Rating of the best drugs
Below is a table of 17 popular vitamin D3 medications, 2 of which are prescription. The overall score is calculated based on price, availability, pros and cons, side effects, and the presence of other beneficial or harmful additives.
Table - Summary of ratings
| Place | Drug name | Age | Points |
| 17 | Alpha D3-Teva | From 3 years | |
| 16 | Baby's Super Daily, Carlos Labs | From 0 | |
| 15 | Vigantol | From 2 weeks of life | |
| 14 | PEDIAKID | After introducing complementary foods | |
| 13 | D-San | From 1.5 years | |
| 12 | Organic Drops, Newborn + | From 0 | |
| 11 | GreenPeach Infants + Kids | From 1 year | |
| 10 | Complivit Aqua D3 | From 4 weeks of life | |
| 9 | Aquadetrim | From 4 weeks | |
| 8 | Baby's Vitamin D3 | From 0 | |
| 7 | Devisol Drops D3 | From 2 weeks of life | |
| 6 | Tiptipot Vitamin D | From 0 | |
| 5 | Baby D3 California Gold | From 0 | |
| 4 | ChildLife Essentials D3 | From 0 | |
| 3 | Fish oil “Amber Drop” | From 3 months | |
| 2 | Minisan | From 1.5 years | |
| 1 | Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby | From 0 | |
Designation of solutions:
Other notes:
| |||
See other comparisons of characteristics below:
by release form: oil or water;
according to the purpose of use;
at the price of a bottle and for 1 serving;
by country of origin;
comparison of all medications by side effects.
Find out which vitamin D is best absorbed, as well as 3 rules to choose the most effective drug. If you are in doubt whether or not to give your child a vitamin, look for signs of deficiency and excess. Select the correct dosage according to age for breastfeeding and IV. Read reviews from other moms and dads and advice from Dr. Komarovsky.
D2 or D3?
The common name "vitamin D" may refer to one of its forms - vitamin D2 or D3. The first, ergocalciferol, is of plant origin. The second, cholecalciferol, is synthesized by the skin or enters the body with food of animal origin.
According to some studies, it is believed that the effectiveness of vitamin D3 is an order of magnitude higher. Some experts do not see a significant difference between them and focus on the choice of the form of release of the solution - oil or water.
Release form
The drug is available in liquid and solid form, depending on the purpose: for an adult or a child.
On the water
Water-based vitamins are absorbed faster. The therapeutic effect lasts longer and occurs faster. High bioavailability, but also the risk of overdose and, as a consequence, side effects.
List of water-based preparations:
- ChildLife Essentials D3;
- Aquadetrim;
- Complivit Aqua D3;
- Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby.
On oil
The oil solution has a thick and viscous consistency, with a good composition: active ingredient and oil. The ingredients are simple, natural and safe.
List of oil-based drugs:
- Baby D3 California Gold;
- Baby's Super Daily, Carlos Labs;
- Baby's Vitamin D3;
- Devisol Drops D3;
- GreenPeach Infants + Kids;
- Organic Drops, Newborn +;
- PEDIAKID;
- Tiptipot Vitamin D;
- Alpha D3-Teva;
- Vigantol;
- D-San;
- Minisan;
- Fish oil "Amber drop".
Which is better, oil or water solution?
Each type of drug excipient has advantages and disadvantages (50 to 50). But the choice is made towards an oil solution due to the minimum number of ingredients in the composition. If the baby suffers from digestive problems or the auxiliary base of the medicine is not suitable, switch to an aqueous solution.
Table - Comparison of auxiliary components of drugs
| On the water | On oil |
| Use polysorbate, citric acid and polyethylene glycol to dissolve vitamin D | No additives or preservatives needed |
| Adverse reactions to supplements | Allergy to oil |
| Suitable for premature and newborn babies | Causes digestive problems in infants |
What vitamin D is best to buy for a newborn baby? The oil-based form is an excellent option for preventing the health of young children, so parents should pay attention to it when prescribing.
Safe composition, no chemicals, only useful and neutral elements. In this form, cholecalciferol is absorbed faster, since the oil medium is preferable for this group of microelements.
