Prominent ears are a congenital abnormality in the formation of the auricle in children, in which the ears do not fit tightly to the head, but protrude to varying degrees. Normally, the angle between the auricle and the head should not exceed 30 degrees, the edge of the auricle should be parallel to the cheek, and the distance between it and the cranial bones should not exceed 20 millimeters. The pathology is well determined visually: one or both ears are located at an angle of 30 to 90 degrees to the head.
This is a fairly common phenomenon: according to the results of the study, it was found that almost half of people are born with congenital protruding ears. This anomaly causes psychological discomfort and often leads to the development of complexes. Psychological barriers erected as a result of the feeling that a given deficiency is ruining one's life can actually result in serious problems. Pathology of the formation of the auricles is equally common in both boys and girls.
Causes of protruding ears in children
The development and growth of the outer ear begins in the third month of intrauterine development, and the formation of the relief of the auricle occurs in the sixth month, so protruding ears are clearly noticeable already during the birth of the child.
Violation of the formation of the auricle can be unilateral or bilateral, in addition, it can have varying degrees of severity. The type and degree of development of the pathology are strictly individual, and this excludes the existence of a single medical tactic for eliminating protruding ears.
There are only two reliable causes of protruding ears in children:
1. Hereditary tendency: in most cases, protruding ears are a genetically determined feature that is passed on even through several generations, regardless of the degree of relationship (for example, a child can inherit such ears from a great-grandfather or a second cousin).
2. Features of the formation of the auricles in the prenatal period: in some cases, cartilage hypertrophy, smoothness or incomplete development of the auricle curl occur.
We should also mention another cause of ear defects in children - microtia. Such a defect can occur due to congenital vascular anomalies, Recklinghausen neurofibromatosis, or due to isolated rapid growth of the auricles or intensive growth of bone tissue of the facial skeleton.
Many parents believe that the cause of protruding ears is malpresentation of the fetus or jamming of the auricle during fetal development, but this theory has not been scientifically confirmed.
Modern methods of testing hearing in children
Diagnosis of hearing impairment in pediatric practice includes anamnesis, objective instrumental and behavioral techniques. Only a comprehensive examination can give correct results.
In the maternity hospital, a visual examination and screening study using the evoked otoacoustic emission (or OAE) method are performed. A record of the results is made in the infant's chart.
At the outpatient stage, the scope of research depends on the age of the baby, the presence of complaints and the technical equipment of the institution. Typically, a hearing test includes:
- Questioning of parents (history, complaints, risk factors);
- visual examination of the child;
- instrumental diagnostic methods according to age;
- methods of behavioral audiometry.
When they talk about testing a child’s hearing using a device, they mean standard methods: screening by recording short-latency auditory potentials (SLAP), OAE, impedance audiometry.
CVSP provides information about the conduction of impulses to the level of the cochlea, brainstem, and cerebral cortex (More details about the structure of the hearing organ). Potentials are recorded directly from the surface of the skin, and hearing acuity is assessed by the reaction to a sound stimulus. The method is convenient for children of any age. The study can be carried out while you are asleep or awake.
The evoked otoacoustic emission method allows you to assess the condition of the cochlea. Normally, nerve cells vibrate in response to a sound stimulus. In sensorineural hearing loss, there is no otoacoustic emission. The method makes it possible to differentiate cochlear lesions from retrocochlear pathology and is convenient for children from the neonatal period.
Impedance audiometry studies the conduction of sound through the outer and middle ear, as well as the mobility of the eardrum. The method is based on the principle of echolocation.
Behavioral audiometry is used in children of any age. It is based on an assessment of the reaction to a sound stimulus. There are:
- unconditional reflex audiometry;
- conditioned reflex audiometry;
- gaming audiometry;
- children's play audiometry.
Degree of development of pathology
Determining the age for surgical intervention, as well as all the nuances of the procedure, directly depend on the degree of development of this anomaly. Experts distinguish three degrees of development of protruding ears in children:
1. At the first stage of development of protruding ears, the angle of the ears does not exceed 45 degrees. Visually, such a defect is not immediately noticeable, and it can be disguised by choosing a suitable hairstyle - this is especially true for girls. To quickly correct protruding ears of the first degree, removal of excess cartilage tissue in the area of the recess of the auricle is most often used.
2. The second degree is characterized by a fairly significant protrusion of the ears, and the angle between the auricle and the head can range from 45 to 90 degrees. This pathology can be eliminated by thinning the cartilage tissue of the antihelix and subsequent surgical formation of the ear.
3. In the third degree of development, protruding ears are extremely pronounced, since the angle between the auricle and the head is more than 90 degrees. The correction technique involves removing excess cartilage tissue and artificially creating an antihelix.
Indications for surgical intervention at an early age are the second and third degrees of development of protruding ears, and in the first degree, correction of the auricles in children is carried out upon reaching adulthood.
Elimination of protruding ears in children
Children with protruding ears are born quite often, but this does not mean that they will have such ears for the rest of their lives. As the cranial bones grow, the angle between the pinna and the head may decrease, making protruding ears less noticeable. In case of obvious pathology, early surgical correction is possible, which is prescribed at the age of 6 to 8 years.
Surgical intervention is aimed at plastic correction of the position, size or shape of the ears. This is a fairly simple operation, which, however, requires a strictly individual approach to planning and performing surgical intervention.
Parents should remember that ear surgery for children is an aesthetic operation that significantly improves the quality of life of young patients.
