What is thrush
Thrush (or candidiasis) is a type of stomatitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth) caused by a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida. It is this fungus that causes the disease, usually transmitted through contact with an infected person.
The fungus is not a “guest” in the body: like other microorganisms, it always lives on the mucous membranes of the intestines, genitals, and mouth, but in small quantities. However, such a normal state is possible only with a “friendly” balance of “good” and “harmful” bacteria representing the microflora of the human body. This balance of equilibrium can be disrupted upon contact with a patient with thrush: in this case, a fungal infection from the outside enters the body of a healthy person and begins to multiply quickly there, disrupting the natural microflora.
This is possible when the immune system is weakened, when the number of “good” bacteria sharply decreases, and they are unable to fight the growing number of “harmful aliens.”
The occurrence of thrush in the mouth in children over the age of one year is explained by the fact that when they come into contact with each other, they pass toys and objects that they take in turn in their mouths, and among them there is often at least one child infected with candidiasis. And since the child’s immunity is still in the development stage, its internal protection is weakened, so infection occurs very quickly.
What kind of disease is candidiasis?
According to statistics, about 30% of infants experience candidiasis. The causative agent of the disease is Candida fungus. These specific microorganisms are normally present in the body of every person, even in the absence of health problems, but only in small quantities.
Oral candidiasis in children is much more common, since the immune system of children is not yet formed and is not able to resist pathogenic microorganisms and the effects of negative external factors.
With weakened immunity and the concomitant influence of provoking factors, the fungus begins to actively multiply, affecting the mucous membranes. Without therapeutic treatment, candidiasis is eliminated in exceptional cases. Much more often, if thrush is not treated, complications arise, and the infection itself spreads throughout the body.
Symptoms of thrush in the mouth of a baby
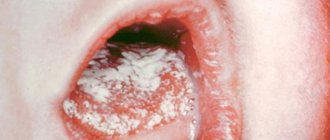
What does thrush look like in a baby? When a fungal infection enters the child’s oral mucosa, its proliferation leads to inflammation in the mouth area. Therefore, quite quickly you will be able to notice small crumbs of white “cereal”, reminiscent of cottage cheese, on the child’s cheeks, palate, gums and tongue. An inexperienced mother may well assume that this is the remains of milk or formula after regurgitation. But checking whether this is so is quite simple: take dry sterile gauze or a bandage and very carefully try to remove the white coating. If these are really leftover food, they will be easily removed; if it is thrush, it will be more difficult to erase the curdled coating. And after removing it, you will notice inflamed redness in the oral cavity. If your baby has thrush, his appetite and sleep will most likely worsen, and he will become restless and moody.
Preventing oral thrush in babies
To prevent the development of fungal infection, you should follow the recommendations of specialists, because the high risk of fungal infection persists for up to 6 months. Basic rules that every mother should know to protect her baby from thrush:
- if pathology occurs during pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment; a few days before birth, a second course of antifungal therapy is carried out;
- do not neglect personal hygiene, thoroughly treat nipples with a solution of water and soda after feeding, wash your hands;
- sterilize nipples, sippy cups and feeding bottles;
- monitor the condition of the child’s oral cavity;
- give boiled water after feeding to remove remaining milk and normalize the microflora of the oral cavity;
- take measures to strengthen the child’s immunity, massage and strengthen him.
Sources
- https://uroki4mam.ru/molochnitsa-u-novorozhdennyh-vo-rtu
- https://dentoland.com/kids/chem-lechit-molochnicu-vo-rtu.html
- https://dentist-pro.ru/detskaya-stomatologiya/polost-rta/stomatit/kak-i-chem-lechit-molochnicu-vo-rtu-u-grudnichka-recepty-proverennye-vremenem.html
- https://MikDent.ru/rebenok/polost-rta/molochnica-vo-rtu-u-grudnichka.html
- https://lechenie-molochnicy.info/molochnica-u-mladenca-vo-rtu.html
- https://LechenieDetej.ru/infekcii/molochnica.html
Causes of oral thrush in newborns
How can Candida fungi get into a baby’s body?