Solid and powdery
Powder, gummies, or tablets have a hard or powdery texture. It is difficult for a small child to absorb such medications. This release form is not suitable for newborns and is dangerous to take. The solid substance is difficult to chew and swallow, especially for an infant.
What happens if there is an excess
It has a great effect on children’s bodies, just like any other product that contains it. As a result, an overabundance may occur, which will cause an accumulation of phosphorus and calcium in the blood, resulting in poisoning.
This will affect the kidneys, liver, cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract. Roughly speaking, the functioning of the body as a whole will go out of order. In case of overdose, the following symptoms occur:
- the child does not want to eat, sleeps poorly;
- may vomit, and this happens very often;
- dispersion appears;
- the baby asks for a drink very often;
- dry mouth;
- begins to lose weight unexpectedly;
- stomach upset occurs;
- the pulse becomes weaker, breathing becomes difficult, convulsions “grab”;
- fever that lasts for several days.
Not only external signs appear that you can easily notice if there is an excess of it, but also hidden defects appear. They can only be installed by a doctor and only after certain tests have been completed:
- the liver and spleen increase in size;
- The baby will develop more slowly mentally.
As soon as you notice the first signs of excess, then you no longer need to give your newborn vitamin D, and make an appointment with your doctor. To avoid the negative consequences of deficiency and overdose of this vitamin, it is always necessary to accurately monitor the dosage.
How to choose a good drug
Compound
The admixture should not contain alcohol-containing elements, as well as nitrates and chlorides - this is harmful to a small child. The ideal composition of the drops would be cholecalciferol and purified oil.
Table - Preparations with additional beneficial microelements
| Name | Vitamins |
| Organic Drops, Newborn + | E |
| ChildLife Essentials D3 | |
| Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby | A, C |
| Fish fat | Omega 3 |
Purpose of application
Infants are prescribed vitamin D to prevent rickets, improve digestion, strengthen the bone frame, and also to maintain immunity. In adults, the prescription of cholecalciferol is associated with complex treatment of problems in the body, so the active substance in the composition will be many times greater.
For intensive treatment, medications are prescribed by a doctor; for prevention, over-the-counter dietary supplements are used.
List of prescription drugs:
- Vigantol;
- Alpha D3-Teva.
Over the counter:
- Baby D3 California Gold;
- Baby's Super Daily, Carlos Labs;
- Baby's Vitamin D3;
- ChildLife Essentials D3;
- Devisol Drops D3;
- GreenPeach Infants + Kids;
- Organic Drops, Newborn +;
- PEDIAKID;
- Tiptipot Vitamin D;
- Aquadetrim;
- D-San;
- Complivit Aqua D3;
- Minisan;
- Fish oil “Amber Drop”;
- Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby.
Best before date
When buying a medicine, you must always look at the storage conditions - expired vitamins, if they do not harm, then simply will not be absorbed in the body, which means taking them is useless.
Price
Please note that when calculating for 1 dose, some drugs are cheaper than the total cost of the drug volume.
Table - Price comparison for vitamin D3
| Name | Cost, rubles | |
| 1 serving | General | |
| Vigantol | 0,97 | 290 |
| D-San | 1,32 | 397 |
| Baby's Super Daily | 1,65 | 603 |
| Baby D3 California Gold | 2,83 | 850 |
| Minisan | 3,57 | 350 |
| Baby's Vitamin D3 | 4,35 | 1589 |
| PEDIAKID | 4,68 | 2341 |
| Tiptipot | 5,32 | 1596 |
| GreenPeach Infants + Kids | 6,17 | 555 |
| ChildLife Essentials D3 | 6,25 | 719 |
| Complivit Aqua D3 | 6,63 | 199 |
| Aquadetrim | 7,30 | 219 |
| Devisol Drops D3 | 9,47 | 625 |
| Fish oil “Amber Drop” | 10,85 | 217 |
| Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby | 14,63 | 349 |
| Alpha D3-Teva | 18,73 | 562 |
| Organic Drops, Newborn + | 20,04 | 1804 |
Marks:
| ||
Which vitamin D drug is best for infants?
