors, in the old-fashioned way, count weight gain from the minimum, they are more used to it this way. However, in modern weight gain standards, the count is based on the initial weight with which the child was born, since this makes it possible to evaluate gains more objectively. Therefore, the norms for weight gain in the first week and first month indicated on this website measure weight gain from the initial weight at birth.
Growth in the first month for boys is 3.5 - 6.0 cm, for girls 3 - 5.5 cm.
Attention to numbers: rate of weight gain
Each person has their own idea of health. So, some parents (as well as grandparents) think that the baby should be a kind of well-fed boletus. And the insufficient, in their opinion, weight and height of the baby leads them to confusion.
In fact, these days there are more and more children with excessive weight gain, and most often this is observed in babies who are bottle-fed. So, some parents, wanting to feed their child more nutritiously, make the mixture more concentrated or increase the number of feedings. As a result, children gain more weight than necessary, which is why many of them lag behind their peers in development - they begin to roll over, crawl, walk later, get sick more often, and are more prone to allergic reactions.
In such a situation, it is necessary to reconsider the child’s diet: strictly observe the number and volume of feedings, after introducing complementary foods, give the baby more fruit and vegetable purees, and limit cereals, crackers, and cookies. It is necessary to do gymnastics with your child and create conditions for physical activity. But one should not go to extremes: insufficient weight gain of the child should also not be ignored. After all, sometimes this can be a symptom of some pathology: for example, anemia or rickets.
When receiving the results of measuring your baby, you need to remember that all children are different, and it is not necessary for every baby to reach the average height and weight by a certain age. It is necessary to take into account height and weight at birth, as well as the rate of increase in these indicators: for example, a newborn with a height of 48 cm and a weight of 2900 g at 1 year can differ significantly in anthropometric indicators from a child born with a height of 55 cm and a weight of 4000 g. And this It’s completely normal – it’s good to have diversity in the world!
Control of weight gain and feeding intensity
In Russia, infants are first brought to a routine examination by a pediatrician at the age of 1 month. And during control weighing, a deviation of weight or BMI from the norm is often detected, which could have been avoided if weighing and control were carried out weekly.
For example, a young mother breastfeeds her baby “on demand,” as is widely recommended. However, if the baby is calm, then he rarely “gives voice”, so an inexperienced mother does not feed him as often as is actually necessary. As a result, the child gains weight very slowly, and at the end of the month, a deficiency in body weight .
The opposite situation is also possible, for example, when a child is fed formula in unlimited quantities, especially under the “sensitive guidance” of the older generation. In such conditions, the baby rapidly gains weight, becoming overweight or obese.
The relevance of this problem is due to the fact that from birth a child begins to form his own eating habits, which will subsequently be difficult to change. As a result, a predisposition to underweight or obesity can last a lifetime.
To avoid such situations in the first month of life, it is recommended to weigh the child weekly (at ages 7, 14, 21 and 28 days), calculate weight gain over the past week and compare it with reference ranges for weekly weight gain.
Weighing can be done at home using a suitable scale with an accuracy of at least 0.1 kg, preferably 0.01 kg. Reference weekly weight gain of newborns, in grams
| Period | Boy | Girl |
| 1 Week | 150 ± 150 | 100 ± 100 |
| 2 week | 250 ± 100 | 200 ± 100 |
| 3 week | 320 ± 80 | 270 ± 70 |
| 4 week | 320 ± 80 | 270 ± 70 |
*See also the continuation of the table up to 6 months
If the actual weekly weight gain turns out to be more or less than the reference range, then this makes it clear in which direction the child’s feeding intensity should be adjusted: towards an increase or a moderate decrease.
For example, if a boy gained 50 grams in the second week (from 7 to 14 days), then the intensity of feeding should be increased slightly. If a girl gained 500 grams in the 3rd week, then the intensity of feeding can be reduced slightly.
Please note that children's actual weekly gains may differ significantly from the reference ones and are often negative, especially in the first week - this is normal.