- infection can occur during the mother’s pregnancy if she suffers from genital candidiasis on the eve of childbirth: during the birth process, a fungal infection enters the placenta and amniotic fluid, and then into the newborn’s body;
- a baby can also become infected from a nursing mother if her nipples are affected by a fungal infection;
- when a child is bottle-fed or sucks on a pacifier, it, as well as bottles and nipples, must be treated in a sterilizer or boiled water before giving it to the newborn; unsterile nipples can cause bacteria to enter the oral cavity;
- the fungus can live not only on the mucous membrane, but also on the skin of the hands, from where it can easily migrate to the skin of the child if he is cared for by a person affected by thrush;
- The fungus can also be found in pet hair, dust, raw vegetables, meat or milk, so after contact with all these “transmitters” of bacteria, you must wash your hands thoroughly before touching the newborn;
- treatment with antibiotics can also disrupt the natural balance of the body's microflora; as a result of antibiotic therapy, candidiasis occurs in mother and baby who did not take medications containing “beneficial” bacteria along with antibiotics;
- candidiasis can occur if the mother has not learned how to properly attach the baby to the breast during feeding; the child may swallow too much air when sucking and, as a result, often burp; under such circumstances, most of the dairy food can remain in the child’s mouth, giving rise to fermentation processes and promoting the proliferation of fungi.
- thrush often develops in premature babies because their immune defenses are still too weak;
- candidiasis during artificial feeding can affect the baby due to the fact that he does not receive substances from mother’s milk that suppress the growth of fungal microflora;
- if the mucous membranes in the child’s mouth often dry out due to too dry air in the room or thirst, then such situations can contribute to the development of thrush;
- if the child’s immunity is reduced due to illness, poor sleep, lack of vitamins, then this can also cause fungi to multiply;
- candidiasis can also have a chronic form: in this case, it is often caused by serious illnesses in the child - diabetes, leukemia, HIV.
What is thrush?
You are probably informed about thrush in women, especially during pregnancy.
So, thrush in newborns is practically no different from the same disease in adults. The causative agent is the same - fungal class Candida, only the location of the infection is different. In children, thrush appears on the tongue, palate, cheeks and gums, while in women the genitals suffer.
Yeast-like fungi are present in small quantities in the body of every person, newborns are no exception. In small quantities they are even useful, but as soon as favorable conditions are created for their growth, a problem called thrush appears that has to be dealt with.
What does thrush in the mouth look like?
Thrush can be confused with milk residues after feeding or a natural coating on the tongue.
White coating on the tongue of a baby is a common occurrence. It does not need to be treated or removed. To distinguish normal white plaque from disease, conduct a mini-experiment:
- A sterile spoon or toothbrush will come in handy. Carefully scrape off the white coating, if there is redness or even wounds underneath it, this is pure thrush.
It can be difficult to recognize thrush or refute this diagnosis on your own, with your first child. Even numerous photos from the Internet do not help. If in doubt, go to the doctor.
Mechanism of occurrence
Fungi of the genus Candida are an opportunistic microorganism; 50-90% of people are carriers.
Under normal conditions, there are no symptoms of candidiasis; fungi begin to actively grow in the presence of certain factors. Then signs of infectious pathology appear.
Routes of infection
Candida fungus
Thrush is an infectious disease that is transmitted from sick people to healthy people. Children most often become infected from their parents or from other children in kindergarten.
Main routes of infection:
- Intrauterine. Candida fungi penetrate the placenta, and the child is born with congenital candidiasis.
- During passage through the birth canal, if the woman has not treated genital candidiasis in time.
- Breasts can become infected during feeding if the fungus lives on the skin of the mammary glands.
- Contact. Infections are transmitted through handshakes, toys, and household items.
- The fungal infection is transmitted from young domestic animals and birds.
But even fungal infection does not always cause the development of an infectious process. It all depends on the state of the immune system and the presence of chronic diseases in the child.