Let's look at the most popular drugs that are often prescribed by doctors. Their main active ingredient is cholecalciferol (D3), the preparations of which are considered more effective and modern compared to ergocalciferol (D2).
Aquadetrim is a water-based vitamin D preparation
The drug is used for vitamin deficiency in the body, for the treatment and prevention of rickets and other bone pathologies (for example, metabolic pathologies). Contraindications for use are individual intolerance to the components of the drug, hypervitaminosis. The drug is prescribed to children from the fourth week of life. This can be an obstacle in young children, so doctors in this case replace Aquadetrim with Vigantol and Vitamin D3, which are prescribed earlier (from the tenth day of life). The drug is diluted in a teaspoon of water. The course of treatment averages 1-1.5 months. Biochemical blood parameters are monitored throughout the entire period. If necessary, the pediatrician prescribes a repeat course with a break of a week. To prevent an overdose of the drug, under no circumstances should you increase the dose prescribed by your doctor. If a child develops convulsions, nausea, vomiting and other alarming symptoms, discontinue the drug and consult a doctor.
Oil-based preparations
Vigantol
The drug is also prescribed to children with vitamin D deficiency to regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphates in the body. In addition, Vigantol is able to normalize the activity of the parathyroid glands. The drug is absorbed in the small intestine, accumulates in the bones, liver, skeletal muscles, cardiac tissue, and kidneys. Maximum accumulation occurs approximately five hours after administration. Metabolites are excreted primarily in bile. The drug is prescribed for the treatment of rickets, to prevent calciferol deficiency in the child’s body, as well as for malabsorption, pathologies of the small intestine, hypocalcemia, and osteoporosis of various origins. Contraindications to the prescription are excess calcium, as well as individual intolerance to the components of the drug.
The drops are diluted in a teaspoon of milk or given with another liquid. The dosage regimen for rickets is as follows - the drug is prescribed in the first and second months of life, and then in the fifth and ninth months. In the second year, the drug is given as prophylactic courses in winter. The dose may be adjusted depending on improvements in the biochemical parameters of the baby's blood test.
Vitamin D3
Available in various dosages, which is very convenient for use. In addition to cholecalciferol, the drug contains alpha-tocopherol. The effect of the drug is similar to Aquadetrim and Vigantol. Therapy lasts about two months, then babies are transferred to preventive dosages.
Dosage and price of vitamin D3 medications
| Drug name, price | Dosage form | Vitamin D content | Age | Dosage for the prevention of rickets | Dosage for the treatment of rickets |
| Aquadetrim (Russia, Poland) 170-200 rub. | Water based drops. | 15,000 IU/ml 1 drop – 500 IU | Children from 1 month to 2-3 years. | 1-2 drops/day. | 4-6 drops. The exact dosage is determined by the doctor. |
| Premature babies from 1 month. | 2-3 drops/day. | ||||
| Wigantol (Austria, Germany, Japan) 180-200 rub. | Oil solution. | 20,000 IU/ml 1 drop – 667 IU | Children from 2 weeks. | 1 drop/day | 2-8 drops/day. |
| Premature babies from 2 weeks. | 2 drops/day | ||||
| Vitamin D3 (Russia) 129 rub. | Oil solution. | 20,000 IU/ml 1 drop – 667 IU | Children from 2 weeks. | 1 drop/day | 2-8 drops/day. |
| Premature babies from 2 weeks. | 2 drops/day |
Rating by country of origin
Table - Comparison of countries of production of drugs according to the overall assessment of the drug
| Name | Manufacturer | Rating |
| Alpha D3-Teva | Germany | 2,0 |
| Baby's Super Daily, Carlos Labs | USA | 3,5 |
| Vigantol | Germany | 3,5 |
| PEDIAKID | France | 3,5 |
| D-San | Brazil | 4,0 |
| Organic Drops, Newborn + | USA | 4,0 |
| GreenPeach Infants + Kids | USA | 4,0 |
| Complivit Aqua D3 | Russia | 4,0 |
| Aquadetrim | Poland | 4,0 |
| Baby's Vitamin D3 | USA | 4,5 |
| Devisol Drops D3 | Finland | 4,5 |
| Tiptipot | Israel | 4,5 |
| Baby D3 California Gold | USA | 4,5 |
| ChildLife Essentials D3 | USA | 4,5 |
| Fish fat | Russia | 4,5 |
| Minisan | Finland | 5,0 |
| Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby | Denmark | 5,0 |
Comparing various offers from countries, Denmark and Finland are the best producers. Russia is in fourth place. The latest is Germany with intensive care drugs that have more side effects than dietary supplements.