At the First Children's Medical Center, operations to correct protruding ears are performed using traditional methods. The operation is performed using a standard set of surgical instruments, one of which is a scalpel. This surgical intervention is performed using local anesthesia or general anesthesia, and consists of changing the shape of the auricle by affecting the cartilage.
Before surgery, the child must not only consult a doctor, but also undergo several laboratory tests:
— general blood and urine tests;
- blood clotting study;
- blood sugar test;
- blood chemistry;
— analysis that determines blood group and Rh factor;
— study of the tolerability of the drugs used;
- venous blood analysis for HIV infection, syphilis and hepatitis types B and C.
In addition, it is necessary to undergo an electrocardiogram. The doctor may also prescribe additional tests - they are prescribed individually, depending on the situation.
It is also worth noting that this surgical intervention has some contraindications:
— acute infectious diseases;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- dermatological problems localized in the ear area;
— endocrine pathologies: diabetes mellitus or thyroid diseases;
- diseases accompanied by blood clotting disorders;
— malignant neoplasms;
— HIV infection, syphilis, chronic hepatitis type B.
Progress of the operation
The operation to correct the auricles in children proceeds as follows: the surgeon makes a small incision at the back of the auricle (taking into account the hairline and the course of the natural fold of the skin). After the incision is made, the doctor forms a new form of cartilage (if necessary, excess cartilage tissue is removed). The surgeon then applies internal sutures. The final stage of the operation is cosmetic stitches, which over time turn into a tiny scar, which is also invisible behind the ear.
After the procedure, the doctor applies rollers aimed at maintaining the newly created position of the cartilage, and a securing bandage or bandage is put on top. The patient will have to wear them for 6 months.
How to remove protruding ears without surgery?
It is recommended to begin this process immediately after the baby is born. You can fix the auricle in the correct position for up to six months using a special silicone mold. The child must wear the clip for six months. In infants, cartilage tissue lends itself well to adjustment, so the problem can be solved quite effectively. Correctors are selected only after consultation with a specialist in the absence of contraindications.
There are contraindications: the presence of damage to the skin at the places where the correctors are attached; individual intolerance to adhesive or silicone.
Another option for home correction is to constantly put on the child, including at night, an elastic bandage that will press the ears to the head.
Rehabilitation period
After a week, the doctor will remove the bandage, and the compression tape will only need to be worn at night. In about 2–3 weeks, the sutures heal, minor swelling disappears, and you can forget about correction once and for all.
The percentage of complications after ear correction surgery is quite low and occurs in only 5 people per 1000 operations performed. In order to eliminate the risk of developing any complications, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period. These recommendations include:
1. Wearing an elastic bandage for at least one and a half weeks (the exact period is determined individually). You also need to use the bandage at night for another 5-6 months. This is necessary for the normal formation of ear cartilage.
2. Prohibition of physical activity (gym classes, etc.), as well as heavy physical labor for a period of 6 months.
3. Ban on visiting the sauna, bathhouse, solarium or beach for 3-4 months.
4. Mandatory attendance at prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, which will speed up healing.
5. Mandatory dressings - usually on days 1-3-5 after surgery, day 12 - removal of sutures.
FAQ
— How can you get rid of protruding ears in an infant?
To correct the defect at the age of up to six months, special silicone molds are used that press the ears to the head. If they are not available, you can use tight-fitting hats. However, it is worth noting that the use of these methods does not guarantee 100% elimination of the defect.
— At what age should ear correction surgery be performed?
By the age of 6–8 years, a child’s ears are 90% formed—it is at this age that it is advisable to undergo surgery to correct protruding ears.
With the modern development of plastic surgery, correcting protruding ears is not a problem. However, it must be remembered that the operation will need to be performed on both ears, even if the defect is expressed in only one.
Correcting protruding ears at an early age can save the child from possible psychological discomfort and, as a result, the formation of complexes. Parents should not worry about scars, since they will not be noticeable behind the ears and the marks will disappear over time. The result obtained after the operation will remain for life.
The First Children's Medical Center sees pediatric surgeons of the highest category. Sign up for a consultation on surgical treatment from 8.00 to 20.00. Reception is by appointment only.
Children's health means parents' peace of mind!
Make an appointment with a surgeon
Choose a doctor
Earfold implants
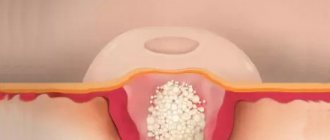
The latest solution at the intersection of surgery and conservative treatment methods. This is a minimally invasive alternative to surgery that provides good cosmetic results. The patented technique allows you to remove protruding ears, provided that the implants are constantly worn. Elimination of protruding ears is based on the fact that special mini-implants several millimeters in size are implanted into the ears. With their help, the cartilage is gradually rebuilt, the shape of the ear changes, and a correction effect is achieved. EarFolds are biocompatible, so there is no need to get rid of them in the future.
How are implants designed?
Each implant is a thin curved metal plate made of an alloy based on nickel and titanium, coated with medical gold. Thanks to this composition, biological compatibility is achieved, which is important because products for correcting protrusion must be located under the skin.
How to get rid of protruding ears using earfold?
The implantation procedure is carried out under local anesthesia and takes 20-30 minutes. Before it, precise positioning is carried out on an individual basis. Through an incision of about 1 cm, the implant is inserted under the skin and takes the desired shape, fixing the cartilage in the correct position. After this, two stitches are applied. The product holds the ear in the desired position.
So far, this technique is not very widespread, and the products themselves are expensive.