Causes
The main cause of thrush in newborns is the growth of Candida fungus. But you are probably interested in another question - why did these fungi suddenly decide to grow in your baby’s mouth? Let's see which of the possible reasons may shed light on your situation:
- Weakening of the immune system;
Perhaps your baby has recently suffered from a cold, or maybe you are already starting to teethe, with all the consequences known to medicine, including dysbiosis. The newborn’s body is weakened and cannot resist the growth of various bacteria; it is this weakening that fungi that cause thrush take advantage of. Find out how to protect your baby from various diseases in our course: Healthy Child>>>
- Prescribing antibiotics;
There are often cases when you decide to treat your baby with an antibiotic or undergo treatment yourself, and the baby partially receives the substance through breast milk. And even if you do everything according to the prescription, giving Linex along with the medicine (Read the article: Linex for newborns>>>) or other drugs, there is no guarantee that the flora will not be disturbed. While killing only bacteria, antibiotics do not affect fungal ones, and the latter, without competition, begin to multiply quickly.
- Violation of hygiene rules;
You don't need to wash your breasts before and after each feeding, but maintaining good hygiene and taking a refreshing shower is essential. Change your underwear promptly, especially if milk is still leaking.
By the way! A pacifier or bottle can also cause thrush infection; be careful and thoroughly rinse the available products.
- From mother to child;
A newborn could become infected with thrush during childbirth if the mother had this disease. So, if you know that you have such an error, carefully monitor your baby’s oral cavity.
Know! If you have nipple thrush on your breasts, then the cause of the infection in your baby is understandable.
- Regurgitation;
Thrush in the mouth of a newborn can also appear due to frequent regurgitation. You understand that milk is not returned in its pure form, and not always immediately, and the lactic acid environment has already been changed. Even a small amount of such treasure is enough to increase the number of fungi that cause thrush. Read about the causes of regurgitation>>>
As you can see, there are various reasons, some beyond your control, but as far as hygiene is concerned, here you have the right to control the situation 100%.
Symptoms of thrush in a newborn
Before moving on to describing the symptoms, I would like to note that thrush has three stages of development, and can also have acute and chronic forms. Depending on this gradation, it is worth talking about the symptoms of the disease.
- Stage 1. The initial and easy stage, but also the most important - after all, you should not miss it and allow the disease to move to a more complex stage. So, if your baby is fussy and doesn't want to latch on, check his mouth. Examine the oral cavity for the presence of a milky-white coating, try to scrape it off; underneath there are probably inflamed areas, which are what cause itching and burning. Regarding the smell, at the first stage the thrush does not manifest itself in this direction;
- Stage 2. I don’t want to scare you, but a few days are enough for thrush to affect the baby’s entire oral cavity, even the lips. It is impossible to remove the plaque at this stage; the newborn feels pain and burning, and under the coating of curd consistency there may be bleeding wounds. There is a distinct bad breath in the infant;
- Stage 3. The third stage of thrush in newborns in the mouth is already very serious. The symptoms of the disease only worsen, the cheesy plaque spreads beyond the oral cavity into the nasopharynx, it is impossible to remove the plaque, there is a film underneath that cannot be painlessly separated. The baby not only feels discomfort, he is in pain, he refuses to eat;
- Gradually, thrush can also affect the baby’s intestines and even manifests itself on the genitals of a newborn. The smell from the mouth is very noticeable.
This is interesting: A child’s baby tooth falls out, but a new one doesn’t grow in place of the one that fell out—what’s the reason?
As for the forms of thrush in newborns, there are acute and chronic. From what thrush looks like in newborns, we can talk about its character and form.
- Acute thrush most often develops as a result of taking antibiotics or decreased immunity of the newborn. The symptoms are obvious, develop quickly, redness and plaque go away easily with timely treatment;
- Chronic thrush with curd spots in the mouth, including the gums, is provoked by violations of hygiene standards. Having arisen once, it will manifest itself under favorable conditions.
Any stage or form of thrush is curable, but if you do not pay attention to the symptoms and waste time, the treatment will be much more difficult, and complications cannot be ruled out.
Stages
There are several stages of candidal stomatitis:
Initial form:
- the child is not capricious, his mood and appetite are good;
- no temperature;
- small islands of cheesy plaque on the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- Redness of the gums is rarely observed.
Middle stage:
- low-grade fever, general health is poor;
- weakness and breast refusal, anxiety;
- the mucous membrane is reddish, slight swelling is noticeable;
- the plaque increases, and when you try to remove it, bloody wounds appear.