Table - Final comparison of all manufacturers and overall rating
| № | A country | Rating |
| 8 | Germany | 2,8 |
| 7 | Finland | 3,5 |
| 6 | Poland | 4,0 |
| 6 | Brazil | 4,0 |
| 5 | USA | 4,2 |
| 4 | Russia | 4,3 |
| 3 | Israel | 4,5 |
| 2 | Finland | 4,8 |
| 1 | Denmark | 5 |
What does this mean?
Too much vitamin D in children can cause harm that will last the rest of their lives. The main problem is that when there is an excess of vitamin, bones grow too quickly - faster than joints and muscles can strengthen. In the long term, this leads to various curvatures of the spine, frequent fractures and dislocations. There are a number of other risks:
- Osteoporosis is a deficiency of calcium in bone tissue. As a result, bones become brittle, joint covers may become ossified, and the spine may become deformed.
- Resorption of bone marrow connective tissue. Our bones have a spongy structure. White and red blood cells mature in the cells of this sponge. If the connective tissue is not strong enough, hematopoiesis and immunity suffer.
- Atherosclerosis is deposits on the walls of blood vessels. Leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the arteries, deterioration of blood supply to organs. In the most severe cases, it can lead to blockage of blood vessels with blood clots and necrosis.
- Increased calcium deposition in internal organs - organs lose elasticity, increasing the risk of internal injuries and a number of diseases.
Reviews
Table - Disadvantages of drugs according to patient reviews
| Name | Minuses | Rating |
| Alpha D3-Teva | There are side effects and contraindications. Difficulties in selecting a dose. From 3 years. | 2,0 |
| Baby's Super Daily, Carlos Labs | In rare cases, it causes overexcitation and sleep disturbance. | 3,5 |
| Vigantol | Has side effects, inconvenient dispenser. Disappeared from pharmacies. | 3,5 |
| PEDIAKID | In case of overdose, it excites the central nervous system. | 3,5 |
| D-San | Price. | 4,0 |
| Organic Drops, Newborn + | High price. | 4,0 |
| GreenPeach Infants + Kids | Not sold in all pharmacies. Fastens. | 4,0 |
| Complivit Aqua D3 | Contains sucrose, benzyl alcohol. Has contraindications. | 4,0 |
| Aquadetrim | Slight specific smell and taste. Possible side effects. There are contraindications. | 4,0 |
| Baby's Vitamin D3 | Price. | 4,5 |
| Devisol Drops D3 | Not sold in Russian pharmacies, no instructions in Russian. | 4,5 |
| Tiptipot | Not always available, price. | 4,5 |
| Baby D3 California Gold | The dispenser is not convenient for children over 1 year old. Not always available. | 4,5 |
| ChildLife Essentials D3 | A bit overpriced. | 4,5 |
| Fish fat | Not tasty. | 4,5 |
| Minisan | No. | 5,0 |
| Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby | Keep refrigerated. | 5,0 |
Designations:
| ||
Anna, Ira’s mother, about the drug Minisan. When taking other medications, it is easy to overdose while bottle-feeding. Vitamin D3 in oil form is less excreted from the body than in water-based form. Therefore, my husband and I chose Minisan, since it has the smallest dosage - 100 IU per serving.
Which vitamin D solution is better: oil or water?