Heavy stage:
- heat;
- infant refusal to eat;
- the filmy coating is not removed from the mucous membrane at all;
- Thrush is already spreading to the throat.
The last stage of the disease is very dangerous because it is difficult to treat.
How quickly will thrush go away? It depends on the form of the disease.
Forms of the disease
There are acute and chronic forms of the disease, and accordingly, the approaches to treating thrush will be different.
Acute thrush. There are two types of this form of the disease: pseudomembranous and atrophic. The first is characterized by the presence of a white cheesy coating, swelling, and sticking on the lips. This type of candidiasis goes away quickly if treatment is started right away.
The atrophic variety of thrush is characterized by the fact that the mucous membrane is fiery red in color, the tongue is crimson in places, there is no plaque or it is located in folds and cannot be removed in any way. The child's anxiety and irritability increase. It is difficult for the baby to sleep due to burning and pain in the mouth.
Chronic form. It has hyperplastic and atrophic variants. The first is characterized by the presence of yellow formations in the mouth, tightly adherent to the mucous membrane. In terms of volume, they rise slightly above its surface; when scraped, bleeding is noted.
The second option is rarer and is more common in older people who use prostheses. There is a red color of the membranes and dry mouth. Treatment of this form takes a long time and is difficult to cure.
Dangers of candidiasis for a newborn
Candidiasis can occur in simple and complex forms. And depending on the degree, it contains certain dangers:
- in severe forms of thrush, the fungus can reduce immunity and disrupt the gastrointestinal tract;
- candidiasis in a girl can spread to the vaginal mucosa, creating the risk of a pathology called synergy - fusion of the labia or vaginal mucosa;
- a mild form of thrush, in which it is enough to treat the plaque, usually does not pose any danger;
- with moderate thrush, inflammation forms under the white coating, which begins to bleed during treatment; this form brings additional discomfort and pain to the child; in the absence of proper treatment, the disease can become more severe;
- in severe cases of the disease, the fungal infection spreads throughout the entire oral cavity; in addition to pain and discomfort, the child may have a fever; Difficulties with swallowing can lead to the baby refusing not only food, but also water, which leads to rapid dehydration; this condition is life-threatening for the child, so its treatment is sometimes carried out in a hospital;
- thrush can occur not only in the acute, but also in the chronic stage: in such cases, exacerbation is characterized by the appearance of plaque on the mucous membranes and dry mouth; as a result of the infection spreading to the skin, small ulcers appear in the corners of the child’s mouth, and dense lymph nodes become noticeable to the touch under the jaw; reddish inflammations acquire a brownish tint and become painful, their area increases.
Is research necessary?
Usually, thrush in the mouth of a baby does not require additional research, since it is not difficult for an experienced specialist to diagnose it based on obvious signs. But sometimes, in case of serious lesions, additional studies may be prescribed:
- microscopic: in this case, the doctor will take scrapings from the oral mucosa to examine the yeast-like fungal cells more carefully;
- bacteriological: during such a study, a scraping is also taken and then bacteria are cultured to understand how large the volume of fungal colonies is and how amenable to treatment they are with antifungal drugs; in addition, bacteriological testing helps determine which drug is the most effective in treatment, because some of them may not have an effect in the treatment of thrush;
- serological: this study requires a blood test, in the serum of which antibodies to fungal infection are examined.
How to treat oral thrush in infants
Treatment of oral thrush in an infant is not a complicated process, but it requires the systematic implementation of certain procedures several times a day until the child recovers. If you find a mild degree of thrush in your baby, but at the moment you cannot call a doctor (for example, on a day off), then you can use traditional methods of eliminating thrush. If the degree of damage to the mucous membrane has already reached serious forms, it is better not to risk it and call an ambulance.