Despite the fact that vitamin D is a frequently prescribed remedy for children and almost all mothers give vitamin preparations to their infants, the pharmacy chain is not at all replete with vitamin D products that can be prescribed to infants. Among the whole variety of drugs, including various forms of calciferol, there are not many drugs indicated for children from birth.
Vitamin D preparations, depending on the base, are divided into two types:
- oil form;
- an aqueous form containing tiny fat globules containing the vitamin.
Advantages of the water form:
- absorbed 5 times faster, reaching higher concentrations;
- the effect of taking it lasts twice as long as from the oil form;
- high bioavailability;
- well absorbed regardless of food intake;
- the effect of taking the drug occurs faster;
- convenient form for dosing.
How is this effect achieved? The thing is that any fat entering the digestive tract is exposed to bile salts, which break it into separate fat droplets, creating an emulsion. This ensures enzyme access to fat and its further breakdown. Thus, if vitamin D enters the body in oil form, then the drug must go through this stage before it is absorbed, and if in aqueous form (more correctly, micellar), then absorption begins much faster. The aqueous form is prescribed to babies born prematurely. Their gastrointestinal tract does not produce enough special substances to break down the vitamin in a fatty environment (in mother’s milk), so such patients are only shown an aqueous solution.
Some of the advantages of the water form also have negative sides:
- the body’s ability to absorb vitamin D from these drugs is higher, which increases the risk of overdose if instructions are not followed or if treatment is inadequate;
- aqueous forms contain many excipients that can cause individual intolerance.
Important! If there really are serious reasons for prescribing vitamin D, then for correction as soon as possible and subject to good tolerance, it is better to give preference to the aqueous form.
To give or not
Definitely yes, even if the body is able to produce vitamin D on its own with the help of sunlight. It is recommended to be in the fresh air more often and organize walks with the newborn immediately after discharge from the hospital. Cholecalciferol is present in fish oil, cheese, liver, meat, and butter.
For breastfed babies, vitamin D comes from milk, so the mother should eat enough to avoid deficiency or supplement with formula milk.
Should I give my baby vitamin D every day? Yes, definitely in the autumn-winter period. It is at this time that there is not enough sunlight. Also if the mother has poor nutrition during breastfeeding and prematurity at birth.
Metabolism of vitamin D in children
The substance can be synthesized in the skin or enter the body from the outside with special milk formulas. In the first 2-3 weeks after birth, children have a supply of vitamin D obtained during fetal development.
The substance is also partially formed in the skin, after which it is metabolized to active forms in the liver and kidneys. But in infants, all organs and systems are immature, so this option for replenishing the deficiency does not work well enough.
Breast milk cannot serve as a source of D3, since 1 liter contains only 25 IU of the nutrient.
To synthesize the vitamin, you need a sufficient amount of sunlight, which is sorely lacking for residents of middle and northern latitudes, especially in winter. Low levels of nutrients are also observed in premature babies, children with developmental defects, and gastrointestinal pathologies. Therefore, about 2/3 of infants have signs of vitamin D deficiency.
Signs of Deficiency
With a lack of vitamin D, infants experience developmental delays. When a baby is unable to hold his head up after 4 months and cannot sit independently after 6 months.
Sleep problems, irritability, poor teeth cutting and low muscle tone begin. A symptom of deficiency in infants may be profuse sweating of the feet, hands and neck. In rare cases, diarrhea or constipation and vomiting begin.
If the baby’s body does not absorb vitamin D in concentrated form, then its absence must be replenished with a formula or the mother’s nutrition through breastfeeding. It is also advisable to be in the sun more often for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
What role does vitamin D play in the body?
The key task of vitamin D is to regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. This ensures proper growth and formation of the child’s bone skeleton, and thereby prevents the development of rickets (softening of bone tissue, skeletal deformation). A lack of vitamin D in the first year of a baby’s life, when the body is growing very rapidly, is extremely dangerous. This explains the increased attention of doctors to preventive measures regarding young children.
In addition, vitamin D is responsible for the health of the baby’s teeth (regulates the accumulation of calcium in dentin) and helps resist colds (involved in the functioning of the immune system). It is also important for the functioning of the endocrine system, as it takes part in metabolism and prevents the development of some autoimmune diseases.
Dosage by age
Children from birth to 6 months are recommended to consume 400-500 IU of vitamin D3 per day, this is considered the norm. In the first year of a child’s life, you need to give a couple of drops of the drug, depending on age, once a day. The course lasts a long time - up to 3 years.
Table - Daily requirement for vitamin D in children
| Age | IU per day |
| Premature | 200 |
| From 0 to 6 months | 400 |
| From six months to 1 year | 500 |
| 1 – 3 years | 600 |
| 39 years | 600 |
On GW
How to properly give vitamin D to a breastfed baby? They begin to give from 2 weeks of age, 1 drop of an aqueous or oil solution, after applying to the breast in the first half of the day.
The daily requirement of vitamin D3 for a nursing mother is from 400 to 600 IU.
The amount of microelement in breast milk depends on the mother's nutrition. During lactation, it is necessary to absorb a sufficient amount of sunlight and take supplements with cholecalciferol.
On IV
A formula-fed baby should be given vitamin D in the morning so as not to disturb the process of falling asleep in the evening. Cholecalciferol invigorates and prevents the child from falling asleep normally. The drops are dissolved in a spoon of water or formula and given to the baby.
Table - Rating of drugs by recommended age of the child
| Name | Age |
| Baby's Super Daily, Carlos Labs | From birth |
| Baby's Vitamin D3 | |
| Tiptipot | |
| Baby D3 California Gold | |
| Organic Drops, Newborn + | |
| ChildLife Essentials D3 | |
| Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby | |
| Vigantol | From 2 weeks of life |
| Devisol Drops D3 | |
| Complivit Aqua D3 | From 4 weeks |
| Aquadetrim | |
| Fish oil “Amber Drop” | From 3 months |
| PEDIAKID | After introducing complementary foods |
| GreenPeach Infants + Kids | From 1 year |
| Minisan | From 1.5 years |
| D-San | |
| Alpha D3-Teva | From 3 years |
Times of Day
When should you give your baby vitamin D, before or after meals? It is recommended to take the drug in the morning, immediately after breakfast and in no case before bedtime. The time of day matters.
Vitamin D and fetal and newborn growth
Of great interest is the study of the influence of the level of vitamin D metabolites in the mother’s blood on the development of the child. A few studies in recent years have shown a linear relationship between the dynamics of physical development of infants at the age of 18 months. on the level of vitamin D in umbilical cord blood [15]. M.K. Javaid et al. (2006) did not find a relationship between the level of 25(OH)D in the mother’s blood and the weight and length of the child’s body at birth, the weight of the placenta, and the circumference of the head and chest of the child at the age of 9 months. [24]. Having analyzed the anthropometric indicators of children aged 9 years, the authors identified a significant correlation between the level of vitamin D in the mother’s blood in late pregnancy and low anthropometric indicators in the child. Maternal blood vitamin D levels below 27.5 nmol/L were associated with decreased fetal bone mass. These data suggest that vitamin D may be involved in the in utero programming of skeletal system development [24].
N.T. Viljakainen et al. (2011) showed that when the level of vitamin D in the blood of pregnant women exceeded 42.6 nmol/l, there was an increase in the cross-sectional area and mass of bone tissue of the tibia in the fetus, while at the same time no differences were identified in weight, body length and mineral tibial bone density at birth in these children [25]. A prospective cohort study conducted in Northeast India found that maternal hypovitaminosis D was associated with reduced skeletal (femoral) growth in the fetus and neonate (p < 0.01). At the same time, there was no significant connection between birth weight and head circumference of newborns and the level of vitamin D in the mother’s blood [26].
According to a systematic review that included 24 randomized clinical trials, supplementation of low doses of vitamin D (≤2000 IU/day) during pregnancy reduces the risk of intrauterine or neonatal mortality, as well as small fetal size for gestational age, while the use of higher doses doses (>2000 IU/day) did not cause similar effects. The dose and method of administration of vitamin D to a pregnant woman did not affect the concentration of vitamin D in umbilical cord blood. Initiation of vitamin D supplementation at ≥20 weeks' gestation. was associated with higher fetal birth weight, in contrast to earlier initiation of vitamin D supplementation (<20 weeks), in which no such relationship was found [27].