Traditional methods for eliminating thrush:
- using a soda solution: prepare a solution (dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water), then wrap a sterile bandage around your finger, moisten the winding in the solution and very carefully wipe the areas of fungal infections; Do not rub them under any circumstances, because under the plaque there may be bleeding plaques, through which you risk allowing bacteria to enter the baby’s body; such light rubbing can be done 4 times a day until you have the opportunity to visit a doctor;
- use of honey solution: prepare a solution (dissolve 1 tsp honey in 2 tsp warm boiled water); however, please note that it is unacceptable to use a honey solution if a child is allergic to bee products; if the child tolerates honey well, then treatment with the solution can be carried out similarly to treatment with soda; You can also treat your baby’s pacifiers and toys, which he likes to put in his mouth, with any of these solutions;
- for candidiasis of the nipples, treat them with any of the above solutions;
- You can use other natural antiseptics for rinsing and treating the oral cavity - for example, herbal infusions; you can prepare a decoction of chamomile, green tea, calendula, taking 1 tsp. dry herbs for 1 cup of boiling water; Sage, elecampane, yarrow, burdock, and oak bark also have antiseptic properties, but it is also necessary to understand that any of the herbal preparations can cause an allergic reaction;
- sometimes the contents of aloe vera stems are used as antiseptics, lubricating the affected areas with this juice;
- Among the natural oils that can be used to lubricate the oral cavity, rosehip, flax or peach oils can be used after rinsing or treating plaque.
Treatment of oral thrush in babies
Treatment tactics depend on the form and severity of the disease, the presence of concomitant pathology and the root cause of the disease.
Don’t miss the material on how and how to treat oral thrush in adults!
Methods
For a localized process use:
- Local antimycotic drugs (Nystatin, Miramistin).
- Antiseptic solutions (Metrogil, Tantum Verde).
- Drugs that correct intestinal microflora (Linex, Bifidumbacterin).
- Diet and compliance with thermal regime.
In case of widespread, or generalized, candidiasis, the following is prescribed:
- Systemic antifungal drugs in age-specific dosages (“Fluconazole”).
- Local ointments and antiseptics to relieve itching, plaque and soreness (Miramistin, soda solution).
- Pro- or eubiotics (“Eneterogermina”, “Bifiform”, etc.).
- Immunostimulants (“Immunal”, “Immunovenin”).
Local therapy
Local exposure involves treating the oral cavity with various antiseptic agents:
- Sodium tetraborate (borax);
- Hydrogen peroxide 1%;
- Potassium permanganate.
Sodium tetraborate has a sweetish taste, children like it. The treatment is carried out with a gauze swab dipped in the medicine.
The antiseptic hexoral also has a good effect. It is used twice a day in the same way as other medications.
Among antiseptics, treatment with a solution of potassium permanganate 6 times a day helps at the initial stage.
After each treatment with antiseptics, it is necessary to carry out the procedure for applying aniline dyes:
- methylene blue (blue);
- gentian violet.
Blue is applied 5 times a day. Symptoms subside after three days.
No less effective solutions:
- iodinol (1:2);
- Lugol (1:3).
Treatment is carried out before feeding and after no more than 6 times a day.
Among the effective antifungal agents are:
- candida (clotrimazole in the composition);
- stomatidine;
- nystatin;
- levorin.
All substances are applied to the affected areas using tampons. Treatment must be carried out very carefully, since if the mucous membrane is damaged, there is a high risk of infection.
Candide is used 4 times a day. The duration of treatment is about 10 days.
Stomatidin - 2 times a day.
Nystatin and levorin are used in the form of a suspension, which is prepared independently. Dissolve one tablet 250 units. (100 units of levorin) in an ampoule with vitamin B12 and lubricate the mucous membrane 2 times a day.
The vitamin can be replaced with plain water (5 ml). The course of treatment is 10 - 14 days.
General therapy
People try not to prescribe drugs with general effects on the body due to their side effects. But in particularly advanced cases, the doctor may prescribe:
- diflucan or fluconazole;
- nystatin.
In severe cases, medication is administered intravenously, for example, Diflucan (not for newborns and infants under 11 months) or fluconazole.
The dosage of both medications is 3 mg/kg of body weight; fluconazole droppers are given no more than once every 72 hours for newborns and 48 hours for infants 2–4 weeks old.
Nystatin is an antifungal antibiotic effective against thrush, taken orally in a dosage of 1/4 tablet.
The duration and frequency of administration depends on the form and stage of the disease and is prescribed only by a doctor. After taking the tablet, it is not recommended to eat or drink for 30 minutes. The average course is 10 days.