Vitamin D also plays an important role in modulating immune function [28] and oxidative stress [29], which can be associated with fetal growth. Vitamin D has been proven to influence the regulation of genes responsible for trophoblast invasion and angiogenesis, which are critical for placental implantation and its normal functioning, which is also important for fetal growth [30].
Signs of overdose
During the autumn-winter period, pediatricians indiscriminately prescribe vitamin D to infants, in different doses, without thinking about overdose.
It is impossible for a newborn to obtain large amounts of cholecalciferol from food, and the natural skin pigment melanin does not allow excess of the substance during UV radiation.
Table - Vitamin content in one daily dose of the drug
| Name | Amount of IU in 1 serving |
| Vigantol | 500 |
| PEDIAKID | 500 |
| Alpha D3-Teva | 500 |
| ChildLife Essentials D3 | 500 |
| Complivit Aqua D3 | 500 |
| Aquadetrim | 500 |
| Devisol Drops D3 | 400 |
| Baby's Super Daily | 400 |
| Baby's Vitamin D3 | 400 |
| Baby D3 California Gold | 400 |
| Organic Drops, Newborn + | 400 |
| GreenPeach Infants + Kids | 400 |
| Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby | 400 |
| Tiptipot | 200 |
| D-San | 200 |
| Fish fat | 200 |
| Minisan | 100 |
Designation of IU content in 1 serving of the drug:
| |
Side effects and symptoms of vitamin D overdose in children under one year of age:
- skin rash, allergic reaction;
- the baby is worried about constipation or diarrhea;
- excessive irritability and tearfulness, even when the indicator is slightly exceeded.
It is extremely rare, but an excess causes vomiting, the child becomes restless, nervous, and the daily routine and sleep are disrupted. The consequence is a change in the cardiovascular system, kidney failure, and attacks of pneumonia.
Table - Risk of adverse reactions when taking the drug
| Name | Side effects | Rating |
| Alpha D3-Teva | + | 2,0 |
| Baby's Super Daily, Carlos Labs | + | 3,5 |
| Vigantol | + | 3,5 |
| PEDIAKID | + | 3,5 |
| D-San | — | 4,0 |
| Organic Drops, Newborn + | — | 4,0 |
| GreenPeach Infants + Kids | — | 4,0 |
| Complivit Aqua D3 | + | 4,0 |
| Aquadetrim | + | 4,0 |
| Baby's Vitamin D3 | — | 4,5 |
| Devisol Drops D3 | — | 4,5 |
| Tiptipot | — | 4,5 |
| Baby D3 California Gold | — | 4,5 |
| ChildLife Essentials D3 | — | 4,5 |
| Fish fat | — | 4,5 |
| Minisan | — | 5,0 |
| Ferrosan Multi-tabs baby | — | 5,0 |
Side effect indications:
| ||
Allergy
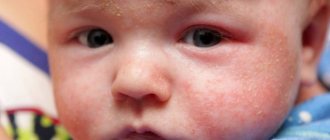
Can a baby be allergic to vitamin D? A reaction to the drug is extremely rare; in most cases, the rash is caused by the excipients that are in the composition. These are potential allergens: sucrose, citric acid, anise flavors, macrogol glyceryl ricinoleate or benzene spit.
Photo of a baby's allergy to vitamin D. Red spots can be localized in one place or evenly distributed over the skin.
Diarrhea and constipation
Can a baby be constipated from vitamin D? Yes, if the drug enters the body in large quantities. The doctor prescribes the wrong dosage or the parents use the dispenser incorrectly.
It is necessary to monitor the child's nutrition. If the baby is breastfed, the mother needs to exclude foods with intestinal strengthening properties from the diet and increase the amount of fluid the baby drinks.
Diarrhea in infants from vitamin D is caused by an incorrect overdose or type of drug.