Therapy with folk remedies
To alleviate the manifestations of the disease and as an auxiliary therapy, folk recipes approved for children are used:
- How to treat thrush using oak bark, chamomile, sage and calendula: the above ingredients in equal volume (2 tablespoons) are mixed together and poured with one glass of boiled water. The cooled mixture is used to treat inflamed areas covered with plaque three times a day.
- St. John's wort decoction: 500 ml of clean water is poured into 50 grams of dried leaves of the plant, after which the mixture is placed on low heat until it boils. The decoction is infused for half an hour and the oral cavity is irrigated with it 3-4 times a day.
- To prepare a solution with hydrogen peroxide, 2 tbsp. spoons of the product are diluted in a standard glass of warm water. They are used in the same way: with gauze soaked in the solution, the oral cavity is cleaned of fungal plaque, preferably 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days.
Drug treatment
Often, treatment of oral thrush in infants is based on the use of only local medications and antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity:
- Miramistin for thrush in infants can be used both on the skin and mucous membranes. Possessing antiseptic, antibacterial and antifungal effects, this product not only cleanses the oral cavity of plaque, but also destroys the fungi themselves. Available in the form of ointment and 0.01% solution. Technique for using the solution: gauze or bandage is moistened in the solution and wrapped around the index finger, after which the child’s mouth is opened and plaque is removed from the mucous membrane with gentle movements from the inside out. Frequency of application – 3-4 times per day for 7-10 days.
- Using a similar scheme, you can use 0.1% Hexoral or 2% sodium bicarbonate solution (regular baking soda, one teaspoon of which is diluted in a 200 ml glass of clean water).
- To effectively get rid of candidal plaque, Nystatin is also used. ¼ of the tablet is crushed and added to a regular glass of warm water. With gauze soaked in the resulting solution and wrapped around a finger, wipe the affected areas 4-5 times a day, for 5-7 days.
- It is possible to use the usual Metrogyl solution, which is available in 100 ml bottles for infusion therapy. You can use a pure solution or diluted 1:1 with water. They also wipe the inflamed mucous membrane covered with fungal plaques 4-5 times a day in a standard course of 7-10 days.
This is interesting: A white coating has formed on the tongue of a 3-year-old child, what should I do?
Previously, sodium tetraborate was used for thrush in infants, but modern clinical protocols recommend refraining from using this drug in pediatrics due to its high toxicity.
In severe forms, treatment of oral thrush in newborns involves the use of local antiseptics and systemic antimycotic drugs. There are only three of them: Amphotericin B, Nystatin and Fluconazole, of which the latter is most often the drug of choice, since it is the most harmless and safe, has both an injection and tablet form and is administered only once a day (6 mg per 1 kilogram of body weight body).
Diet
Diet therapy is one of the main components in the treatment of oral candidiasis. Yeast-like fungi love sweets, so sugar in any form should be excluded during treatment.
| Prohibited Products | Authorized Products |
|
|
To avoid increased pain and discomfort in the mouth, all food should be warm and have a soft consistency.
If a fungal infection is detected, a nursing mother also needs to review her diet. You can eat vegetables, unsweetened fruits, dietary meat and fish, buckwheat, oatmeal, eggs. Completely give up coffee and black tea, sweets and baked goods, milk, mushrooms.
Advice! In order for the body to quickly cleanse itself of toxic fungal waste, it is necessary to consume more fluid. This can be purified water without gas, chamomile and mint tea, or a decoction of rose hips.
Self-medication precautions
When choosing methods for self-treatment of oral thrush in a baby, you need to understand that sometimes such procedures may not correct the situation, but on the contrary, harm the child.
For example, improper use of soda solution when treating the oral mucosa can cause additional injuries. Therefore, carefully prepare the soda solution, not exceeding its concentration more than 1-2%, because a stronger concentration leads to a burn to the mucous membrane.
You can complicate the situation with candidiasis by using a honey solution. After all, beekeeping products are one of the most powerful allergens, so when using them you need to be absolutely sure that there is no allergic reaction.
In addition, when using herbal infusions, do not use several herbs at the same time. In this case, if an allergy suddenly arises, you will know which plant caused it.
Similar folk recipes can be used when treating an older child, but it is better not to experiment with the baby’s health. If the situation is urgent and you cannot see a doctor today, it’s better to play it safe and call an ambulance. At your appointment at the clinic, your doctor will prescribe medications to combat the fungal infection. When treated with medications, you can avoid additional risks, and candidiasis will go away faster.
Causes
The main reason for the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa in children is weakened immunity. If a baby is born premature, the likelihood of developing thrush is very high. Children who are breastfed or have congenital pathologies are also often exposed to fungal infections.
Provoking factors include:
- the presence of vaginal candidiasis in the mother during pregnancy (the child can become infected when passing through the birth canal);
- insufficient hygiene of the female breast during breastfeeding (the fungus is often localized specifically on the nipples due to the environment favorable for it);
- poor handling of the child’s initial things (bottles, pacifiers, etc.);
- parents’ habit of licking nipples (even if the adult has no signs of thrush, there may be a fungus in the mouth that can be passed on to the child);
- long-term use of drugs from the “antibiotics” group (medicines help reduce one’s own immunity);
- frequent regurgitation in infants (after regurgitation, an increased acidic environment will remain inside the oral cavity, favorable for fungus);
- excessive and frequent dry mouth (lack of saliva as a protective agent against the activity of pathological microorganisms).
Infection with Candida fungus in children over 2 years of age can occur as a result of consuming unwashed foods, raw milk or running water. If a child over 3 years of age suddenly shows signs of thrush, they should be examined not only for a fungal infection, but also for other possible diseases that may be accompanied by a “decay” of the immune system.
Treatment of thrush with medications
If the treatment is prescribed correctly, then after a couple of days the child will feel much better even with a severe form of the disease. However, this does not mean that taking the drug should be stopped - it is necessary to complete the full course of treatment until all symptoms of candidiasis are eliminated.
Thrush that is not completely treated is at risk of returning during the next vaccinations or during the baby’s teething period. During such periods, do not use the previously prescribed medication yourself and under no circumstances increase the dosage of the medications. After all, an increased dose of an antiseptic can provoke the opposite effect - the occurrence of bacterial stomatitis due to the proliferation of pathogenic microflora. Independent and uncontrolled use of medications is always risky because beneficial bacteria living on the surface of the mucous membranes may die, and their place will quickly be taken by pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, wait for a doctor’s appointment, who will accurately determine the required dosage of the drug.
In addition, in parallel with drug treatment, do not forget about treating your baby’s nipples, bottles and toys: they can be regularly boiled and kept in a soda solution. When breastfeeding, do not forget to wash your nipples before each time your baby latches on.
Treatment
Fungal diseases in children can be treated by a pediatrician, an infectious disease specialist or a dermatologist. If we are talking about the treatment of oral thrush, then therapy can also be carried out by a dentist.
The diagnosis of candidiasis is determined in most cases based on an examination of the oral cavity performed by a specialist. If there is any doubt, the doctor refers the patient for additional examinations. More often, to confirm the disease, a laboratory test is used to test a smear taken from the mouth for the presence of fungus.
Treatment of thrush in children requires an integrated approach. If the disease is not advanced, then local therapy is carried out in combination with measures to strengthen the immune system. In severe cases, oral candidiasis in children is treated with systemic drugs, local agents and compliance with preventive recommendations.
To prevent your baby from getting thrush
To prevent thrush from reaching the baby’s mucous membranes, special precautions must be taken:
- Regularly care for your child’s mucous membranes, monitor their condition when the baby is sick, and especially when he suffers from infectious diseases;
- If your child is prescribed antibacterial drugs, be sure to remember to use special means to protect the microflora;
- If candidiasis occurs during pregnancy in an expectant mother, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and undergo treatment. In addition, on the eve of birth, maternity hospitals carry out special prophylaxis for newborns with an increased risk of candidiasis. Thrush is especially susceptible to infants whose mothers suffer from chronic candidiasis and those who have foci of infection already in the immediate vicinity of birth. Mothers with inflammatory gynecological diseases or difficult childbirth can also transmit the risk of fungal infection to the newborn.