With a large amount of colecalciferol or cholecalciferol in infants, hypervitaminosis begins, which adversely affects the functioning of internal organs and greatly weakens them. It is recommended to reduce the dose of the drug, increase the consumption of plant products and fiber, and remove calcium from the child’s diet.
Effect on sleep
The effect of vitamin D on infant sleep occurs with an overdose. Parents give their child the drug all year round, regardless of the season. Starting in the spring, reduce the dosage or stop taking it completely.
Not only insomnia is considered a sleep disorder, but also when a newborn cannot sleep for more than an hour, it becomes irritable and whiny.
Alternative
What can replace vitamin D for an infant? To avoid side effects, pediatricians prescribe fish oil. Mothers are advised to eat foods: fatty fish (especially salmon), yolks, dairy products.
How does vitamin D enter the human body?
Vitamin D is unique in that it not only enters the body with certain foods, but is also produced by the body itself. Vitamin D synthesis occurs in human skin under the influence of ultraviolet rays. And we get only a small part of it from food. For adults and older children, sources of vitamin D are fish oil, fatty fish, cod liver, chicken, beef and pork liver, dairy products, and eggs. When foods are cooked, some of the vitamin D is lost.
Komarovsky's advice
Children urgently need colecalciferol or cholecalciferol when they are born in the fall, winter, or before their due date. There is a theory that if you walk with your baby more often in sunny weather, you can avoid a deficiency of the element, but this is not so.
Komarovsky recommends giving infants vitamin D for preventive purposes in aqueous form. And if there are existing symptoms of rickets, you should switch to an oil preparation.
An aqueous solution is also suitable for premature babies. This will avoid problems with the development of the body as a whole, and not just with rickets.
Is excess vitamin D dangerous for a child?
The “sunshine vitamin” can accumulate in the body. And if there is more of it than required, this is also a serious problem.
Due to incorrect routine prescription of prophylactic doses, uncontrolled intake of vitamin D, and increased sensitivity of the body to it, hypervitaminosis may occur.
In this case, the baby usually experiences poor sleep, irritability, lethargy, thirst, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and diarrhea. The fontanel and skull sutures close prematurely.
To confirm the diagnosis, the baby may undergo laboratory blood tests, as well as a Sulkovich urine test. A sharply positive result of this test indicates hypervitaminosis D.
Prevention of vitamin deficiency
Be sure to consult your doctor and do not make a decision on your own. The prophylactic dose, according to the instructions, is 500 IU, starting from the second month of life. It is recommended to take up to 3 years inclusive.
The oil form of the drug is better absorbed by the child's body, but there are cases of poor tolerance. The aqueous form rarely causes allergies and is not toxic.
Breast milk contains a small amount of cholecalciferol and does not satisfy the need for the microelement. Formula-fed children receive about 400 IU of vitamin D per day.
Jaundice in infants
According to numerous reviews from mothers, vitamin D is an integral part of the fight against jaundice in newborns. It is recommended to give the child plenty of water and organize more walks in the sun and fresh air.
Breastfeeding and vitamin D - is prevention necessary?
A breastfed baby receives from breast milk everything he needs for normal growth and development. Of course, if the mother eats well and does not forget to take special vitamin complexes for nursing mothers. Appealing to this fact, some pediatricians believe that children who are gaining weight well and who do not have signs of rickets do not need to be prescribed vitamin D for prevention.
According to other experts, even such a storehouse of vitamins and microelements as mother’s milk cannot fully provide the baby with the required amount of vitamin D. Therefore, the baby still needs additional intake.
How to avoid overdose
It should be remembered that not a single vitamin preparation is useful on its own. All of them only make up for the deficiency and can be harmful if there is no deficiency. A healthy child whose mother receives normal nutrition should not have a lack of vitamin D in the sunny season. In cold weather, when there is little light, preventive vitamin intake is justified, but only as prescribed by a doctor.
The most common cause of excess vitamin D is self-medication. Parents noticed some symptoms, interpreted them based on information from popular literature or the Internet, and independently decided that the child needs more vitamin D. Don’t be overly arrogant, consult a pediatrician - and you will avoid this and many other problems.